Summary
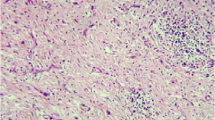
On the basis of clinical and biochemical findings, Factor XIII subunita (FXIII A) has been conjectured to play an important role in fibrotic processes. Epulis samples at different stages of fibrotic tissue formation were used as a model system for studying the localization and tissue distribution of FXIII A during the course of connective tissue generation. Marker characteristics of cells containing FXIII A (FXIII A+ cells) were determined as well. In double immunofluorescent labelling systems, FXIII A was localized in monocyte-derived (CD-14+), activated (HLA-DR+), and phagocytosing (Ki-M7+) tissue macrophages, which are widely distributed homogeneously in granulation tissues, but start to accumulate around foci of fibrosis as soon as the foci appear. During the relatively long process of fibrosis, FXIII A+ macrophages continuously decrease in number, and their morphological appearance changes from stellate to spindle-shaped. The nuclei of these cells were not labelled by Ki-67 monoclonal antibody; this indicating that they represent a non-proliferating cell population in the connective tissue stroma. The present findings may help to link theories concerning the role of FXIII A and those of macrophages in the connective tissue formation so far found separately in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ádány,R.,Kappelmayer,J. &Muszbek,L. (1987a) Expression of factor XIII subunita in different types of macrophages.Adv. Biosci. 66, 323–33.
Ádány,R.,Kiss,A. &Muszbek,L. (1987b) Factor XIII: a marker of mono- and megakariocytopoesis.Br. J. Haematol. 76, 167–72.
Ádány,R.,Glukhova,A. M.,Kabakov,A. Y. &Muszbek,L. (1988) Characterization of human connective tissue cells containing factor XIII subunita.J. Clin. Pathol. 41, 49–56.
Anderson,K. B.,Sletten,K. &Bertzen,H. B. (1988) The leucocyte L1 protein: identity with the cystic fibrosis antigen and the calcium-binding MRP-8 and MRP-14 macrophage components.Scand. J. Immunol. 28, 241–5.
Barry,E. L. &Mosher,D. F. (1988) Factor XIII crosslinking of fibronectin at cellular matrix assembly sites.J. Biol. Chem. 263, 10 464–9.
Barry,E. L. &Mosher,D. F. (1989) Factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of fibronectin in fibroblast cell layers. Cross-linking of cellular and plasma fibronectin and of amino-terminal fibronectin fragments.J. Biol Chem. 264, 4179–85.
Brandtzaeg,P.,Jones,D. B.,Flavell,D. J. &Fagerhold,M. K. (1988) Monoclonal antibody to a human macrophage marker (Mac 387) detects the formalin-resistant myelomonocytic L1 antigen.J. Clin. Pathol. 41, 963–70.
Brandtzaeg,P.,Dale,I. &Gabrielsen,T. O. (1992) The leucocyte protein L1 (calprotectin): usefulness as an immunohistochemical marker antigen and putative biological function.Histopathology 21, 191–6.
Bruhn,H. D.,Bernsmeier,R.,Boers,H. &Pohl,J. (1981) Regulation der Fibroblasten- und Endothelzellenproliferation durch Thrombin, Factor XIII und Fibronectin. InVerhandlungbericht der 25. Tagung der Deutschen Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Blutgerinnungsforschung in Munchen. pp. 257–283. Stuttgart: Schattauer.
Buchner,A.,Calderon,S. &Ramon,Y. (1977) Localised hyperplastic lesions of the gingiva: a clinico-pathological study of 302 lesions.J. Periodontol. 48, 101–4.
Burger,P. C.,Shibata,T. &Kleihuse,P. (1986) The use of monoclonal antibody Ki-67 in the identification of proliferating cells.Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 10, 611–17.
Clark,R. A.,Stoney,R. D.,Leung,D. Y. K.,Silver,I.,Hohn,D. C. &Hunt,T. K. (1976) Role of macrophages in wound healing.Surg. Forum 27, 16–9.
Dimitriu-Bona,A.,Burmester,G. R.,Waters,S. J. &Winchester,R. J. (1983) Human mononuclear phagocyte differentiation antigens. I. Patterns of antigenic expression on the surface of human monocytes and macrophages defined by monoclonal antibodies.J. Immunol. 130, 145–52.
Duckert,F. (1972) Documentation of the plasma factor XIII deficiency in man.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 202, 190–9.
Dvorak,H. F. (1986) Wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumour stroma generation and wound healing.N. Engl. J. Med. 315, 1650–9.
Flavell,D. J.,Jones,D. B. &Wright,D. H. (1987) Identification of tissue histiocytes on paraffin sections by a new monoclonal antibody.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 35, 1217–26.
Greenburg,G. B. &Hunt,T. K. (1978) The proliferative response in vitro of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells exposed to wound fluids and macrophages.J. Cell. Physiol. 97, 353–60.
Henriksson,P.,Becker,S.,Lynch,G. &Mcdonagh,J. (1985) Identification of intracellular Factor XIII in human monocytes and macrophages.J. Clin, Invest. 76, 528–34.
Hoythya,M.,Myllyla,R.,Siuva,J.,Kivirikko,K. iI. &Pyggvason,K. (1984) Monoclonal antibodies to human prolyl 4-hydroxylase.Eur. J. Biochem. 141, 477–82.
