Summary
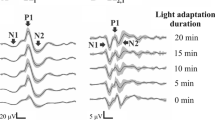
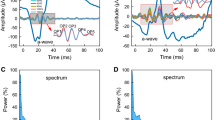
The influence of adaptation and flash-intensity on the early components of the α-wave of averaged responses has been investigated in the course of dark-adaptation. Up to seven multiple components being rather inconstant in their latency could be seen, in the eye previously having been light- or dark-adapted with large intensities. Photopical conditions exhibit small wavelets and shorter latencies. The non-uniform effect of adaptation and flash-intensity on the different components of the α-wave suggests two adapting functions superposing themselves within the cone-apparatus.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde der Einfluß des Adaptationszustandes und der Blitzstärke auf die frühen Antworkomponenten der α-Welle bei ausreichender Antwortsummenbildung untersucht. Bis zu 7 wenig latenzkonstante multiple Komponenten wurden im Verlauf der Dunkeladaptation, besonders nach schwachen Weiß- oder mittelstarken Rotblitzen im vorher intensiv hell- oder dunkeladaptierten Auge beobachtet. Unter photopischen Bedingungen kommen zu den geringen Oszillationen schnellere Latenzen hinzu. Die uneinheitliche Wirkung von Adaptation und Blitzstärke auf die verschiedenen Komponenten der α-Welle spricht für zwei sich überlagernde adaptierende Funktionen innerhalb des Zapfenapparates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allegra, A. Genest: Oscillatory potentials in the ERG of the normal human eye. Vision Res.4, 595–604 (1964).
Arden, G. B., C. D. B. Bridges, H. Ikeda, andI. M. Siegel: Isolation of a new fast component of the early receptor potential. J. Physiol. (Lond.)186, 123–124 (1966a).
—, andH. Ikeda: A new property of the early receptor potential of the rat retina. Nature (Lond.)208, 1100–1101 (1965).
——: Effects of hereditary degeneration of the retina on the early receptor potential of the cornea — fundal potential of the rat eye. Vision Res.6, 171–184 (1966a).
——, andI. M. Siegel: Effects of light adaptation on the early receptor potential on their relation to visual photochemistry. Vision Res.6, 373–387 (1966b).
Armington, J. C.: A component of the human electroretinogram associated with red color vision. J. opt. Soc. Amer.42, 393–401 (1952).
—, andL. A. Riggs: The scotopic α-wave in the electrical response of the human retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.)118, 289 (1952).
Baumann, C.: Receptorpotentiale der Wirbeltiernetzhaut. Pflüger Arch. ges. Physiol.282, 92–101 (1965).
Best, W.: Das menschliche Elektroretinogramm während der Dunkeladaptation. Acta ophthal. (Kbh.)31, 95–116 (1953).
Bornschein, H.: Der Einfluß vom Adaptationszustand und Reizintensität auf die Komponenten des menschlichen Elektroretinogramms. Z. Biol.105, 454 (1953).
—, andG. Goodman: Studies of the α-wave in the human ERG. Arch. Ophthal.58, 431–437 (1957).
—, andR. D. Gunkel: The effect of a rate of rise of photopic stimuli on the human ERG. Amer. J. Ophthal.42, 239–243, (1956).
Brindley, G. S., andA. R. Gardner-Medwin: The origin of the early receptor potential of the retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.)182, 185–194 (1966).
Brown, K. T., andM. Murakami: A new receptor potential of the monkey retina with no detectable latency. Nature (Lond.)201, 626–628 (1964).
Cobb, W. A., andH. B. Morton: The human electroretinogram in response to high-intensity flashes. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.4, 547 (1952).
——: A new component of the human ERG. J. Physiol. (Lond.)123, 36–37 (1954).
Cone, R. A.: Early receptor potential of the vertebrate retina. Nature (Lond.)204, 736–739 (1964).
Denden, A., u.O. Vatter: Einfluß von Blitzstärke und Adaptationszustand auf die frühe Komponente des menschlichen Elektroretinogramms. Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal.176, 95–99 (1968).
Dodt, D., R. M. Copenhaven, andR. D. Gunkel: Electroretinographic measurement of the spectral sensitivity in albinos, Caucasions and negroes. Arch. Ophthal.62, 755–883 (1959).
Dodt, E., andV. Elenius: Change of threshold during dark adaptation after exposure to moderate and strong lights. Abstr. of communications. The 2nd Scand summer meeting of Biochem., Med., Chem., Pharmacol. and Physiol. Turku/Abo 1959.
Elenius, V.: Recovery in the dark of the rabbit's electroretinogram in relation to intensity, duration and colour of light adaptation. Acta physiol. scand.44, Suppl. 150, 1 (1958). Ref. Zbl. ges. Ophthal.77, 219 (1959).
Heck, J., andI. Rendhal: Components of the human electroretinogram. An analysis in normal and in colour blindness. Acta physiol. scand.39, 167–175 (1957).
Johnson, E. P., L. A. Riggs, andA. M. L. Schick: Photopic retinal potentials evoked by phase alternation of a barred pattern, p. 75–91. Proc. of the 3rd International Symp. Illinois. London: Pergamon Press 1964.
Motokawa, K., u.T. Mita: Über eine einfache Untersuchungsmethode und Eigenschaften der Aktionsströme der Netzhaut des Menschen. Tohoku J. exp. Med.42, 114–133 (1942).
Pakh, W. L., andR. A. Cone: Isolation and identification of the initial peak of the early receptor potential. Nature (Lond.)204, 836–338 (1965).
—, andT. G. Ebrey: Visual receptor potential observed at sub-zero temperatures. Nature (Lond.)205, 481–486 (1965).
Rendhal, I.: The scotopic α-wave of the human electroretinogram. Acta ophthal. (Kbh.)36, 329–344 (1958).
—: The electroretinogram of the ligh adapted human eye. Clinical recording with the electronic flash as light stimulus. Acta ophthal. (Kbh.)36, 916 (1958).
Schmöger, E.: Die Rolle der Präadaptation im klinischen ERG. Acta ophthal. (Kbh.)70, 32–52 (1962).
Vatter, O.: Frühe Antwortkomponenten im photisch evozierten Potential beim Kaninchen und beim Menschen. Z. vgl. Physiol.57, 218–231 (1967).
Yonemura, K., Y. Masuda, andM. Hatta: The oscillatory potential of the ERG. Acta Soc. ophthal. jap.67, 339–344 (1963).
Yonemura, K., andK. Kawasaki: The early receptor potential in the human electroretinogram. Jap. J. Physiol.17, 235–244 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denden, A., Vatter, O. Die raschen Antworkomponenten der α-Welle im menschlichen ERG. Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. 176, 160–171 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02385045
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02385045