Abstract
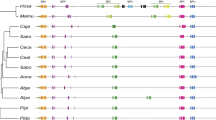
The evolution of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus was investigated by the comprehensive analysis of variable region (Vh) gene family content and restriction fragment polymorphism in the genusMus. The examination of naturalMus domesticus populations suggests an important role for recombination in the generation of the considerable restriction fragment polymorphism found at theIgh-V locus. Although the sizes of individualVh gene families vary widely both within and between differentMus species, evolutionary trends ofVh gene family copy number are revealed by the analysis of homologues of mouseVh gene families inRattus andPeromyscus. Processes of duplication, deletion, and sequence divergence all contribute to the evolution ofVh gene copy number. CertainVh gene families have expanded or contracted differently in the various muroid lineages examined. Collectively, these findings suggest that the evolution of individualVh family size is not driven by strong selective pressure but is relatively neutral, and that gene flow, rather than selection, serves to maintain the high level of restriction fragment polymorphism seen inM. domesticus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Igh-V :
-
immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region locus
- Vh :
-
immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene
- V κ :
-
immunoglobulin light chain (kappa type) variable region gene
References
Akolkar, P. N., Sikder, S. K., Bhattacharya, S. B., Liao, J., Gruezo, F., Morrison, S. L., and Kabat, E. A.: Different VL and Vh germline genes are used to produce similar combining sites with specificity for α (1→6) dextrans.J Immunol 138: 4472–4477, 1987
Alt, F. W., Blackwell, T. K., and Yancopolous, G. D.: Development of the primary antibody repertoire.Science 238: 1079–1087, 1987
Berry, R. J.: Genetical processes in wild mouse populations: past myth and present knowledge.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 86–94, 1986
Blankenstein, T., Bonhomme, F., and Krawinkel, U.: Evolution of pseudogenes in the immunoglobulinV h-gene family of the mouse.Immunogenetics 26: 237–248, 1987
Boersch-Supan, M. E., Agarwal, S., White-Scharf, M. E., and Imanishi-Kari, T.: Heavy chain variable region: multiple gene segments encode anti-4-(hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl idiotypic antibodies.J Exp Med 161: 1272–1292, 1985
Bonhomme, F.: Evolutionary relationships in the genusMus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 19–34, 1986
Bonhomme, F., Catalan, J., Britton-Davidian, J., Chapman, V. M., Moriwaki, K., Nevo, E., and Thaler, L.: Biochemical diversity and evolution in the genusMus. Biochem Genet 22: 275–403, 1984
Brodeur, P. H. and Riblet, R.: The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundredIgh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes.Eur J Immunol 14: 922–940, 1984
Brodeur, P. H., Thompson, M. A., and Riblet, R.: The content and organization of mouseIgh-V families.In E. Sercarz, H. Cantor, and L. Chess (eds.):Regulation of the Immune System, UCLA Symp Mol Cell Biol, New Series, Vol. 18, pp. 445–453, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York, 1985
Brownell, E.: DNA/DNA hybridization studies of muroid rodents: symmetry and rates of molecular evolution.Evolution 37: 1034–1051, 1983
Busto, P., Gerstein, R., Dupre, L., Giorgetti, C. A., Selsing, E., and Press, J. L.: Molecular analysis of heavy and light chains used by primary and secondary anti-(T, G)-A-L antibodies produced by normal andXid mice.J Immunol 139: 608–618, 1987
Clarke, S. H., Claflin, J. L., Potter, M., and Rudikoff, S.: Polymorphisms in anti-phosphocholine antibodies reflecting evolution of immunoglobulin families.J Exp Med 157: 98–113, 1983
Clarke, S. H., Huppi, K., Ruezinsky, D., Staudt, L., Gerhard, W., and Weigert, M.: Inter-and intraclonal diversity in the antibody response to hemagglutinin.J Exp Med 161: 687–704, 1985
Connor, J. L.: Genetic mechanisms controlling the domestication of a wild house mouse population (Mus musculus L.).J Comp Phys Psych 89: 118–130, 1975
Crews, S., Griffin, J., Huang, H., Calame, K., and Hood, L.: A single Vh gene segment encodes the immune response to phosphorylcholine: somatic mutation is correlated with class of antibody.Cell 25: 59–66, 1981
D'Hoostelaere, L. A. and Potter, M.: Igκ polymorphism inM. musculus domesticus populations from Maryland and Delaware.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 175–185, 1986