Keski-Oja,J.,Mosher,D. F. &Vaheri,A. (1976) Cross-linking of major fibroblast surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) catalyzed by blood coagulation factor XIII.Cell 9, 29–35.
Knapp,W.,Dorken,B.,Gilks,W. R.,Rieber,E. P.,Schmidt,R. E.,Stein,H. &Von DenBorne,A. E. G. (1989)Leucocyte Typing IV. White Cell Differentiation Antigens. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kradin,R. L.,Lynch,G. W.,Kurnick,J. T.,Erikson,M.,Colvin,R. B. &Mcdonagh,J. (1987) Factor XIIIa is synthesized and expressed on the surface of U937 cells and alveolar macrophages,Blood 69, 778–85.
Kreipe,H.,Radzun,H. J.,Parwaresch,M. R.,Haislip,A. &Hansmann,M. L. (1987) Ki-M7 monoclonal antibody specific for myelomonocytic cell lineage and macrophages in human.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 35, 1117–26.
Landberg,G.,Tan,E. M. &Roos,G. (1990) Flow cytometric analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin and Ki-67 antigen.Exp. Cell Res. 187, 111–8.
Lee,K. W. (1986) The fibrous epulis and related lesions.Periodontics 6, 277–99.
Leibovich,S. J. &Ross,R. (1975) The role of the macrophages in wound repair.Am. J. Pathol. 78, 71–100.
Loftus,B.,Loh,L. C.,Curran,B.,Henry,K. &Leader,M. (1991) Mac 387: its non-specificity as a tumour marker or marker of histiocytes.Histopathology 19, 251–5.
MacLeod,R. I. &Soames,J. V. (1987) Epulides: a clinicopathological study of a series of 200 consecutive lesions.Br. Dent. J. 163, 51–3.
Mosher,D. F. (1976) Action of fibrin stabilizing factor on cold insoluble globulin and α2-macroglobulin in clotting plasma.J. Biol. Chem. 251, 1639–45.
Mosher,D. F. (1984) Cross-linking of fibronectin to collagenous proteins.Mol. Cell Biochem. 53, 63–8.
Mosher,D. F.,Schad,P. E. &Kleinman,H. K. (1979) Cross-linking of fibronectin to collagen by blood coagulation factor XIIIa.J. Clin, Invest. 64, 781–7.
Muszbek,L. &Laki,K. (1984) Interaction of thrombin with proteins other than fibrinogen (thrombin-susceptible bonds). Activation of factor XIII. InThe Thrombin (edited byMachovich,R.). pp. 321–342. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Muszbek,L.,Ádány,R.,Szegedi,G.,Polgár,J. &Kávai,M. (1985) Factor XIII of blood coagulation in human monocytes.Thrombos. Res. 37, 401–10.
Paye,M.,Nusgens,B. V. &Lapiere,C. M. (1989) Factor XIII of blood coagulation modulates collagen biosynthesis by fibroblasts in vitro.Haemostasis 19, 274–83.
Paye,M.,Read,D.,Nusgens,B.,Lapiere,C. M. (1990) Factor XIII in scleroderma: in vitro studies.Br. J. Dermatol. 122, 371–82.
Polverini,P. J.,Cotran,R. S.,Gimbrone,M. A. &Unanue,E. R. (1977) Activated macrophages induce vascular proliferation.Nature 269, 804–6.
Simmons, D. L., Shencao, T., Tenen, D. G., Nicholson-Weller, A. & Seed, B. (1989) Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein.Blood 73, 284–9.
Smith,M. E. F.,Holgate,C. S.,Williamson,J. M. S.,Grigor,I.,Quirke,P. &Bird,C. C. (1987) Major histocompatibility complex class II antigen expression in B and T cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.J. Clin. Pathol. 40, 34–41.
Spouge,J. D. (1973) Localized overgrowths of the gingivaeepulides. InOral Pathology (edited bySpouge,J. D.). pp. 225–234. Sainte Louis: C. V. Mosby Co.
Steel,C. M. (1984)Human MHC Class II Antigens, Structure and Function. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Toida,M.,Okumura,Y. &Takami,T. (1991) Cells containing factor XIIIa and pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin.J. Clin. Pathol. 44, 255–6.
Ueyama,M. &Urayama,T. (1977) The role of factor XIII in fibloblast proliferation.Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 48, 135–42.
Verheijen,R.,Kuipers,H. J. H.,Schlingemann,R. O.,Boehmer,A. L. M.,Driel,R.,Brankenhoff,G. G. &Ramaekers,F. C. S. (1989) Ki-67 detects a nuclear matrix associated proliferation-related antigen.J. Cell Sci. 92, 123–30.
Weisberg,L. J.,Shiu,D. T.,Conkling,P. R. &Shuman,M. A. (1987) Identification of normal human peripheral blood monocytes and liver as sites of synthesis of coagulation factor XIIIa-chain.Blood 70, 579–82.
Zain,R. B. &Fei,Y. J. (1990) Fibrous lesions of the gingiva: a histopathologic analysis of 204 cases.Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 70, 466–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toida, M., Oka, N., Takami, T. et al. Accumulation of cells containing factor XIII subunita around the foci of intense fibrosis in human epulides. Histochem J 27, 440–448 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388800
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388800