Summary
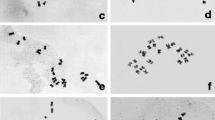
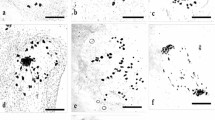
212 Genotypes of theMalus wild species collection in Dresden were analysed for their chromosome numbers. The most frequent chromosome number is 2n=2x=34. Some genotypes are polyploid (2n=3x=51 or 2n=4x=68). The chromosome numbers of the following species are reported for the first time:Malus x arnoldiana 2n=34,M. x dawsoniana, M. x moerlandsii 2n=34 andM. x sublobata 2n=34,M. trilobata 2n=34,M. tschonoskii 2n=34.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dermen, H., 1936. Aposporic parthenogenesis in a triploid apple,Malus hupehensis. J. Arnold Arboretum 17: 90–105.
Einset, J. & B. Imhoff, 1949. Chromosome numbers of apple varieties and sports II. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 53: 197–201.
Fischer, M. G. Mildenberger, R. Büttner, K. Hammer & J. Schmidt, 1984. Der Genfonds an Malus-Arten in der DDR und seine Nutzung. Kulturpflanze 32: 123–142.
Guo-Lu, L., 1987. Observation of Chromosomes ofMalus species in China. Acta Phytotaxonimca Sinica 25: 437–441.
Guo-Lu, L. & L. Xiao-Lin, 1993. Chromosome studies of chinese species ofMalus Mill. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 31: 236–251.
Huckins, C.A., 1977. Chromosome Numbers of Phanerogams 7. Annals Missouri Bot. Garden 64: 142–143.
Lincoln, F.B. & L.P. McCann, 1937. Polyploidy in Native Species ofMalus. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 34: 26.
Nebel, B.R., 1929. Zur Cytologie vonMalus undVitis. Gartenbauwissenschaflen 1: 549–595.
Nebel, B.R., 1931. Recent findings in cytology of fruits (Cytology ofPyrus III). Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 27: 406–410.
Ponomarenko, V.V., 1989. Spontaneous interspecific and intergeneric hybridization in the genusMalus Mill. Res. Bull. Vavilov Inst. Plant Industry, No. 194: 53–58.
Rybin, V.A., 1926. Cytological Investigations of the GenusMalus. Bulletin of Applied Botany and Plant Breeding, Leningrad 16: 187–200.
Sax, K., 1931. The origin and relationships of thePomoideae. J. Arnold Arboretum 12: 3–22.
Sax, K., 1932. Chromosome relationships in thePomoideae. J. Arnold Arboretum 13: 363–367.
Sax, K., 1959. The cytogenetics of facultative apomixis inMalus species. J. Arnold Arboretum 40: 289–297.
Soloveva, L.V., 1979. Study of ploidy in cultured varieties ofMalus domestica (L.) Borkh. and wild species ofMalus Mill. genus. Tsitologia i Genetika 13: 366–369.
Way, R.D., H.S. Aldwinckle, R.C. Lamb, A. Rejman, S. Sansavini, T. Shen, R. Watkins, M.N. Westwood & Y. Yoshida, 1990. Apples (Malus. Acta Horticultura) 290: 3–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuster, M., Büttner, R. Chromosome numbers in theMalus wild species collection of the genebank Dresden-Pillnitz. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42, 353–361 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02432139
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02432139