Abstract
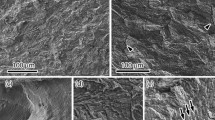
A dual-phase steel containing niobium, vanadium and titanium as microalloying elements was tested for hydrogen embrittlement (HE). The susceptibility to HE was observed to be closely related to the microstructural state. Hydrogenated specimens intercritically annealed at relatively low temperatures to develop martensite islands in a ferrite matrix basically exhibited quasi-cleavage fracture with some ductile dimpling. The mode of fracture in charged specimens quenched from higher intercritical annealing temperatures was predominantly intergranular fracture along prior austenite grain boundaries and cracking of martensite laths. The detrimental role of residual stresses, retained austenite and microalloying carbides in the process of HE is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Norberg andB. Aronsson,J. Iron Steel Inst. 206 (1968) 1263.
K. Narita,Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn 15 (1975) 147.
G. L. Dunlop andP. J. Turner,Met. Sci. 9 (1975) 370.
D. C. Houghton, G. C. Weatherby andJ. D. Embury, in “Thermomechanical Processing of Microalloyed Austenite”, edited by A. J. De Ardo, G. A. Ratz and P. J. Wang (Metals Society, AIME, Warrendale, 1982) p. 267.
N. K. Balliger andR. W. K. Honeycombe,Met. Sci. 14 (1980) 121.
G. L. Dunlop andR. W. K. Honeycombe,ibid. 14 (1980) 367.
T. Gladman,Proc. R. Soc. 294 (1966) 298.
Idem., in “Recrystallization and Grain Growth of Multi-Phase and Particle Containing Materials”, edited by N. Hansen, A. R. Jones and T. Leffers (Riso National Laboratory, Riso, Denmark, 1980) p. 183.
C. J. Tweed, N. Hansen andB. Ralph,Met. Trans. 14A (1983) 2235.
W. B. Morrison andJ. H. Woodhead,J. Iron Steel Inst. 201 (1963) 43.
A. T. Davenport, F. G. Berry andR. W. K. Honeycombe,Met. Sci. 2 (1968) 104.
F. G. Berry andR. W. K. Honeycombe,MeT. Trans,1 (1970) 3279.
R. W. K. Honeycombe, in “Phase Transformation in Ferrous Alloys”, edited by A. R. Marder and J. I. Goldstein, (Metals Society, AIME, 1984) p. 259.
J. M. Gray, T. Ko, Zhang Shouhau, Wu Baorong andXIE Xishan (eds), “HSLA Steels, Metallurgy and Applications”, Proceedings of International Conference, November 1985, Beijing (ASM, Ohio, 1986).
A. J. De Ardo (ed.), “Processing, Microstructure and Properties of HSLA Steels”, Proceedings of International Symposium, November 1987, Pittsburg, Pennsylvania (Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Warrendale, 1988).
I. M. Bernstein, R. Garber andG. M. Pressouyre, in “Effects of Hydrogen on Behaviour of Materials”, edited by A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein (TMS, New York, 1976) p. 27.
D. A. Ryder, T. Grundy andT. J. Davies, in Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Current Solutions to Hydrogen Problems in Steels, Washington, DC, November 1982, edited by C. G. Interrante and G. M. Pressouyre (ASM, Metals Park, 1982) p. 272.
P. Lacombe, M. Aucouturier andJ. Chene, in “Hydrogen Embrittlement and Stress Corrosion Cracking”, edited by R. Gibala and R. F. Hehemann (ASTM, Metals Park, 1984) p. 79.
T. Alp, B. Dogan andT. J. Davies,J. Mater. Sci. 22 (1987) 2105.
A. McNabb andP. K. Foster,Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 227 (1963) 618.
H. H. Johnson andR. W. Lin, in “Hydrogen Effects in Metals”, Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Effects of Hydrogen on Behaviour of Materials, Wyoming, August 1980, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, 1981) p. 3.
R. A. Oriani,Acta Metall. 18 (1970) 147.
R. Gibala, in “Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittlement of Iron Base Alloys”, edited by R. W. Staehle, J. Hochmann, R. D. McCright and J. E. Slater (NACE, Houston, 1977) p. 244.
J. P. Hirth,Met. Trans. 11A (1980) 861.
B. B. Rath andI. M. Bernstein,Met. Trans. A 2 (1971) 2845.
G. M. Pressouyre, PhD thesis, Carnegie-Mellon University (1977).
G. M. Pressouyre andI. M. Bernstein,Corrosion Sci. 18 (1978) 819.
G. M. Pressouyre,Acta Metall. 28 (1980) 1980.
S. Hayami andT. Furukawa, in Proceedings, “Micro-alloying 75”, London, Session 2A (Vanitec, London, 1975) p. 78.
M. S. Rashed, “A Unique High-Strength Sheet Steel with Superior Formability”, SAE reprint 760 206 (1976).
R. A. Kot andJ. W. Morris (eds), “Structure and Properties of Dual-Phase Steels” (AIME, New York, 1979).
J. M. Rigsbee andP. J. Vanderarend, in “Formable HSLA and Dual-Phase Steels”, edited by A. T. Davenport (AIME, New York, 1979).
R. A. Oriani,Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 8 (1978) 327.
I. M. Bernstein andA. W. Thompson, in “Hydrogen Embrittlement and Stress Corrosion Cracking”, edited by R. Gibala and R. F. Rehemann (ASM, Ohio, 1984) p. 135.
J. H. Woodhead, “Vanadium in High Strength Steels” (Vanitec, London, 1979) p. 3.
K. J. Irvine, F. B. Pickering andT. Gladman,J. Iron Steel Inst. 205 (1967) 161.
A. W. Thompson andI. M. Bernstein,Adv. Corros. Sci. Technol. 7 (1980) 53.
W. Cao andX.-P. Lu,Met. Trans. 18 (1987) 1569.
D. K. Matlock, G. Krauss, L. Ramos andG. S. Huppi, in “Structure and Properties of Dual-Phase Steels”, edited by R. A. Kot and J. W. Morris (AIME, New York, 1979) p. 62.
G. R. Speich, in “Metals Handbook”, Vol. 1, 10th Edn (ASM, Ohio, 1990) p. 424.
S. S. Hansen andR. R. Pradhan, in “Structure and Properties of Dual-Phase Steels” edited by R. A. Kot and J. W. Morris (AIME, New York, 1979) p. 113.
N. C. Goel, J. P. Chakravarty andK. Tangri,Met. Trans. A 18 (1987) 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alp, T., Iskanderani, F.I. & Zahed, A.H. Hydrogen effects in a dual-phase microalloy steel. J Mater Sci 26, 5644–5654 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02403969
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02403969