Abstract
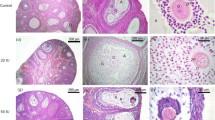
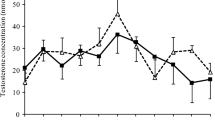
Chorionic gonadotropin exerts a protective effect on irradiated animals: it increases survival rate and number of peripheral blood leukocytes, improves the structure of liver parenchyma, and increases body weight.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. I. Gerasimova, I. F. Kolpashchikova, and I. M. Solopaeva,Byull. Izobret., No. 4, 15 (1981).
I. M. Solopaeva,—Ibid., No. 3, 25, (1994).
I. M. Solopaeva and B. P. Solopaev,Stimulation of Regeneration in Pathologically Changed Liver and Chorionic Gonadotropin [in Russian], N. Novgorod (1991).
R. B. Strelkov,Calculation of Standard Error and Confidence Interval of the Arithmetic Mean using Tables [in Russian], Sukhumi (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated fromByulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 127, No. 5, pp. 536–538, May, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solopaeva, I.M. Effect of chorionic gonadotropin on irradiated animals. Bull Exp Biol Med 127, 483–484 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02434946
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02434946