Abstracts
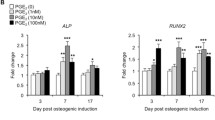
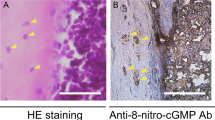
Prostaglandins (PG's) are well known as an important local regulator of bone metabolism. In this study, we examined to characterize the effects of PGs on osteoblasts, using a clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Among PG metabolites, PGE2 is a main prostanoid released in bone tissues. MC3T3-E1 cells also produced predominantly PGE2. PG E2 at low doses (1–100 ng/ml) and PGE1 increased activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), an marker enzyme of early differentiation of osteoblasts, with positive correlation of elevating intracellular cAMP content. The stimulatory effects are amplified by the addition of isobutylmethyl xanthine (IBMX) and mimicked those of forskolin, a direct activator of adenylate cyclase. those results suggest that PGE2 at low doses and PGE1 act predominantly on adenylate cyclase to stimulate the early differntiation of the cells. On the other hand, PGE2 at high doses (500–2000 ng/ml) and PGF2α stimulated DNA synthesis of the cells in a dose-related manner. In the same range of concentrations, PGE2 and PGF2α augmented the accumulation of inositol triphosphates. Further, the effect of these PGs on the DNA synthesis is negated by addition of H-7, a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C. These date suggest that PGE2 at high doses and PGF2α stimulate the proliferation of the cells via enhance of phosphatidyl inositol (PI) turnover system and following activation of protein kinase C. Since PGE2 reveals diverse effects on the cells dependent on its concentration, it is difficult to clarify the mechanism of PGE2 action. Thus, we chose PGF2α to elucidate the stimulatory effect of PGs on the prolferation of the cells. At least 12h time-lag was present between PG F2α-signal transduction and an increase in DNA synthesis, and α-amanitin and cyclohexamide counteracted the effects, suggesting that some proteins involved in DNA synthesis are produced by the addition of PGF2α in the duration. Further, neutralizing anti IGF-I antibody blocked the stimulation of DNA synthesis by PGF2α. However, PGF2α didn't affect the endogenous production of IGF-I of the cells. On the other hand, PGF2α greatly elevated level of IGF-I binding sites on the cells, and the increase appeared bout 3h earlier than did the stimulation of DNA synthesis, indicating increase in responsiveness of the cells to IGF-I. These results suggest that the proliferation of the cells is stimulated by synergistic action of PGF2α and IGF-I produced endogenously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raisz, L.G., and Martin, T. J.: Prostaglandins in bone and mineral metabolism. In: Peck W.A. (ed.) Boneand Mineral Research, Annual 2. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, the Netherlands pp 286–310, 1983.
Mundy G.R., and Roodman G.D.: Osteoclast ontogeny and function. In: Peck WA (ed) Bone and Mineral Research, Annual 2. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, the Netherlands pp 209–279, 1987.
Hakeda Y., and Kumegawa M.: Prostaglandins and bone cell activity. J. Bone Mineral Metab. 6, 55–70, 1988.
Nolan R.D., Partridge N.C., Godfrey H.M., and Martin T.J.: Cyclooxygenase products of arachidonic acid metabolism in rat osteoblasts. Calcif. Tissue Int. 35, 294–297, 1983.
Rodan S.B., Rodan G.A., Simmons H.A., Walenga R.W., Feinsein M.B., and Raisz L.G.: Bone resorptive factor produced by osteosarcoma cells with osteoblastic features is PGE2. Biochem.Biophys. Res. Commun. 102, 1358–1365, 1981.
Rodan S.B., Rodan G.A., Simmons H.A., Walenga R.W., Feinstein M.B., and Raisz L.G.: Bone resorptive activity in conditioned medium from rat osteosarcoma cell line. In Bockman R. and Powles T.J. (ed) Prostaglandins and cancer: First International Conference. Alan R. liss, New York pp 573–578, 1982.
Yokota K., Kusaka M., Oshima T., Yamamoto S., Kurihara N., Yohino T., and Kumagawa M.: Stimulation of prostaglandin E2 synthesis in cloned osteoblastic cells of mouse (MC3T3-E1) by epidermal growth factor. J. Biol.Chem. 261, 15410–15415, 1986.
Sumitani K., Kawata T., Yoshimoto T., Yamamoto S., and Kumegawa M.: Fatty acid cyclooxyganase activity simulated by transforming growth factor-β in mouse osteoblastic cell (MC3T3-E1). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 270, 588–595, 1989.
Feyen J.H.M., Di Bon A., van der Plas A., Lowik C.W.G.M., and Nijweide P.J.: Effects of exogenous prostanoids on the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Prostaglandins 30, 827–840, 1985.
