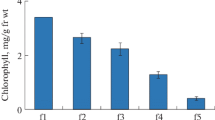
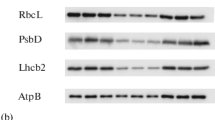
Abstract
Etiolated pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Lincoln) seedlings do not show any capability for the biosynthesis of chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase), but the rate of biosynthesis of the increases with the pre-illumination time. This light-induced FBPase synthesis appears to be regulated at the transcriptional level, the response of young leaves being greater than that of mature ones. In-vivo labelling experiments demonstrated by immunoprecipitation, followed by sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoresis and fluorography, the presence of a 49-kilodalton (kDa) band which corresponds to the mature FBPase subunit. In-vitro translation experiments with a wheat-germ synthesizing system and polyadenylated mRNA isolated from illuminated young pea seedlings have demonstrated the appearance of a 59-kDa labelled band corresponding to the precursor of the FBPase basic subunit. When intact pea chloroplasts were added to the above in-vitro incubation mixture, a labelled 49-kDa subunit similar to that of the in-vivo experiments appeared in the organelle under illumination. From these results we can conclude that a 10-kDa transit peptide bound to the translated pea FBPase subunit exists in the cytosol; this transit peptide is lost during passage through the chloroplast envelope, leaving the mature subunit inside the organelle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FBPase:
-
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- kDa:
-
kilodalton
- MW:
-
molecular weight
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- poly(A)mRNA:
-
polyadenylated mRNA
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
References
Anderson, L.E. (1986) Light/dark modulation of enzyme activity in plants. Adv. Bot. Res.12, 1–45
Anderson, C.W., Straus, J.W., Dudock, B.S. (1983) Preparation of cell-free protein-synthesizing system from wheat germ. Methods Enzymol.101, 635–644
Apel, K., Kloppstech, K. (1978) The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA encoding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur. J. Biochem.85, 581–588
Arnon, D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol-oxidase inBeta vulgaris. Plant Physiol.24, 1–15
Bard, J., Bourque, D.P., Hildebrand, M., Zaitlin, D. (1985) In vitro expression of chloroplast genes in lysates of higher plant chloroplasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA82, 3983–3987
Bassham, J.A., Krause, G.H. (1969) Free energy changes and metabolism regulation in steady-state photosynthetic carbon reduction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta189, 207–221
Berry, J.O., Nikolau, B.J., Carr, J.P., Klessig, D.F. (1985) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in light- and dark-grown amaranth cotyledons. Mol. Cell Biol.5, 2238–2246
Berry-Lowe, S.L., McKnight, T.D., Shah, D.M., Meagher, R.B. (1982) The nucleotide sequence, expression, and evolution of one member of a multigene family encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean. J. Mol. Appl. Genet.1, 483–498
Bloom, M.V., Milos, P., Roy, H. (1983) Light-dependent assembly of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA80, 1013–1017
Briat, J.F., Lescure, A.M., Mache, R. (1986) Transcription of the chloroplast DNA: A review. Biochimie68, 981–990
Broglie, R., Coruzzi, G., Lamppa, G., Keith, B., Chua, N.H. (1983) Structural analysis of nuclear genes coding for the precursor protein to the small subunit of wheat ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Bio/Technology1, 55–61
Buchanan, B.B. (1980) Role of light in the regulation of chloroplast enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.31, 341–374
Buchanan, B.B., Schürmann, P., Kalberer, P.P. (1971) Ferredoxin-activated fructose diphosphatase of spinach chloroplasts. J. Biol. Chem.246, 5952–5959
Chueca, A., Lázaro, J.J., López Gorgé, J. (1984) Light-induced nuclear synthesis of spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Plant Physiol.75, 539–541
Coruzzi, G., Broglie, R., Edwards, C., Chua, N.H. (1984) Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J.3, 1671–1679
Cuming, A.C., Bennett, J. (1981) Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Control of messenger RNA activity by light. Eur. J. Biochem.118, 71–80
Ellis, R.J. (1981) Chloroplast proteins: Synthesis, transport and assembly. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.32, 111–137
Freyssinet, G., Buetow, D.E. (1984) Regulation and expression of genes for chloroplast proteins. Isr. J. Bot.33, 107–131
Fromm, H., Devic, M., Fluhr, R., Edelman, M. (1985) Control of psbA gene expression: in matureSpirodela chloroplasts light regulation of 32-kd protein synthesis is independent of transcript level. EMBO J.4, 291–295
