Summary
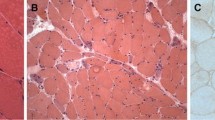
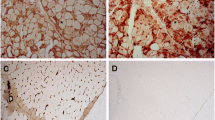
19 biopsies of polymyositis patients were compared with 19 matched controls. The presence of smaller fibres in the periphery of the fascicles has been analyzed quantitatively using a perifascicular atrophy factor. The thinner fibres are multiplied by a factor from 1–4, considering their significance for the diagnosis of fibre atrophy. The value obtained with this method from centrally located fibres as related to the value from peripherally located ones is called the perifascicular atrophy factor. If this is less than — 300 a myopathy of the group of the polymyositis/dermatomyositis can be assumed. 47% of dermatomyositis biopsies and none of the controls were below this range.
Zusammenfassung
Unter 1430 Muskelbiopsien der Neurologischen Universitätsklinik Bern der Jahre 1962 bis 1974 fanden sich 19 geeignete Muskelbiopsie-Präparate von an Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis erkrankten Patienten. Die in Bouin oder Formalin fixierten, in Paraffin eingebetteten und mit Masson-Trichrom, Van Gieson-Elastica oder Haematoxylin-Eosin gefärbten Präparate wurden nach der Methode des «Größten kleineren Durchmessers» ausgemessen und den in gleicher Weise behandelten Vergleichsbiopsien gegenübergestellt. Die Untersuchung zeigt, daß bei geeigneter quantitativer Analyse bei allen unseren Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis-Fällen die an den Faszikelrändern gelegenen Fasern dünner sind als die im Zentrum gelegenen. Der Unterschied beträgt durchschnittlich 5,641 μ, mit einem Maximum von 19,58μ und einem Minimum von 0.82μ. In drei Fällen beträgt die Differenz der Faserdurchmesser peripher—zentral weniger als 1,7μ (=1 Teilstrich im Meßocular), so daß bei der Routineuntersuchung im Lichtmikroskop dieser Unterschied nicht beachtet werden kann. Die statistische Auswertung zeigt für die Gruppe der Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis-Fälle als Ganzes einen hochsignifikanten Unterschied in bezug auf das Kaliber zwischen peripher
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. D.: Pathological reactions of sceletal muscle. In: Disorders of coluntary muscle. 3rd edition (ed. J. N. Walton), pp. 168–333. London: Churchill Livingstone 1974
Adams, R. D., Denny-Brown, D., Pearson, C. M.: Diseases of muscle. 1st ed. New York: Harper 1954
Adams, R. D., Denny-Brown, D., Pearson, C. M.: Diseases of muscle. 2nd ed. New York: Harper 1962
Banker, B. Q.: Dermatomyositis of Childhood. Trans. Amer. Neurol. Assoc.87, 11–15 (1962)
Banker, B. Q.: Dermatomyositis of Childhood. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol.34, 46–75 (1975)
Bethlem, J.: Muscle pathology. Amsterdam: North Holland Publ. Co. 1970
Bohan, A., Peter, J. B.: Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis. New Engl. J. Med.292, 344–347, 403–407 (1975)
Brooke, M. H.: The pathologic interpretation in muscle histochemistry. In: Striated muscle (eds. C. M. Pearson, F. K. Mastofi), International Academy of Pathologic Monograph, No. 12. Basel: Karger 1974
Brooke, M. H., Engel, W. K.: Muscle biopsy as a clinical diagnostic aid. In: Neurologic Diagnostic Techniques (ed. W. S. Fields), pp. 90–146. Springfied (Ill.): Thomas 1966
Brooke, M. H., Engel, W. K.: The histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types I. Neurology (Minneap.)19, 221–233 (1969)
Brooke, M. H., Engel, W. K.: The histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types II. Neurology (Minneap.)19, 378–393 (1969)
Brooke, M. H., Kaplan, H.: Muscle pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Polymyositis. Arch. Path.94, 101–118 (1972)
Camp, W.A., Engel, W. K.: Myopathies associated with other diseases: Clinical orthopaedics and related research. Philadelphia39, 19–38 (1965)
Cancilla, P. A., Verity, A. M.: Histochemical fibres types in clinical disorders of muscle. In: Striated muscle (eds. C. M. Pearson, F. K. Mastofi), International Academy of Pathologic Monograph, No. 12, Basel: Karger 1974
Climie, A. R. W.: Muscle biopsy: Technic and interpretation. Am J. Clin. Path.60, 753–770 (1973)
