Abstract
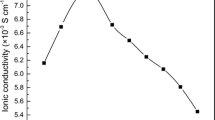
The paper reports the synthesis of protonic polymer gel electrolytes containing different hydroxy benzoic acids (ortho-, meta- and para-) and aliphatic dicarboxylic acids. Gel electrolytes were prepared by adding polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) in different weight ratios to the 1M solution of above acids in a ternary solvent mixture of propylene carbonate (PC), ethylene carbonate (EC) and dimethylformamide (DMF) in equal volume ratio. The conductivity of these gel electrolytes has been found to depend upon the amount of PMMA added to the system. A “Breathing Polymeric Chain Model” has been proposed to explain the variation of conductivity with PMMA concentration in these gel electrolytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
6. References
B.E. Fenton, J.M. Parker and P.V. Wright, Polymer14, 589 (1973).
P.V. Wright, Br. Polym. J.7, 319 (1975).
M.B. Armand, J.M. Chabagno and M.J. Duclot, in: Fast ion transport in solids (P. Vashishta, J.N. Mundy and G.K. Shenoy, Eds.) Elsevier North-Holland, New York, 1979, pp. 131.
Polymer Electrolyte Reviews Vol. 1 & 2, (J.R. MacCallum and C.A. Vincent, Eds.) Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1987 & 1989.
Electrochemical Science and Technology of Polymers Vol. 1 & 2, (R.G. Linford, Ed.) Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1987 & 1990.
S. Chandra, K.K. Maurya and S.A. Hashmi, in: Recent advances in fast ion conducting materials and devices (B.V.R. Chowdari, Q.G. Lin and L.Q. Chen, Eds.) World Scientific, Singapore, 1990, pp. 549.
C. Berthier, W. Gorecki, M. Minier, M.B. Armand, J.M. Chabagno and P. Rigaud, Solid State Ionics11, 91 (1983).
I.E. Kelly, J.R. Owen and B.C.H. Steele, J. Electroanal. Chem.168, 467 (1984).
I.E. Kelly, J.R. Owen and B.C.H. Steele, J. Power Sources14, 13 (1985).
K.E. Doan, M.A. Ratner and D.F. Shriver, Chem. Mater.3, 418 (1991).
C.C. Liang, J. Electochem. Soc.120, 1289 (1973).
J.E. Weston, B.C.H. Steele, Solid State Ionics7, 75 (1982).
F. Croce, F. Bonino, S. Panero, B. Scrosati, Phil. Mag.59, 161 (1989).
F. Croce., F. Capuano, B. Scrosati, J. Electochem. Soc.138, 1918 (1991).
E. Morales, J.L. Acosta, Solid State Ionics111, 109 (1998).
F.M. Gray, Polymer Electrolytes, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 1997, pp. 13.
S.S. Sekhon, Pradeeep and S.A. Agnihotry, in: Solid State Ionics: Science and Technology (B.V.R. Chowdari, K. Lal, S.A. Agnihotry, N. Khare, S.S. Sekhon, P.C. Srivastava, and S. Chandra, Eds.) World Scientific, Singapore, 1998, pp. 217.
R. Koksbang, I.I. Oslen, D. Shackle, Solid State Ionics69, 320 (1994)
G. Feuillade and Ph. Perche, J. Appl. Electrochem.5, 63 (1975).
B. Scrosati and R.J. Neat, in: Applications of Electroactive Polymers (B. Scrosati, Ed.) Chapman & Hall, London, 1993, pp. 182.
S.A. Agnihotry, Pradeep, S.S. Sekhon, Electochim. Acta44, 3121 (1999).
S.S. Sekhon, Deepa, S.A. Agnihotry, Solid State Ionics, in Press (2000).
S.S. Sekhon, N. Arora, S.A. Agnihotry, Solid State Ionics, in Press (2000).
Proton conductors, Solids, membranes and gels-materials and devices (P. Colomban, Ed.) Cambridge University Press, 1992.
W. Wieczorek, Z. Florjanczyk, J.R. Stevens, Electrochim. Acta40, 2327 (1995).
A.M. Grillone, S. Panero, B.A. Retamal and B. Scrosati, J. Electochem. Soc.146, 27 (1999).
J.B. Wagner Jr., Mater. Res. Bull.15, 1691 (1980),
K. Shahi and J.B. Wagner Jr., J. Solid State Chem.42, 107 (1982).
J. Maier, Ber. Bunsenger Phys. Chem.88, 1057 (1984).
J. Maier, in: Superionic Solids and Solid Electrolytes (A. Lasker and S. Chandra, Eds.) Academic press, San Diego, 1989, pp. 137.
A. Bunde, W. Dieterich and E. Roman, Phys. Rev. Letters55, 5 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, S., Sekhon, S.S. & Arora, N. PMMA based protonic polymer gel electrolytes. Ionics 6, 112–118 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375554
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375554