Gallagher, T.F., Ellis, R.J. (1982) Light-stimulated transcription of genes for two chloroplast polypeptides in isolated pea leaf nuclei. EMBO J.1, 1493–1498
Grossman, A.S., Bartlett, S.G., Schmidt, G.W., Mullet, J. E., Chua, N.H. (1982) Optimal conditions for post-translational uptake of proteins by isolated chloroplasts. J. Biol. Chem.257, 1558–1563
Hermoso, R., Chueca, A., Lázaro, J.J., López Gorgé, J. (1987) An immunological method for quantitative determination of photosynthetic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in leaf crude extracts. Photosynth. Res.14, 269–278
Herzog, B., Stitt, M., Heldt, H.W. (1984) Control of photosynthetic sucrose synthesis by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate. 3. Properties of the cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Plant Physiol.75, 561–565
Hurn, B.A.L., Chantler, S.M. (1980) Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol.70, 105–142
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature227, 680–685
Lázaro, J.J., Chueca, A., López Gorgé, J., Mayor, F. (1974) Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase from spinach leaf chloroplasts: Purification and heterogeneity. Phytochemistry13, 2455–2461
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275
Maniatis, T., Frisch, E.F., Sambrook, J. (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Marcus, F., Fickenscher, K. (1988) Amino-terminal sequence of spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Arch. Biol. Med. Exp.21, 117–121
Marcus, F., Harrsch, P.B., Moberly, L., Edelstein, F., Latshaw, S.P. (1987) Spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Identification of the subtilisin-sensitive region and of conserved histidines. Biochemistry26, 7029–7035
Mills, W.R., Joy, K.W. (1980) A rapid method for isolation of purified, physiologically active chloroplasts, used to study the intracellular distribution of amino acids in pea leaves. Planta148, 75–83
Palmer, J.D. (1985) Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet.19, 325–354
Pfisterer, J., Lachmann, P., Kloppstech, K. (1982) Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Binding of nuclear-coded chloroplast proteins to the chloroplast envelope. Eur. J. Biochem.126, 143–148
Plá, A., López Gorgé, J. (1981) Thioredoxin/fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase affinity in the enzyme activation by the ferredoxin-thioredoxin system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta636, 113–118
Portis, A.R. Jr., Heldt, H.W. (1976) Light-dependent changes of the Mg2+ concentration in the stroma in relation to the Mg2+ dependency of CO2 fixation in intact chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta449, 434–446
Preiss, J., Kosuge, T. (1970) Regulation of enzyme activity in photosynthetic systems. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.21, 433–466
Raines, C.A., Lloyd, J.C., Longstaf, M., Bradley, D., Dyer, T. (1988) Chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The product of a mosaic gene. Nucleic Acids Res.16, 7931–7942
Sahrawy, M., Chueca, A., Hermoso, R., Lázaro, J.J., López Gorgé, J. (1988) Effect of light quality and intensity on the biosynthesis of photosynthetic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. Life Sci. Adv.7, 55–59
Schmidt, G.W., Devilliers-Thiery, A., Desruisseaux, H., Blobel, G., Chua, N.H. (1979) NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of precursor and mature forms of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunits fromChlamydomonas reinhardii. J. Cell Biol.83, 615–622
Vidal, J., Gadal, P. (1981) Evidence for the novo synthesis of nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide phosphate malate dehydrogenase during greening of corn leaves. Physiol. Vég.19, 483–489
Wallace, D.M. (1987) Large- and small-scale phenol extractions. Methods Enzymol.152, 33–41
Wasmann, C.C., Reiss, B., Bartlett, S.G., Bohnert, H.J. (1986) The importance of the transit peptide and the transported protein for protein import into chloroplasts. Mol. Gen. Gent.205, 446–453
Zhu, Y.S., Kung, S.D., Bogorad, L. (1985) Phytochrome control of levels of mRNA complementary to plastid and nuclear genes of maize. Plant Physiol.79, 371–376
Zimmermann, G., Kelly, G.J., Latzko, E. (1978) Purification and properties of spinach leaf cytoplasmic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem.253, 5952–5956
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahrawy, M., Chueca, A., Hermoso, R. et al. In-vivo and in-vitro synthesis of photosynthetic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 182, 319–324 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411381
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411381