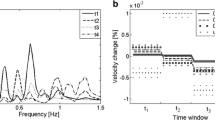
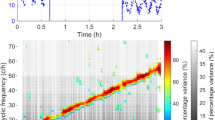
Abstract
Traditionally, linear mean-square (MS or stochastic) estimation coefficients are calculated using cross-correlations between each of the data at reference and estimation locations. Since the cross-correlation between data at reference and estimation locations typically decreases rapidly with increasing separation distance, the resulting estimated fluctuations diminish away from the reference locations. Two new schemes have been developed to optimally determine estimation coefficients which yield an improved estimated energy representation. One approach involves a non-linear least-square fit toboth the estimation covariance and the cross-correlation between data at reference and estimation locations. By also minimizing the error in the estimation covariance, realistic energy levels can be estimated without significantly altering the correlation between true and estimated velocity signals as given by the traditional MS method. Another scheme, developed for use with a single-point, two-component reference, maximizes the correlation coefficient between the estimate and its measured counterpart. It is shown that for this simple case, the estimated covariance can be setequal to the measured covariance without compromising the correlation coefficientat all. The effectiveness of the proposed techniques is demonstrated by comparing their estimates with those given by the MS method in a plane turbulent mixing layer. In general, the estimation schemes appear to give improved results when references from the edge of the mixing layer are employed. It is also demonstrated how the results of the proposed estimation methods can be used to infer details regarding the mixing layer structure and kinematics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (1977) On the role of conditional averages in turbulence theory. In: Turbulence in Liquids, (eds. Patterson, GK. and Zakin, JL) Princeton: Science Press, 323
Adrian RJ (1979) Conditional eddies in isotropic turbulence. Phys Fluids 22: 2065–2070
Adrian RJ;Jones BG;Chung MK;Hassan Y;Nithianandan CK;Tung AT-C (1989) Approximation of turbulent conditional averages by stochastic estimation. Phys Fluids A 1: 2065–2070
Adrian RJ;Moin P (1988) Stochastic estimation of organized turbulent structure: homogeneous shear flow. J Fluid Mech 190: 531–559
Bell JH;Mehta RD (1992) Measurements of the streamwise vortical structures in a plane mixing layer. J Fluid Mech 239: 213–248
Cole DR;Glauser MN;Guezennec YG (1992) An application of the stochastic estimation to the jet mixing layer. Phys Fluids A 4: 192–194
Guezennnec YG (1989) Stochastic estimation of coherent structures in turbulent boundary layers. Phys Fluids A 1: 1054
Ho C-M;Huerre P (1984) Perturbed Free Shear Layers. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 16: 365–424
LeBoeuf RL;Mehta RD (1993) Streamwise vortex meander in a mixing layer. Phys Fluids A 5: 1983–1991
Papoulis A (1984) Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes. 2nd Edition, New York: Mc-Graw Hill, 407–414
Press WH;Flannery BP;Teukolsky SA;Vetterling WT (1986) Numerical Recipes, The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 523–528.
Tung TC;Adrian RJ (1980) Higher-order estimates of conditional eddies in isotropic turbulence. Phys Fluids A 23, 1469–1470
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was conducted in the Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, NASA Ames Research Center and was supported by the NASA Ames Research Center — Stanford University, Center for Turbulence Research, Postdoctoral Fellowship Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LeBoeuf, R.L., Mehta, R.D. Improved methods for linear estimation of velocity records. Experiments in Fluids 17, 32–38 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02412801
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02412801