Abstract
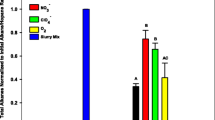
Bioremediation of crude oil in salt marsh mesocosms growingSpartina alterniflora was investigated during winter and summer to determine the influence of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) fertilization, flooding, and season. Fertilization with urea and ammonium (NH +4 ) applied at 75 or 150 kg N ha−1 with or without P did not significantly (p=0.05) increase oil or hydrocarbon degradation in continuously flooded mesocosms over an 82 day period during winter (temperature range of 17 to 30 °C). Phosphorus applied at 40 kg P ha−1 significantly (p = 0.05) increased oil and hydrocarbon degradation. Nitrate (NO −3 ) ) added alone did not increase oil or hydrocarbon degradation, but when added with P, it significantly (p = 0.05) increased degradation above that for P alone. Up to 70% of applied oil and 75% of applied hydrocarbons were degraded in P supplemented treatments. Inipol, an oleophilic fertilizer containing N, P, and a dispersant, significantly increased oil and hydrocarbon degradation. During a 40 day summer experiment (temperature range of 27–42 °C), N and P fertilization did not increase oil or hydrocarbon degradation. For continuously flooded treatments, 72% of applied hydrocarbons were degraded while 51% were degraded in alternately flooded treatments. Mesocosms provided conditions suitable for quantitative recovery of oil and results indicated that N and P fertilization, flooding, and season interacted to influence oil bioremediation. Even under the most favorable conditions, more than 1 month was required for most of the oil to disappear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. and Scow, K. M.: 1989, ‘Kinetics of Biodegradation in Soil’, in B. L. Sawhney and Brown, K. (eds.),Reactions and Movement of Organic Chemicals in Soils, Soil Sci. Soc. of Am. and Soc. of Agron., Madison, WI, pp. 243–269.
Alexander, S. K. and Webb, J. W.: 1983, Effects of a Simulated Oil Spill on Growth and Decomposition ofSpartina alterniflora in a Galveston Bay, Texas salt marsh, in report to the Center for Energy and Mineral Resources, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX.
Alexander, S. K. and Webb, J. W.: 1987, ‘Relationship ofSpartina alterniflora Growth to Sediment Oil Content Following an Oil Spill’, inProc. of the 1987 Oil Spill Conf., Am. Petroleum Inst., Washington, DC, pp. 445–449.
Atlas, R. M.: 1981,Microbial. Rev. 45, 180–209.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R.: 1972a,Biotech. Bioeng. 14, 309–318.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R.: 1972b,Can. J. Microbiol. 18, 1851–1855.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R.: 1973,Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 538–541.
Bender, M. E., Shearls, E. A., Ayers, R. P., Hershner, C. H., and Huggett, R. J.: 1977, ‘Ecological Effects of Experimental Oil Spills on Eastern Coastal Plain Estuarine Ecosystems’, inProc. of the 1977 Oil Spill Conf., Am. Petroleum Inst., Washington, DC, pp. 505–509.
Bossert, I. and Bartha, R.: 1984, ‘The Fate of Petroleum in Soil Ecosystems’, in R. M. Atlas (ed.),Petroleum Microbiology, MacMillan Publishing Co., New York, NY, pp. 434–476.
Brown, E. J. and Braddock, J. F.: 1990,Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 3895–3896.
Burns, K. A. and Teal, J. M.: 1979,Estuarine Coastal Mar. Sci. 8, 349–360.
Bushnell, L. D. and Haas, F. F.: 1941,J. Bacteriol. 41, 653–673.
Churchill, S. A., Griffin, R. A., Jones, L. P., and Churchill, P. F.: 1995,J. Environ. Qual. 24, 19–28.
EPA Method 418.1.: 1979, ‘Petroleum Hydrocarbons, Total Recoverable’, inMethods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes. U.S. EPA, Washington, DC, EPA 600/4-79/020.
Hambrick, G. A., DeLaune, R. D. and Patrick, W. H.: 1980,Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 40, 365–369.
Hampson, G. R. and Moul, E. T.: 1978,J. Fish. Res. Board. Can. 35, 731–734.
Hollaway, S. L., Faw, G. M. and Sizemore, R. K.: 1980,Mar. Pollut. Bull. 11, 153–156.
Holt, S., Rabalais, S., Rabalais, N., Cornelius, S. and Holland, J. S.: 1978, Effects of an oil spill on salt marshes at Harbor Island, Texas, inProc. of the Conf on Assessment of Ecological Impacts of Oil Spills. Am. Inst. Biol. Sci., Arlington, VA, pp. 344–352.
Huesemann, M. H.: 1995,Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 7–18.
Kiesling, R. W., Alexander, S. K. and Webb, J. W.: 1988,Environ. Pollut. 55, 221–238.
Leahy, J. G. and Colwell, R. R.: 1990,Microbiol. Rev. 54, 305–315.
Long, B. F. and Vandermeulen, J. H.: 1983, ‘Geomorphological Impact of Cleanup of an Oiled Salt Marsh (Ile Grande, France)’, inProc. of the 1953 Oil Spill Conf., Am. Petroleum Inst., Washington DC, pp. 501–505.
Macko, S. A., Parker, P. L. and Botello, A. V.: 1981,Environ. Pollut. 2, 119–128.
Nixon, S. W., Kelly, J. R., Furnas, B. N., Oviatt, C. A. and Hale, S. S.: 1980, ‘Phosphorus Regeneration and the Metabolism of Coastal Marine Bottom Communities’, in K. R. Tenore and Coull, B. G. (eds.),Marine Benthic Dynamics, Univ. of South Carolina Press, Columbia, SC, pp. 219–242.
Pritchard, P. H. and Costa, C. F.: 1991,Environ. Sci. Technol. 25, 372–379.
Shelton, T. B. and Hunter, J. V.: 1975,Water Pollut. Control Fed. J. 47, 2256–2270.
Walker, J. D. and Colwell, R. R.: 1973, ‘Microbial Ecology of Petroleum Utilization in Chesapeake Bay’, inConf on Prevention and Control of Oil Spills, Am. Petroleum Inst., Washington, DC, pp. 685–690.
Ward, D., Atlas, R. M., Boehm, P. D. and Calder, J. A.: 1980,Ambio.9, 277–283.
Webb, J. W. and Alexander, S. K.: 1991,Contrib. Mar. Sci. 32, 9–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, A.L., Weaver, R.W. & Webb, J.W. Oil bioremediation in salt march mesocosms as influenced by N and P fertilization, flooding, and season. Water Air Soil Pollut 95, 179–191 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02406164
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02406164