Chyun Y.S., and Raisz L.G.: Stimulation of bone formation by prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins 27, 97–103, 1984.
Partridge N.C., Alcorn D., Michelangeli V.P., Kemp B.E., Ryan G.B., and Martin T.J.: Functional properties of hormonally responsive cultured normal and malignant rat osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology 108, 213–219, 1981.
Raisz L.G., and Koolemans-Beynen A.R.: Inhibition of bone collagen synthesis by prostaglandin E2 in organ culture. Prostaglandins 8, 377–385, 1974.
Lund J.E., Brown W.P., and Treman L.: The toxicology of PGE2. In Wu K.K., and Rossi E.C. (ed) Prostaglandin in clinical Medicine: Cardivascula and thombotic disordes. Yearbook Medical Publish, Inc., Chicago pp 93–109, 1982.
Ringel R.E., Brenner J.I., Haney P.J., Burns J.E., Moulton A.L., andBerman M.A.: Prostaglandin-induced periostitis: A complication of long-term PGE1 infusion in an infant with congenital heart disease. Radiology 142, 657–658, 1982.
Ueda K., Saito A., Nakano H., Aoshima M., Yokota M., Muraoka R., and Iwaya T.: Cortical hyperostosis following long-term administration of prostaglandin E1 in infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease. J. Pediatr. 97, 834–836, 1980.
Sudo H., Kodama H., Amagai Y., Yamamoto S., and Kasai S.: In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J. Cell Biol. 96, 191–198, 1983.
Kodama H., Amagai Y., Sudo H., Kasai S., and Yamamoto S.: Establishment of a clonal osteogenic cell line from newborn mouse calvaria. Jpn. J. Oral. Biol. 23, 899–901, 1981.
Hakeda Y., Yoshino T., Nakatani Y., Kurihara N., Maeda N., and Kumegawa M.: Prostaglandin E2 stimulates DNA synthesis by a cyclic AMP-independent pathway in osteoblastic clone MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 128, 155–161, 1986.
Hakeda Y., Hotta T., Kurihara N., Ikeda E., Maeda N., Yagyu Y., and Kumegawa M.: Prostaglandin E1 and F2a stimulate differentiation and proliferation, respectively, of clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by different second messengers in vitro. Endocrinology 121, 1966–1974, 1987.
Hakeda Y., Nakatani Y., Hiramatsu M., Kurihara N., Tsunoi M., Ikeda E., and Kumegawa M.: Inductive effects of prostaglandins on alkaline phosphatase in osteoblastic cells, clone MC3T3E1. J. Biochem. 97, 97–104, 1985.
Honma M., Satoh T., Takezawa J., and Ui M.: An ultrasensitive method for the simultaneous determination of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in small-volume samples from blood and tissue. Biochem. Med. 18, 257–273, 1977.
Downes C.P., and Wusteman M.M.: Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem. J. 216, 633–640, 1983.
Yang H.C., and Pardee A.B.: Inslin-like growth factor I regulation of transciption and replicating enzyme induction necessary for DNA synthesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 127, 410–416, 1986.
Pardee A.B.: G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science 246, 603–608, 1989.
Ernst M., Heah J.K., and Rodan G.A.: Esatrdiol effects on proliferation, messenger ribonucleic acid for collagen and insulin-like growth factor-I, and parathyroidhormone-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in osteoblastic cells from calvariae and long bones. Endocrinology 125, 825–833, 1989.
Schmid C., Guler H.-P., Rowe D., and Froesh E.R.: Insulin-like growth factor I regulates Type I procollagen messenger ribonucleic acid steady state levels in bone of rats. Endocrinology 125, 1575–1580, 1989.
Centrella M., McCarthy T.L., and Canalis E.: Transforming growth factor is a bifunctional regulator of replication and collagen synthesis in osteoblast-enriched cell cultures from fetal rat bone. J. Biol.Chem. 262, 2869–2874, 1987.
Pfeilschifter J., D'Souza S.M., and Mundy G.R.: Effects of transforming growth factor- on osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells. Endocrinology 121, 212–218, 1987.
Kurose H., Yamada K., Okada S., Nakajima S., and Sino Y.: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3] increases insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptors in clonal osteoblastic cells. Study on interaction of IGF-I and 1,25(OH)2 D3. Endocrinology 126, 2088–2094, 1990.
Tamura K., Kobayashi M., Suzuki S., Ishii Y., Koyama S., Yamada H., Hashimoto K., Niwa M., and Shibayama F.: Enzymelike growth factor-I using monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies with defined epitope recognition. J. Endocrinol. 125, 327–335, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Hakeda, Y., Okawa, M. & Kumegawa, M. Action of prostaglandins on clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Bone Miner Metab 9, 49–56 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02377986
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02377986