Abstract
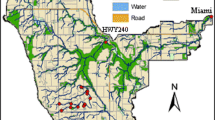
Soils will behave differently when used for agriculture, forestry, and other purposes and must be managed differently. The difference is most evident in the Inverbrackie Creek catchment area in South Australia where the study reported in this article was conducted and where the soils are used extensively for grazing and dairy farming. This catchment covers an area of 8.38 km2, comprising an undulating upland plain with irregularly high hills and broad interfluves.
Previous information-gathering methods used to model the catchment's hydrologic activity have been derived from the downstream pluviographic point-source technique. The model input samples obtained by this technique are not truly representative of the catchment. The potential for using remote sensing color infrared imagery to delineate the areas contributing to soil sediment flow is demonstrated as a better alternative to obtaining representative samples to model this activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anderson, M. G., and T. P. Burt. 1977. Automatic monitoring of soil moisture conditions in a hillslope spur and hollow.Journal of Hydrology 33:27–36.
Boughton, W. C. 1986. Hydrograph analysis as a basis for infall runoff modelling. Hydrology and waters resources symposium. Griffith University, Brisbane, 25–27 November.
Chow, V. T. (ed.). 1964. Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Crawford, N. H. and R. K. Linsley. 1962. The synthesis of continuous streamflow hydrographs on a digital computer. Department of Civil Engineering, Stanford University.
Crow, E. L., F. A. Davis, and M. W. Maxfield. 1960. Statistics manual. Dover Publication, New York.
Curran, P. J. 1981. The estimation of surface moisture of a vegetated soil using aerial infrared photography.International Journal of Remote Sensing 2(4):369–378.
Doyle, F. J. 1978. The next decade of satellite remote sensing.Photogrammatric Engineering and Remote Sensing 44:155–164.
Draper, S. E., and S. G. Rao. 1986. Runoff prediction using remote sensing imagery.Water Resources Bulletin, American Water Resources Association 22(6):941–949.
Ishaq, A. M., and D. D. Huff. 1974. Application of remote sensing to the location of hydrodynamical active (source) areas. 9th international symposium on remote sensing environment, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 15–19 April.
Ishaq, A. M., and D. D. Huff. 1979. Hydrologic source area. Pages 495–510in Modelling hydrologic processes. Proceedings international hydrology symposium, Colorado State University.
Kolawole, M. O. 1988. Detection of partial areas using remote sensing and hydrological analyses. Master of environmental studies thesis. University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia.
Kolawole, M. O. 1990. Remote sensing and land use management. ANZAAS (Australian and New Zealand Association for the Advancement of Science) Conference, Hobart, 12–16 February.
Lal, R., and D. J. Greeland. 1979. Soil physical properties and crop production in the tropics. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Linsley, R. K., M. A. Kohler, and J. L. Paulhus. 1975. Hydrology for engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Marshall, T. J., and J. W. Holmes. 1979. Soil physics. Cambridge University Press, London.
Maulders, M. A. 1987. Remote sensing in soil science. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
McColl, R. H. S., D. J. McQueen, A. R. Gibson, and J. C. Heine. 1985. Storm areas of storm runoff in a pasture catchment.Journal of Hydrology (NZ) 24(1):1–19.
McMahon, T. A. 1988. Drought and arid zone hydrology in Australia. IEAust Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium, Canberra.
Moore, I. D., and R. G. Mein. 1975. An evaluation of three rainfall-runoff models. Hydrology symposium Institution of Engineers (Australia) 75/3.
Myers, V. I. 1983. Remote sensing application in agriculture. Pages 2111–2228in Manual of remote sensing, vol II. American Society of Photography.
O'Loughlin, E. M. 1986. Prediction of surface saturation zones in natural catchments of topographic analysis.Water Resources Research 22(5):794–804.
Ragan, R. M., and T. J. Jackson. 1980. Runoff synthesis using Landsat and SCS model.Journal of Hydraulics, ASCE 106(HY5):667–678.
Sittner, W. T., C. E. Schauss, and J. C. Monro. 1969. Continuous hydrograph synthesis with an API-type hydrological model.Water Resources Research 5:1007–1022.
Tucker, C. J. 1979. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation.Remote Sensing of Environment 8:127–150.
van de Griend, A. A., and E. T. Engman. 1985. Partial area hydrology and remote sensing.Journal of Hydrology 81:211–251.
Woodwell, G. M. 1984. Pages 1–17In G. M. Woodwell (ed.). The role of terrestrial vegetation in the global carbon cycle: Measurement by remote sensing. SCOPE 23. Wiley, New York.
Zachar, D. 1982. Soil erosion. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article reports on part of the work supported by the University Research Grant, University of Adelaide.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolawole, M.O. Using remote sensing technique to study soil sedimentation flow. Environmental Management 17, 73–81 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02393796
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02393796