Abstract
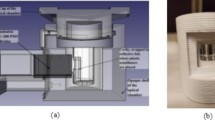
A large volume scintillation cell has been designed to detect low levels of radon and its progeny. The cell has a cylindrical shape (nominal volume 1.2 liters) with two photomultiplier tubes. In this study, the detection efficiency was estimated with Monte-Carlo calculations for 3-dimensional before fabrication. Counting efficiencies for241Am were measured along the axial of the cell with different distances between the source and the scintillation screen to confirm the calculation method. The counting efficiencies for the alpha particles from the226Rn and its short-live progenies were measured using a radon generator. The efficiency was estimated to be 0.36 count per alpha-particle as the average of three alpha-particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.F. Lucas, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 28 (1957) 680.
M. Raghaayya, Health Phys., 40 (1981) 894.
J. Kristan, I. Kobal, Health Phys., 24 (1973) 103.
T. M. Semkow, P. P. Parekh, C. D. Schwenker, R. Dansereau, J. S. Webber, Nucl. Inst. Methods, A353 (1994) 515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakamoto, S., Takakura, H. Efficiency of a large size scintillation cell. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 236, 257–260 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386353
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386353