Dildrop, R.: A new classification of mouse Vh sequences.Immunol Today 5: 85–87, 1984
Duncan, W. R., Wakeland, E. M., and Klein, J.: Heterozygosity ofH-2 loci in wild mice.Nature 281: 603–605, 1979
Ferris, S. D., Sage, R. D., and Wilson, A. C.: Evidence from mt DNA, sequences that common laboratory strains of mice are descended from a single female.Nature 295: 163–165, 1982
Ferris, S. D., Sage, R. D., Prager, E. M., Ritte, U., and Wilson, A. C.: Mitochondrial DNA evolution in mice.Genetics 105: 681–721, 1983a
Ferris, S. D., Sage, R. D., Huang, C. M., Nielsen, J. T., Ritte, U., and Wilson, A. C.: Flow of mitochondrial DNA across a species boundary.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 2290–2294, 1983b
Hartman, A. B. and Rudikoff, S.: Vh genes encoding the immune response to β-(1,6)-galactan: somatic mutation in IgM molecules.EMBO J 3: 3123–3140, 1984
Hartman, A. B., D'Hoostelaere, L. A., Potter, M., and Rudikoff, S.: The X-24 Vh gene family in inbred mouse strains and wild mice.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 157–166, 1986
Hilbert, D. M. and Cancro, M. P.: A comparative analysis of the antiphosphoryl-choline response of CLA and BALB/c mice.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 206–216, 1986
Huppi, K., Jouvin-Marche, E., Scott, C., Potter, M., and Weigert, M.: Genetic polymorphism at the kappa chain locus in mice: comparisons of restriction enzyme hybridization fragments of variable and constant region genes.Immunogenetics 21: 445–457, 1985
Johnson, M. J., Natali, A. M., Cann, H. M., Honjo, T., and Cavalli-Sforza, L. L.: Polymorphisms of a human variable heavy chain gene show linkage with constant heavy chain genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 7840–7844, 1984
Kaartinen, M., Pelkonen, J., and Mäkelä, O.: Several V genes participate in the early phenyloxazalone response in various combinations.Eur J Immunol 16: 98–105, 1986
Klein, J. and Figueroa, F.: Evolution of the major histocompatibilty complex.CRC Crit Rev Immunol 6: 295–386, 1986
Kofler, R.: A new murine Ig Vh gene family.J Immunol 140: 4031–4034, 1988
Loh, D., Bothwell, A. L. M., White-Scharf, M., Imanishi-Kari, T., and Baltimore, D.: Molecular basis of a mouse strain-specific antihapten response.Cell 33: 85–93, 1983
Margolies, M. N., Marshark-Rothstein, A., and Gefter, M. L.: Structural diversity among anti-p-azophenyl arsonate monoclonal antibodies from A/J mice: comparison of Id− and Id+ sequences.Mol Immunol 18: 1065–1077, 1981
Marshall, J.: Systematics of the genusMus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 12–18, 1986
Marshall, J. and Sage, R. D.: Taxonomy of the house mouse.Symp Zool Soc Lond 47: 15–25, 1981
Morse, H. C.: Historical perspectives on the development of inbred mice.In H. C. Morse, III (ed.):Origins of Inbred Mice, pp. 3–21, Academic Press, New York, 1978
Nadeau, J. H., Wakeland, E. K., Gotze, D., and Klein, J.: The population genetics of theH-2 polymorphism in European and North African Populations of the house mouse (Mus musculus L).Genet Res 37: 17–31, 1981
Nadeau, J. H., Britton-Davidian, J., Bonhomme, F., and Thaler, L.:H-2 polymorphisms are more uniformly distributed than alloenzyme polymorphisms in natural populations of house mice.Genetics 118: 131–140, 1988
Naparstek, Y., Andre-Schwartz, J., Manser, T., Wysoki, L. Breitman, L., Stollar, B. D., Gefter, M., and Schwartz, R. S.: A single germline Vh gene segment of normal A/J mine encodes autoantibodies characteristics of systemic lupus erythmatosus.J Exp Med 164: 614–626, 1986
Near, R. I., Juszczak, E. C., Huang, S. Y., Sicari, S. A., Margolies, M. N., and Gefter, M. L.: Expression and rearrangement of homologous Vh genes in two mouse strains.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 2167–2171, 1984
Pennell, C. A., Sheehan, K. M., Brodeur, P. H., and Clarke, S. H.: Organization and expression of Vh gene families preferentially expressed by Ly-1 B cells.Eur J Immunol, in press, 1989
Perlmutter, R. M., Berson, B., Griffin, J. A., and Hood, L.: Diversity in the germiline antibody repertoire: molecular evolution of the T15 Vh gene family.J Exp Med 162: 1998–2016, 1985
Potter, M.: Comments on the relationship of inbred strains to the genusMus.In H. C. Morse, III (ed.):Origins of Inbred Mice, pp. 497–509, Academic Press, New York, 1978
Reininger, L., Kaushik, A., Izui, S., and Jaton, J.-C.: A member of a new Vh gene family encodes anti-bromelinized mouse red blood cell autoantibodies.Eur J Immunol 18: 1521–1526, 1988
