Abstract
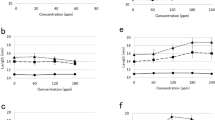
The relationship between elongation growth and the incorporation of [3H]gibberellin A1 ([3H]GA1) into a 2,000g pelletable (2KP) fraction from lettuce (Lactuca sativa L., cv. Arctic) hypocotyl sections has been examined. Sections were loaded with incremental amounts of GA1 under conditions where growth was arrested (5° C) or permitted (30° C) and, after 16 h, all were transferred to a GA-free medium at 30° C. Growth and 2KP radioactivity were measured at this point and after a further 24 h in the chase medium. Uptake was reduced by 80% at 5° C, as compared to 30° C, but 2KP labelling and protein synthesis were only reduced by half. The growth rate of the 5° C pretreated sections during the chase period was comparable to that observed during the pulse in the 30° C material but the dose/response relationship was flatter. Low temperature sections incorporated a much higher percentage of GA1 uptake into the 2KP fraction (27% at maximum) but the absolute levels of labelling at this temperature were lower than those measured at 30° C. The data are interpreted as showing that 2KP labelling is not a consequence of growth. It must either precede response or be an unconnected concurrent process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2KP:
-
2,000g pelletable fraction
- GA1 :
-
gibberellin A1
References
Bollum, F.J.: Filter paper disc techniques for assaying radioactive macromolecules. In: Methods in Enzymology vol. 12B, pp. 169–173. Grossman, L., Moldave, K. eds. New York: Academic Press, 1968
Jones, T.W.A., Stoddart, J.L.: Gibberrellin-induced changes in protein synthesis and enzyme activity in shoot apices ofTrifolium pratense. J. Exp. Bot.21, 452–461 (1970)
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Nadeau, R., Rappaport, L.: The synthesis of [3H]gibberellin A3 and [3H]gibberellin A1 by the palladium-catalysed actions of carrier-free tritium on gibberellin A3. Phytochemistry13, 1537–1545 (1974)
Silk, W.K., Jones, R.L.: Gibberellin response in lettuce hypocotyl sections. Plant Physiol.56, 267–272 (1975)
Stoddart, J.L., Tapster, S.M., Jones, T.W.A.: Temperature dependence of the gibberellin response in lettuce hypocotyls. Planta141, 283–288 (1978)
Stoddart, J.L.: Interaction of [3H]gibberellin A1 with a sub-cellular fraction from lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) hypocotyls. I. Kinetics of labelling. Planta146, 353–361 (1979a)
Stoddart, J.L.: Interaction of [3H]gibberellin A1 with a sub-cellular fraction from lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) hypocotyls. II. Stability and properties of the association. Planta146, 363–368 (1979b)
Stoddart, J.L., Williams, P.D.: Interaction of [3H]gibberellin A1 with a sub-cellular fraction from lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) hypocotyls. Requirement for protein synthesis. Planta147, 264–268 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoddart, J.L., Williams, P.D. Interaction of [3H]gibberellin A1 with a sub-cellular fraction from lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) hypocotyls. Planta 148, 485–490 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02395319
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02395319