Abstract
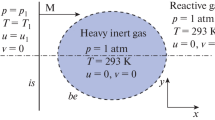
The process of explosion venting to air in a cylindrical vent vessel connected to a duct, filling with a stoichiometric methane-oxygen gas mixture, was simulated numerically by using a colocated grid SIMPLE scheme based onk-epsilon turbulent model and Eddydissipation combustion model. The characteristics of the combustible cloud, flame and pressure distribution in the external flow field during venting were analyzed in terms of the predicted results. The results show that the external explosion is generated due to violent turbulent combustion in the high pressure region within the external combustible cloud ignited by a jet flame. And the turbulence and vortex in the external flow field were also discussed in detail. After the jet flame penetrating into the external combustible cloud, the turbulent intensity is greater in the regions with greater average kinetic energy gradient, rather than in the flame front; and the vortex in the external flow field is generated primarily due to the baroclinic effect, which is greater in the regions where the pressure and density gradients are nearly perpendicular.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mccann D P J, Thomas G O, Edwards D H. Gasdynamics of vented explosions—Part I: Experimental studies[J].Combustion and Flame, 1985,59(3):233–250.
Cooper M G, Fairweather M, Tite J P. On the mechanisms of pressure generation in vented explosions[J].Combustion and Flame, 1986,65(1):1–14.
Ponizy B, Leyer J C. Flame dynamics in a vented vessel connected to a duct—1: Mechanism of vessel-duct interaction[J].Combustion and Flame, 1999,116(2):259–271.
Catlin C A. Scale effects on the external combustion caused by venting of a confined explosion[J].Combustion and Flame, 1991,83(4):399–411.
Hjertager B H. Simulation of transient compressible turbulent reactive flows[J].Combustion Science and Technology, 1982,27(5):159–170.
TAO Wen-quan.Advanced Progress of Numerical Hear Transfer[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000,181–186. (in Chinese)
WANG Ji-hai.Two Dimensional Nonsteady Flow and Shock Waves[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994,348–383. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by LIN Jian-zhong
Foundation items: the National Key Basic Research Special Foundation of China (2001 CB409600); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (19832030)
Biographies: JIANG Xiao-hai (1975∼); FAN Bao-chun (1945∼)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao-hai, J., Bao-chun, F. & Jin-fang, Y. Turbulence, vortex and external explosion induced by venting. Appl Math Mech 25, 1390–1397 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438296
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02438296