Summary
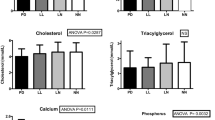
In order to assess the usefulness of intestinal biopsies as indicators of end-organ responsiveness to vitamin D in uremic patients, calcium binding activity and calcium binding protein (CaBP) content were measured in intestinal biopsies from 12 uremic patients (glomerular filtration rate<5.0 ml/min) and 12 adult controls. Values for both were found to vary with the site of biopsy, highest values being obtained in the duodenal bulb, with lower values distally. Values for activity correlated with values for CaBP content in both normals and uremics and no difference was observed between groups. Levels of calcium binding activity and content of CaBP did not correlate with serum immunoreactive parathormone levels, but were directly related to circulating 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (25-OHD) levels. The data show that intestinal CaBP is normal in activity, quantity, and affinity for calcium in malabsorbing uremic patients, and are consistent with the hypothesis that calcium malabsorption in uremia is unrelated to deficiency of intestinal calcium binding protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coburn, J.W., Koppel, M.H., Brickman, A.S., Massry, S.G.: Study of intestinal absorption of calcium in patients with renal failure, Kidney Int.3:264–272, 1973
Parker, T.F., Vergne-Marini, P., Hull, A.R., Pak, C.Y.C., Fordtran, J.S.: Jejunal absorption and secretion of calcium in patients with chronic renal disease on hemodialysis, J. Clin. Invest.54:358–365, 1974
Brickman, A.S., Coburn, J.W., Rowe, P.H., Massry, S.F., Norman, A.W.: Impaired calcium absorption in uremic man: evidence for defective absorption in the proximal small intestine, J. Lab. Clin. Med.84:791–801, 1974
Lie, S.G., Chu, H.I.: Studies of calcium and phosphorus metabolism with special reference to the pathogenesis and effect of dihydrotachysterol (AT 10) and iron, Medicine (Baltimore)22:103–161, 1943
Clarkson, E.M., McDonald, S.J., deWardener, H.E.: The effect of a high intake of calcium carbonate in normal subjects and patients with chronic renal failure, Clin. Sci.30:425–438, 1966
Brickman, A.S., Coburn, J.W., Norman, A.W.: Action of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, a potent, kidney-produced metabolite of vitamin D3 in uremic man, N. Engl. J. Med.287:891–895, 1972
Wasserman, R.H., Taylor, A.N.: Vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein: response to some physiological and nutritional variables, J. Biol. Chem.243:3987–3993, 1968
Martin, D.L., Melancon, M.J., DeLuca, H.F.: Vitamin D-stimulated, calcium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from brush borders of rat small intestine, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.35:819–823, 1969
Piazolo, P., Hotz, J., Helmke, K., Franz, H.E., Schlayer, M.: Calcium-binding protein in the duodenal mucosa of uremic patients and normal subjects, Kidney Int.8:110–118, 1975
Piazolo, P., Schlayer, M., Franz, H.E.: Das calcium bindende protein in der menschlichen darmschleihaut bei uraemie, Klin. Wochenschr.50:603–605, 1972
Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Fullmer, C.S., Taylor, A.N.: Some aspects of vitamin D action, calcium absorption and the vitamin D dependent calcium binding protein, Vitam. Horm.32:299–324, 1974
Suda, T., DeLuca, H.F., Schnoes, J.R.: 25,26-Dihydroxycholecalciferol, a metabolite of vitamin D3 with intestinal calcium transport activity, Biochemistry9:4776–4780, 1970
Freund, T., and Bronner, R.: Stimulation in vitro by 1, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 of intestinal cell calcium uptake and calcium-binding protein, Science190:1300–1301, 1975
Kasugai, T.: Gastric biopsy under direct vision by the fiber-gastroscope, Gastrointest. Endosc.15:33–38, 1968
Brandborg, L.L., Rubin, C.E., Quinton, W.E.: A multipurpose instrument for suction biopsy of the esophagus, stomach, small bowel, and colon, Gastroenterology37:1–16, 1959
Carey, J.B., Jr.: A simplified gastrointestinal biopsy capsule, Gastroenterology46:550–557, 1964
Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Taylor, A.N.: Vitamin D dependent calcium binding protein: purification and some properties, J. Biol. Chem.243:3978–3986, 1968
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem.193:265–275, 1951
Alpers, D.H., Lee, S.W., Avioli, L.V.: Identification of two calcium binding proteins in human small intestine: a preliminary report, Gastroenterology62:559–564, 1972
Hruska, K.A., Kopelman, R., Rutherford, W.E., Klahr, S., Slatopolsky, E.: Metabolism of immunoreactive parathyroid hormone in the dog. The role of the kidney and the effects of chronic renal disease, J. Clin. Invest.56:39–48, 1975
Haddad, J.G., Chyu, J.C.: Competitive protein binding radioassay for 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.33:992–995, 1971
Rutherford, W.E., Hruska, K., Blondin, J., Holick, M., DeLuca, H., Klahr, S., Slatopolsky, E.: The effect of 5,6 trans vitamin D3 on calcium absorption in chronic renal disease, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.40:13–18, 1975
Curtis, F.K., Fellows, H., Rich, C.: Estimation of human calcium absorption by external radioisotope counting, J. Lab. Clin. Med.69:1036–1041, 1967
Murtle, J.F., Norman, A.W.: Vitamin D: a cholecalciferol metabolite highly active in promoting intestinal calcium transport, Science171:79–82, 1970
Teitlebaum, S.L., Bone, J.M., Stein, P.M., Gilden, J.J., Bates, M., Boisseau, B.C., Avioli, L.V.: Calcifidiol in chronic renal insufficiency, J. Am. Med. Assoc.235:164–167, 1976
Eastwood, J.B., Harris, E., Stamp, T.C.B., deWardener, H.E.: Vitamin D deficiency in the osteomalacia of chronic renal failure, Lancet2:1209–1211, 1976
Haussler, M.R., Nagode, R.A., Rasmussen, H.: Induction of intestinal brush border alkaline phosphatase by vitamin D: identity with Ca-ATPase, Nature228:1199–1201, 1970
Kowarski, S., Schachter, D.: Vitamin D-dependent, particulate calcium binding activity and intestinal calcium transport, Am. J. Physiol.229:1199–1204, 1975
Avioli, L.V.: Intestinal absorption of calcium, Arch. Intern. Med.129:345–355, 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gleason, W.A., Grimme, N.L., Avioli, L.V. et al. Intestinal calcium binding protein in uremia. Calcif Tissue Int 27, 205–210 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441187
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441187