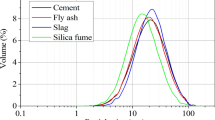
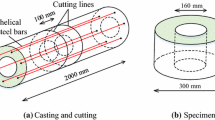
Conclusions
-
1.
The phenomenon of internal sealing exerts the principal effect on the reduction of permeability of old concrete in the seepage process. For younger concrete a noticeable effect is exerted also by the process of secondary hydration. Along with the internal, external sealing can take place. Special investigations are needed to determine the extent of the influence of external sealing.
-
2.
The magnitude of the seepage coefficient of concrete after protracted seepage depends on the pressure gradient. With an increase in the gradient up to a final value, the seepage coefficient decreases.
-
3.
There is a limiting minimum value of the seepage coefficient for concrete of a given composition; after this value is reached, the coefficient remains practically constant for any gradient.
-
4.
During the initial period of seepage, the permeability of concrete diminished continously. The value of the seepage coefficient reached in the process of seepage with a given pressure gradient is considerably lower than the initial value. This must be taken into account in designating the safety factor of concrete when analyzing it for seepage and also when specifying testing pressures in certain pressure structures (pipelines, reservoirs, etc.).
Similar content being viewed by others

Additional information
Translated from Gidrotekhnicheskoe Stroitel'stvo, No. 5, pp 28–31, May, 1968.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirillov, A.P. The mechanism of water seepage through concrete. Hydrotechnical Construction 2, 411–415 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376111
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376111