Abstract
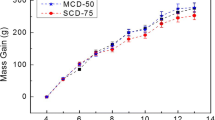
Effects of dietary supplementation of calcium (Ca) and vitamin D(D) on bone growth in growing male rats were investigated. We performed this study using D-deficient rats of 3-month-old. In the experiment 1, the D-deficient rats were fed either low-Ca (0.22% Ca) or high-Ca (1.20% Ca) diets with oral supplementation of different amounts of D3 (0, 0.7, 7 or 70 IU/week) for 28 days. In the dxperiment 2, the D-deficient rats were fed diets containing different concentrations of Ca (0.22, 0.44, 0.88 or 1.20%) with oral D3 supplementation of either low-dose (0.7 IU/week) or relatively high-dose (70 IU/week) for 28 days. After the feeding period, plasma levels of Ca, 1α, 25 (OH)2D3, PTH, bone Gla protein were measured. Bone ash weight, bone mineral density, mechanical bone strength were also measured. In the both experiments, the plasma levels of PTH decreased to the normal levels in response to the increased amounts of dietary Ca intakes as well as D supplementation. In contrast, the bone markers increased to the respective normal levels in response to the increased amounts of dietary Ca intakes as well as D supplementation. In the experiments 1 and 2, a high correlation between the plasma levels of PTH and the bone markers was observed. These results suggest that both dietary Ca and D supplementation may affect bone growth in growing rats by controlling PTH secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Need AG, Horowitz M, Philcox JC et al.: 1,25-dihydroxy-calciferol and calcium therapy in osteoporosis with calcium malabsorption. Miner Electr Metab 11: 35–40, 1985
Chapuy MC, Arlot ME, Duboeuf F et al.: Vitamin D3 and calcium to prevent hip fractures in elderly women. N Engl J Med 327: 1637–1642, 1992
Dawson-Hughes B, Dallal GE, Krall EA et al.: A controlled trial of the effect of calcium supplementation on bone density in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 328: 878–883, 1993
Raisz LG, Trummel CL, Holick MF et al.: 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol: A potent stimulator of bone resorption on in tissue culture. Science 175: 768–769, 1972
Suda T, Deluca HF, Tanaka Y: Biological activity of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol in rats. J Nutr 100: 1049–1052, 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, T., Okano, T., Tsugawa, N. et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of calcium and vitamin don bone growth in growing male rats. J Bone Miner Metab 12 (Suppl 1), S7–S11 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375667
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375667