Abstract
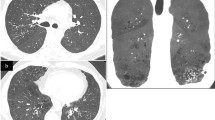
The Hyper IgE syndrome is a rare disease consisting of recurrent sinusitis and pneumonia, pneumatoceles, chronic dermatitis, and elevated serum levels of IgE. The primary radiographic abnormalities are recurrent alveolar lung disease and pneumatoceles. Pneumothorax may occasionally occur as in one of our cases. Other causes of pneumatoceles are usually easily excluded by the history and other clinical data. Pulmonary scintigraphy and computed tomography may add information valuable to the management of these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis SD, Schaller J, Wedgwood RJ (1966) Job's syndrome: recurrent, “cold”, staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet 1: 1013–1015
Buckley RH, Wray BB, Belmaker EZ (1972) Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics 49: 59–70
Dreskin SC, Goldsmith PK, Gallin JI (1985) Immunoglobulins in the hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infection (Job's) syndrome. Deficiency of anti-staphylococcus aureus immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest 75: 26–34
Hill HR (1982) The syndrome of hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and recurrent infections. Am J Dis Child 136: 767–771
Donabedian H, Gallin JI (1983) The hyperimmunoglobulin E recurrent-infection (Job's) syndrome. A review of the NIH experience and the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 62: 195–208
Geha RS, Reinherz E, Leung D, McKee KT Jr, Schlossman S, Rosen FS (1981) Deficiency of suppressor T cells in the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest 68: 783–791
Kirchner SG, Sivit CJ, Wright PF (1985) Hyperimmunolgobulinemia E syndrome: association with osteoporosis and recurrent fractures. Radiology 156: 362
Merten DF, Buckley RH, Pratt PC, Effmann EL, Grossman H (1979) Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome: radiographic observations. Radiology 132: 71–78
Godwin JD, Webb WR, Savoca CJ, Gamsu G, Goodman PC (1980) Multiple, thin-walled cystic lesions of the lung. AJR 135: 593–604
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitch, S.J., Magill, H.L., Herrod, H.G. et al. Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome: pulmonary imaging considerations. Pediatr Radiol 16, 285–288 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386863
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386863