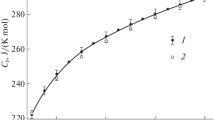
Abstract
The results are given of an experimental study of the thermal capacity of aqueous aerozine solutions in the temperature range 313–450 K, and pressure range 0.101-49.1 MPa. Generalized equations are obtained for calculating the thermal capacities of these solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Grekov and V. Ya. Veselov, The Physical Chemistry of Hydrazine [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1979).
M. M. Safarov, “Thermophysical properties of simple ethers and aqueous hydrazone solutions as a function of temperature and pressure,” Dissertation for degree of doctor of technical science, Dushanbe (1993).
M. M. Safarov and A. I. Bogdanov, Izmer. Tekh., No. 2, 42 (1995).
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel'naya Tekhnika, No. 5, pp. 46–48, May, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safarov, M.M., Zaripova, M.A. & Radzhabov, F.S. Thermal capacity of aqueous aerozine solutions as a function of temperature and pressure. Meas Tech 39, 540–544 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375765
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375765