Summary
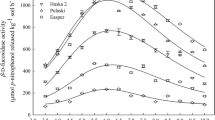
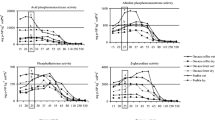
Trehalase is a specific enzyme for the hydrolysis of trehalose, a storage carbohydrate of insect and microbial species. The enzyme is of rare occurrence among higher plants. In cultivated soil, trehalase activity (Ta) was linearly related to both the amount of soil and assay incubation time. Ta increased sharply in response to substrate concentration over the range of 0 to 2% (w/v); higher substrate levels, however, showed a reduced rate of increase. Soil trehalase activity increased proportionally with increased incubation temperature over the range of 20 to 50°C but declined sharply at temperatures above 50°C. Ta was maximal at pH 5.0 when 0.5M acetate or propionate buffers were used; however, activity diminished with increased ionic strength of the buffer. Based on these findings, a standard assay method for Ta was developed. The enzyme was extracted from soil and eluted from a Sephadex G 200 column as high molecular weight organic matter. Treatment of the extract with beta-glucosidase reduced the molecular weights of the elution fractions exhibiting Ta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dixon M 1964 Enzymes. Academic Press, New York, 950 p.
Fischer L 1969 An introduction to gel chromatography. pp. 151–396.In Laboratory techniques in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Eds. T S Work and E, Work. Pergamon Press, New York.
Gottschalk A 1950 Alpha-D-Glucosidases. pp 551–582.In The Enzymes Vol. 1. Eds. J B Summer and K Myrback. Academic Press, New York, 724 p.
Hey A E and Elbein A D 1968 Partial purification and properties of a trehalase fromStreptomyces hygroscopicus. J. Bacteriol. 96, 105–110.
Hofmann E and Hoffmann G G 1966 Die Bestimmung der biologischen Tätigkeit in Böden mit Enzymmethoden. pp 369–390:In Advances in Enzymology, Vol. 28. Ed. F F Nord, Instercience Publishers. New York.
Kalf G R and Rieder S V 1958 The purification and properties of trehalase. J. Biol. Chem. 230. 691–698.
Kiss S, Dragan-Bularda M and Radulescu D 1978 Soil polysaccharidases: activity and agricultural importance. pp 117–147.In Soil Enzymes. Ed. R G Burns. Academic Press, New York, 380 p.
Lukes T M and Phaff H J 1952 Characteristics of trehalase inCandida tropicalis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. J. Microbiol. Serol. 18, 323–335.
Nelson N 1944 A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 153, 375–380.
Roberge M R 1978 Methodology of soil enzyme measurement and extraction. pp 341–370.In Soil Enzymes. Ed. R G Burns, Academic Press, New York.
Rodríquez-Kábana R 1982 The effects of crop rotation and fertilization on soil xylanase activity in a soil of the southeastern United States. Plant and Soil.In press.
Rodríguez-Kábana R 1969 Enzymatic interaction ofSclerotium rolfsii andTrichoderma viride in mixed soil culture. Phytopathology 59, 910–921.
Rodríguez-Kábana R and Curl E A 1968 Saccharase activity ofSclerotium rolfsii and the mechanism of antagonistic action byTrichoderma viride. Phytopathology 58, 985–992.
Skujins J 1978 History of abiontic soil enzyme research. pp 1–49.In Soil Enzymes. Ed. R G Burns. Academic Press, New York, 380 p.
Stahl E 1969 Thin-Layer Chromatography. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1041 p.
Steele R G D and Torrie J H 1960 Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 481 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R.E., Rodriguez-Kabana, R. The extraction and assay of soil trehalase. Plant Soil 65, 335–344 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375054
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375054