Abstract
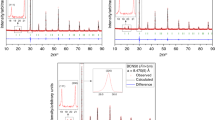
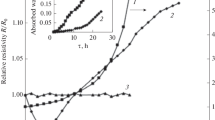
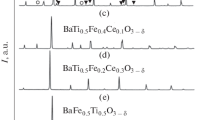
Phenomena and processes either new or not studied in-depth occurring in perovskite oxides and in systems which contain these compounds are reported and summarized. The materials under consideration are well-known for specific properties, e.g., cerates of alkaline earths are high-temperature proton conductors, manganates are electrode materials of SOFCs and show the effect of colossal magnetoresistance or YBa2Cu3O7 cuprates YBa2Cu3O7 are “high-temperature” superconductors. The presented nontraditional approach consists of considering physical and chemical phenomena and processes, which do not relate to the indicated main properties of the compounds. For instance, BaCeO3 undoped and slightly doped has partially cerium in the form of Ce+3, which provides the effect of blue luminescence which is controlled by thermochemical treatment; H2YBa2Cu3O7 manifests mixed proton-electron conduction at 400–550 K under water vapor of 100–300 Pa; La0.67Ca0,33MnO2.84 can dissolve some part of water vapor as this occurs in traditional HTPC. The electrochemical cells Pd | HTPC | hydrocuprate | HTPC | Pd and the more simple one Pd | HTPC | Pd show e.m.f. values near 1 V under certain conditions after polarization by d.c. currents at 420–520 K under different atmospheres. The system water vapor — membrane of undoped BaCeO3-hydride is described. Defect chemistry equations are used to describe some of the phenomena which are employed for the production and storage of pure hydrogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu.M. Baikov, Physics of the Solid State42, 1026 (2000).
Yu.M. Baikov, Yu.P. Stepanov, V.E. Gasumjants, A.Yu. Grigoriev, Tech. Phys. Lett.209, 696 (1994).
Yu.M. Baikov, W. Gunther, V.P. Gorelov. P. Colomban, R. Baddour-Hadjean, Ionics4, 347 (1998).
Yu.M.Baikov, S.E.Nikitin, in: Proceedings of the Third Int. Symp. on Ionic and Mixed Conducting Ceramics, Paris, France, 1997, Electrochem. Soc. Inc. Proc. 97-24, p. 390.
H. Iwahara, T. Esaka, H. Uchida, N. Maeda, Solid State Ionics3/4, 359 (1981).
K.D. Kreuer, Chem.Mater.8, 610 (1996).
Yu.M. Baikov, E.K. Shalkova, J. Solid State Chem.97, 224 (1992).
E.K. Shalkova, Yu.M. Baikov, T.A. Ushakova, Sverkhprovodimost: Fiz., Khim., Tekh.5, 22 (1992).
W. Günther, R. Schöllhorn, Physica C271, 241 (1996).
U. Reichel, R.r. Arons, W. Schilling, Solid State Ionics86–88, 639 (1996).
R. Hempelmann, M. Soetratmo, O. Hartmann, R. Wäppling, Solid State Ionics107, 269 (1998).
J.S. Lord, S.P. Cottrell, K.S. Knight, W.G. Williams, Solid State Ionics113–115, 341 (1998).
B.-T. Melekh, V.M. Egorov, Yu.M. Baikov, N.F. Kartenko, Yu.N. Filin, M.E. Kompan, I.I. Novak, G.B. Venus, V.B. Kulik, Solid State Ionics97, 465 (1997).
Yu.M. Baikov, Solid State Ionics97, 471 (1997).
M.E. Kompan, Yu.M. Baikov, B.A.-T. Melekh, A.V. Yakubovich, Physics of the Solid State44, 1263 (2002).
T. He, P. Ehrhart, P. Meuffels, J. Appl. Phys.79, 3219 (1996).
S. Okamoto, K. Tanaka, and V. Inoue, Appl. Phys. Lett.76, 946 (2002).
M. Raukas, S. A. Basun, W. van Schaik, Appl.Phys.Lett. 69 3300 (1996)
T. Otake, H. Yugami, H. Naito, K. Kawamura, T. Kawada, J. Mizusaki, Solid State Ionics135, 663 (2000).
K.S. Knight, Solid State Ionics74, 109 (1994).
F. Genet, S. Loridant, C. Ritter, G. Lucazeau, J. of Phys. Chem.60, 2009 (1999).
A.V. Kuzmin, V.P. Gorelov, B.T. Melekh, M. Glerup and F.W.Poulsen. in: Abstract of SSPC-11, Guildford, August 2002.
N. Bonanos, K.S. Knight, B. Ellis, Solid State Ionics79, 161 (1995).
E.K. Kurumchin, G.K. Vdovin, V.P. Gorelov, V.B. Balakireva, in: All-Russian workshop on physical chemistry and electrochemistry of molten and solid electrolytes (Kabardino-balkar, Ed.) University, Nal’chik, Russia (2001).
J.M.D. Coey, M. Viret, Adv. Phys.48, 167 (1999).
E.I. Nikulin, V.M. Egorov, Yu.M. Baikov, B.T. Melekh, Yu.P. Stepanov, I.N. Zimkin, Physics of the Solid State5, 920 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baikova, Y.M., Kompan, M.E., Nikulin, E.I. et al. Well-known perovskites (cerates, cuprates, manganates): Problems and facts; A review of nontraditional approaches. Ionics 9, 395–403 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376592