Riblet, R., Tutter, A., and Brodeur, P.: Polymorphism and evolution ofIgh-V gene families.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 167–172, 1986
Riblet, R., Brodeur, P., Tutter, A., and Thompson, M. A.: Structure and evolution of the mouseIgh locus.In G. Kelsoe and D. H. Schulze (eds.):Evolution and Vertebrate Immunity, pp. 53–61, University of Texas, Austin, 1987
Riley, S. C., Connors, S. J., Klinman, N. R., and Ogata, R. T.: Preferential expression of variable region heavy chain segments by predominant 2,4-dinitrophenyl-specific BALB/c neonatal antibody clonotypes.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2589–2593, 1986
Sage, R. D.: Wild mice.In H. L. Forster, J. D. Small, and J. G. Fox (eds.):The Mouse in Biomedical Research, Vol. 1, pp. 39–90, Academic Press, New York, 1981
Sage, R. D., Whitney, J. B., and Wilson, A. C.: Genetic analysis of a hybrid zone between domesticus and musculus mice (Mus musculus complex): hemoglobin polymorphisms.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 75–85, 1986
Sarich, V. M.: Rodent micromolecular systematics.In W. P. Lucket and J.-L. Hartenberger (eds.):Evolutionary Relationships Among Rodents: A Multidisciplinary Analysis, pp. 423–452, Plenum, New York, 1985
Schiff, C., Milili, M., Hue, I., Rudikoff, S., and Fougereau, M.: Genetic basic for expression of the idiotypic network: one unique Ig Vh germline gene accounts for the major family of Ab1 and Ab3 (Ab1') antibodies of the GAT system.J Exp Med 163: 573–587, 1986
Siekevitz, M., Gefter, M. L., Brodeur, P., Riblet, R., and Marshak-Rothstein, A.: The genetic basic of antibody production: the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype response of the strain A mouse.Eur J Immunol 12: 1023–1032, 1982
Siekevitz, M., Huang, S. Y., and Gefter, M. L.: The genetic basic of antibody production: a single heavy chain variable region encodes all molecules bearing the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype in the strain A mouse.Eur J Immunol 13: 123–132, 1983
Tutter, A. and Riblet, R.: Duplications and deletions ofVh genes in inbred strains of mice.Immunogenetics 28: 125–135, 1988a
Tutter, A. and Riblet, R.: Selective and neutral evolution in the murineIgh-V locus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 137: 107–115, 1988b
Van Dijk, K. W., Schroeder, H. W., Perlmutter, R. M., and Milner, E. C. B.: Heterogeneity in the human Ig Vh locus.J Immunol 142: 2547–2554, 1989
Wang, X.-F. and Calame, K.: The endogenous immunoglobulin enhancer can activate tandem Vh promoters separated by a large distance.Cell 43 659–665, 1985
Weiss, S., Lehmann, K., Raschke, W. C., and Cohn, M.: Mice completely suppressed for the expression of immunoglobulin κ light chain.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 211–215, 1984
Winter, E., Radbruch, A., and Krawinkel, U.: Members of novel Vh gene families are found in VDJ regions of polyclonally activated B-lymphocytes.EMBO J 4: 2861–2867, 1985
Yancopolous, G. D., Desiderio, S. V., Paskind, M., Kearney, J. F., Baltimore, D., and Alt, F. W.: Preferential utilization of the most Jh-proximal Vh gene segments in pre-B-cell lines.Nature 311: 727–731, 1984
Yonekawa, H., Moriwaki, K., Gutoh, O., Hayashi, J.-I., Watanabe, J., Miyashita, N., Petras, M. L., and Tagashira, Y.: Evolutionary relationships among subspecies ofM. musculus based on restriction enzyme cleavage patterns of mitochondrial DNA.Genetics 98: 801–816, 1981
Yonekawa, H., Moriwaki, K., Gutoh, O., Miyashita, N., Migita, S., Bonhomme, F., Hjorth, J. P., Petras, M. L., and Tagashira, Y.: Origins of laboratory mice deduced from restriction patterns of mitochondrial DNA.Differentiation 22: 222–226, 1982
Yonekawa, H., Gutoh, O., Tagashira, T., Shi, L.-I., Cho, W. S., Miyashita, N., and Moriwaki, K.: A hybrid origin of Japanese mice “Mus musculus molossinus”.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 127: 62–67, 1986
Yonekawa, H., Moriwaki, K., Gutoh, O., Miyashita, N., Matsushima, Y., Shi, L., Cho, W. S., Zhen, X.-L., and Tagashira, Y.: Hybrid origin of Japanese mice “Mus musculus molossinus”: evidence from restriction analysis of mitochondrial DNA.Mol Biol Evol 5: 63–78, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tutter, A., Riblet, R. Evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the genusMus . Immunogenetics 30, 315–329 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425271
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425271