Abstract
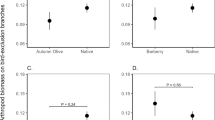
During the wet season, two sympatric species of primates,Alouatta palliata (mantled howlers) andCebus capucinus (white-faced capuchins), were assayed for feeding niche differences through behavioral and habitat use patterns at Refugio de Fauna Silvestre Curu in Costa Rica. Differences in the use of relative diameter and thickness of branches and five different modes of feeding were compared between the species. White-faced capuchins used more manipulative modes of obtaining food, a wider range of arboreal habitat, and had a more diverse diet than mantled howlers. Mantled howlers may be more restricted than white-faced capuchins in arboreal microhabitat use due to their possible need for large support branches during feeding bouts and resting periods. We report that differences in feeding behaviors, diet, and arboreal habitat use seem to play a large role in separating these species niches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. R., 1990. Use of objects as hammers to open nuts by capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella).Folia Primatol., 54: 138–145.
Carpenter, C. R., 1934. A field study of the behavior and social relations of howling monkeys (Alouatta palliata).Comp. Psychol. Monogr., 10: 1–168.
Chapman, C., 1987. Flexibility in diets of three species of Costa Rican primates.Folia Primatol., 49: 90–105.
—, 1988. Patterns of foraging and range used by three species of neotropical primates.Primates, 29: 177–194.
Chivers, D. J., 1969. On the daily behavior and spacing of howling monkey groups.Folia Primatol., 10: 48–102.
Costello, M. B. &D. M. Fragaszy, 1988. Prehension inCebus andSaimiri: I. grip type and hand preference.Amer. J. Primatol., 15: 235–245.
Crockett, C. M. &J. F. Eisenberg, 1987. Howlers: variations in group size and demography. In:Primate Societies,B. B. Smuts,D. L. Cheney,R. M. Seyfarth,R. W. Wrangham, &T. T. Struhsaker (eds.), The Univ. of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 54–68.
Fernandes, M. E. B., 1991. Tool use and predation of oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae) by the tufted capuchin,Cebus apella apella, in brackish water mangrove swamp.Primates, 32: 529–531.
Izawa, K. &A. Mizuno, 1977. Palm-fruit cracking behavior of wild black-capped capuchin (Cebus apella).Primates, 18: 773–792.
Martin, P. &P. Bateson, 1986. Recording methods. In:Measuring Behaviour,P. Martin &P. Bateson (eds.), Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, pp. 48–69.
Parker, S. T. &K. R. Gibson, 1977. Object manipulation, tool use and seniormotor intelligence as feeding adaptations inCebus monkeys and great apes.J. Human Evol., 6: 623–641.
Robinson, J. G. &C. H. Janson, 1987. Capuchins, squirrel monkeys, and atelines: socioecological convergence with old world primates. In:Primate Societies,B. B. Smuts,D. L. Cheney,R. M. Seyfarth,R. W. Wrangham, &T. T. Struhsaker (eds.), The Univ. of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 69–82.
Smith, C. C., 1977. Feeding behaviour and social organization in howling monkeys. In:Primate Ecology,T. H. Clutton-Brock (ed.), Academic Press, London, pp. 97–126.
Sokal, R. R. &F. J. Rohlf, 1981.Biometry (Second edition). V.H. Freeman, San Francisco.
Struhsaker, T. T. &L. Leland, 1977. Palm-nut smashing byCebus apella in Columbia.Biotropica, 9: 124–126.
Visalberghi, E., 1990. Tool use inCebus.Folia Primatol., 54: 146–154.
Westergaard, G. C. &D. M. Fragaszy, 1987. The manufacture and use of tools by capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella).J. Comp. Psychol., 101: 159–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Tomblin, D.C., Cranford, J.A. Ecological niche differences betweenAlouatta palliata andCebus capucinus comparing feeding modes, branch use, and diet. Primates 35, 265–274 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02382724
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02382724