Abstract
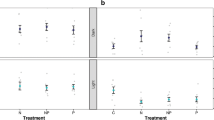
Many bryophytes rely to a large extent on atmospheric deposition for their nutrient uptake. However, increasing levels of atmospheric ammonium (NH +4 ) and nitrate (NO -3 ) attract concern as to the possible harmful effects on bryophytes from these two nutrient sources. Changes in nitrate reductase (NR) activities, cation (Ca, K and Mg), total nitrogen (N) and organic acid concentrations were investigated for the mosses,Racomitrium lanuginosum, Rytidiadelphus loreus andPhilonotis fontana, in response to a single field misting with 3 mol−3 NH +4 and NO -3 . Increases of 20% were recorded for tissue N content, 48 hr after misting with N containing solutions. When labelled15NH +4 or15NO -3 were applied toR. Lanuginosum at 1, 3 and 6 mol m−3 concentrations, partitioning of incorporated15N between different tissue regions occured, with the highest N uptake in the upper stem and leaves. High concentrations of applied N resulted in reduced efficiency of N uptake. NH +4 applications caused declines in NR activities, organic acids and cations, whereas, NO -3 treatments caused the reverse response. Changes in cation contents, organic acids and NR activity reflect short-term regulation of N metabolism in the presence of defined N sources, as well as potential mechanisms of regulating cell pH homoeostasis. The consistency of physiological responses, especially NR activities, over short-term pollution episodes, provides evidence for their use as indicators of both NH +4 and NO -3 pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, R., Wallen, B. and Malmer, N.: 1992,J. Ecol. 80, 131.
Allen, S. E.: 1974,Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Anon.: 1990,Acid Deposition in the United Kingdom 1986–1988. Third report of the United Kingdom Review group on Acid Rain, Department of the Environment.
Baddeley, J. A., Thompson, D. B. A. and Lee, J. A.: 1994,Environ. Pollut. 84, 189.
Barrie, A. and Lemley, M.: 1989,International Laboratory 19, 82.
Bates, J. W.: 1992,J. Bryol. 17, 223.
Bates, J. W.: 1994,Functional Ecology 8, 686.
Van der Eerden, L. J.: 1992,Fertilising Effects of Atmospheric Ammonia on Semi Natural Vegetation, Publication from Agricultural Research Department, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Fangmeier, A. F. Hadwiger-Fangmeier, A., van der Eerden, L. and Jäger, H. J.: 1994,Environ Pollut. 86, 43–82.
Farmer, A. M., Bates, J. W. and Bell, J. N. B.: 1992,Bryophytes and Lichens in a Changing Environment, Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, pp. 284–313.
Flaig, H. and Mohr, H.: 1992,Physiologia Plantarum,84 568.
Filner, P.: 1966,Biochimica and Biophysica Acta 118, 299.
Greven, H. C.: 1992,Dissertationes Botanicae, No. 194.
Hallingbäck, T.: 1992,Biological Conservation 59, 163.
Jönsdöttir, I. S., Callaghan, T. V. and Lee, J. A.: 1995,The Science of the Total Environment,160/161, 677.
Kooijman, A. M. and Bakker, C.: 1994,Aquatic Botany 48, 133.
Lee, J. A. and Studholme, C. J.: 1992,Bryophytes and Lichens in a Changing Environment. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, pp. 314–332.
Lee, J. A., Tallis, J. H. and Woodin, S. J.: 1988,Ecological Change in the Uplands, Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, pp. 151–162.
Lee, R. B., Purves, J. V., Ratcliffe, R. G. and Saker, L. R.: 1992,Journal of Experimental Botany,43, 1385.
McCullough, H.: 1967,Clinica Chimica Acta 17, 297.
Mollering, H.: 1985a,Methods of Enzymatic Analysis: Metabolites 2, 3rd Ed. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp. 39–47.
Mollering, H.: 1985b,Methods of Enzymatic Analysis: Metabolites 2, 3rd Ed. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp. 2–12.
Morgan, S. M., Lee, J. A. and Ashenden, T. W.: 1992,New Phytol. 120, 89.
Padidam, M., Venkateswarlu, K. and Johri, M. M.: 1991,Plant Science 75, 185.
Pearson, J. and Stewart, G. R.: 1993,New Phytol. 125, 283.
Pérez-Soba, M.: 1995,Physiological Modulation of Scots Pine Trees by Atmospheric Ammonia, PhD thesis, Department of Biology, University of Gronigen, The Netherlands.
Pitcairn, C. E. R., Fowler, D. and Grace, J.: 1995,Environ. Pollut. 88, 193.
Raven, J. A.: 1988, CEC Report No. EUR 11738 EN, Belgium, pp. 187–195.
Raven, J. A., Wollenweber, B. and Handley, L. L.: 1992a,New Phytol. 121, 19.
Raven, J. A., Wollenweber, B. and Handley, L. L.: 1992b,New Phytol. 121, 5.
Rodenkirchen, H.: 1992,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 61, 279.
Rudolph, H. and Voigt, J. U.: 1986,Physiologica Plantarum 66, 339.
Smith, A. J. E.: 1980,The Moss Flora of Britain and Ireland, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Soares, A., Ming, J. Y. and Pearson, J.: 1995,Environ. Pollut. 87, 159.
Steinnes, E., Hanssen, J. E. and Rambaek, J. P.: 1994,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 74, 121.
Stewart, G. R. and Orebamjo, T. O.: 1979,New Phytol. 83, 311.
Stewart, G. R., Schmidt, S., Handley, L. L., Turnbull, M. H., Erskine, P. D. and Joly, C. A.: 1995,Plant, Cell and Environment 18, 85.
Sutton, M. A. and Fowler, D.: 1993,Critical Loads Concepts and Applications, ITE Symposium No. 28, HMSO, London, pp. 119–126.
Tallis, J. H.: 1959,J. Ecol. 47, 325.
Thompson, D. B. A. and Baddeley, J.: 1991,Focus on Nature Conservation, No. 26. Nature Conservancy Council, Peterborough, pp. 17–28.
Woodin, S. J. and Lee, J. A.: 1987,New Phytol. 105, 103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, A., Pearson, J. Short-term physiological responses of mosses to atmospheric ammonium and nitrate. Water Air Soil Pollut 93, 225–242 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02404758
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02404758