Abstract
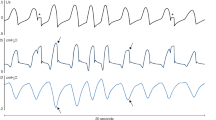
An increase in the negative intrathoracic pressure during deep breathing did not change blood flow rate in the carotid artery in 100% humans and 57.2% cats, while in 42.8% cats this parameter strongly correlated with acceleration of the heart rate. Similar relations were found for the ascending and abdominal aorta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Gaiton,Cardiac Minute Volume and Its Regulation [in Russian], Moscow (1969).
R. Berne and M. N. Levy,Cardiovascular Physiology, 3rd Ed., St. Louis (1977).
H. Bjurstedt, G. Rosenhamer, C. M. Hesser, and B. Lindborg,J. Appl. Physiol.,48, No. 6, 977–981 (1980).
J. A. Innes, S. C. De Cort, W. Kox, and A. Guz,J. Physiol. (London),460, 487–502 (1993).
L. B. Rowell,Human Cardiovascular Control, Oxford (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated fromByulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 129, No. 2, pp. 129–132, February, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tkachenko, B.I., Evlakhov, V.I. & Poyasov, I.Z. Arterial blood flow during deep breathing. Bull Exp Biol Med 129, 109–111 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02434782
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02434782