Abstract
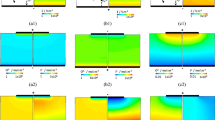
A computer model based on the Poisson, current density and continuity equation, used to study transient and steady state phenomena in insulators and solid electrolytes with one type of mobile species, is extended to the case of materials with two types of mobile species. The derived distributions are compared for the two cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
3. References
A. de Mari, Solid State Electron.11, 1021 (1968)
W.H. Press, B.P. Flannery, S.A. Tenkolsky and W.T. Vetterling, in: Numerical Recipes, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1987
S.F. Potamianou, K.A.Th. Thoma and M.N. Pisanias, J. Phys.A 23, 1313 (1990)
S.F. Potamianou and K.A.Th. Thoma, Solid State Ionics70/71, 533–536 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisanias, M.N., Potamianou, S.F. & Thoma, K.A.T. A computer model for transport processes in solid electrolytes. Ionics 1, 112–114 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388667
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388667