Denny-Brown, D.: The nature of Polymyositis and related muscular diseases. Trans. Coll. Physicians Phila.28, 12–29 (1060)
Denny-Brown, D.: Degeneration of skeletal muscle. Rev. canad. Biol.21, 507–522 (1962)
Dubowitz, V., Brooke, M. H.: Muscle biopsy. A modern approach. Major problems in Neurology, Vol. 2. Philadelphia: Saunders 1973
Engel, W. K.: The multiplicity of pathologic reactions of human sceletal muscle. In: Proceedings of the Vth int. Congress of Neuropathology, Zürich 1965 (eds. F. Lüthy, A. Bischoff) Int. Congress Series No. 100, pp. 613–624. Amsterdam: Exc. Med. Foundation 1965
Engel, W. K.: Diseases of the neuromuscular junction and muscle. In: Neurochemistry (ed. C. Adams), pp. 622–672. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1965
Engel, W. K.: Muscle biopsy — Uses and Limitations. Postgrad. Med.41, 155–160 (1967)
Engel, W. K.: Muscle biopsies in neuromuscular diseases. Pediat. Clin. N. Amer.14, 963–995 (1967)
Engel, W. K.: Selective and nonselective susceptibility of muscle fibre types. Arch. Neurol. (Chicago)22, 97–117 (1970)
Engel, W. K.: Classifications of neuromuscular disorders. In: Birth defects. Original article series. Vol. VII, No. 2, pp. 18–37 (1971)
Goebel, H. H.: Morphologie der Myositiden und Muskeldystrophien. Akt. Neurol.4, 259–269 (1974)
Johns, T. R., Crowly, W. J., Miller, J. Q., et al.: The syndrome of Myasthenia and Polymyositis with comments on Therapy. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.183, 64–71 (1971)
Mastaglia, F. L., Walton, J. N.: An ultrastructural study of sceletal muscle in polymyositis. J. Neurol. Sci.12, 473–504 (1971)
Mumenthaler, M.: Valeur de la biopsie pour le diagnostic des maladies neuro-musculaires. Etudes de 335 cas personnels. Rev. neurol. Paris108, 462–469 (1963)
Mumenthaler, M.: Myopathy in neuropatho. In: Proceedings of an International Congress, Milan 1969 (ed. J. N. Walton), Exc. Med. Int. Congress Series No. 199, pp. 585–598
Munsat, T., Piper, D., Cancilla, P.: Inflammatory myopathy with facioscapulohumeral distribution. Neurology (Minneap.)22, 335–347 (1972)
Munsat, T., Cancilla, P.: Polymyositis without inflammation. Bull. Los Angeles neurol. Soc.39, 113–120 (1974)
Pearson, C. M.: Actualités de pathologie neuromusculaire. In: 2ième Journée int. de Marseille, Oct. 1970 (eds. G. Serratrice, H. Roux), pp. 7–9. Expansion Scientifique Française 1970
Pearson, C. M., Rose, S. A.: Myositis. In: Neuromuscular disorders (eds. R. D. Adams, L. M. Eaton, G. M. Shy), Proceedings of the Association 1958, Chapter 15, pp. 422–478. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1960
Pearson, C. M., Currie, S.: Polymyositis and related disorders. In: Disorders of voluntary muscle (ed. J. N. Walton), 3rd. ed., pp. 614–652. Edinburgh and London: Churchill Livingstone 1974
Vilppula, A.: Muscular disorders in some collagen diseases. Acta med. scand. Supp. 540, 435–438 (1972)
Walton, J. N.: Polymypsitis and related disorders. Presse méd.79, 435–438 (1971)
Walton, J. N.: Polymyositis: New Light on pathogenesis and treatment. Proc. Aust. Assoc. Neurol.9, 1–7 (1973)
Walton, J. N.: Discussion — The aetiology of polymyositis. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Int. Congress on muscle diseases 1971, Perth, Australia (ed. B. A. Kakulas), T.C.S. No. 282, pp. 36–50. Amsterdam: Exc. Med. 1973
Walton, J. N., Adams, R. D.: Polymyositis. Edinburgh: Livingstone 1958
Whitaker, J. N., Engel, W. K.: Vascular deposits of immunoglobulin and complement in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. New Engl. J. Med.286, 333–338 (1972)
Whitaker, J. N., Engel, W. K.: Mechanism of muscle injury in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. New Engl. J. Med.289, 107–108 (1973)
Referate der Tagung über Myasthenie und andere neuromuskuläre Erkrankungen. Würzburg, 20–22. 5. 1976. In: Fortschritte der Myologie. In Vorbereitung
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hans-Peter Baumli, Mumenthaler, M. The perifascicular atrophy factor an aid in the histological diagnosis of polymyositis. J Neurol 214, 129–136 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02430350
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02430350