Summary
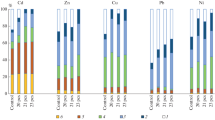
Water-soluble14C-labelled organic material, released into soil from roots of wheat and maize plants, was recovered with a mild percolation technique, without disturbing the root-soil interface. Extraction yields were relatively high for the14C materials (up to 11% of residual soil14C for 6 weeks maize) illustrating the water soluble character of the freshly added material. The complexation potential of the soil extracts was evaluated by adding57Co,65Zn and54Mn to the extract and determining their distribution among the organic fractions by a gel filtration technique. The results show that within four weeks a micro-environment is created around a plant root, characterized by an accumulation of root-derived organic materials. In parallel with this time dependent accumulation, a gradual shift from ionic metal to higher molecular weight forms occurred. The three metals were increasingly complexed throughout the growth period. Extracts from a fallow soil complexed minor amounts of the added tracer (6.4%; 1.9% and 0.2% for57Co,65Zn and54Mn respectively) while cropped soil extracts after 6 weeks complexed 61%; 16% and 6% of respectively Co, Zn and Mn in the case of maize, and 31%, 15% and 1% in the case of wheat. Although the effects are most pronounced in the case of Co and maize, evidence is given for similar effects with wheat and the other metals. The results indicate that the physicochemical status of transition metals in the rhizosphere is entirely different from that in the bulk soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen H E, Hall R H and Brisbin T D 1980 Metal speciation: Effects on aquatic toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 441–443.
Baham J, Ball N B and Sposisto G 1978 Gel filtration studies of trace metal-fulvic acid solutions extracted from sewage sludges. J. Environ. Qual. 7, 181–188.
Bender M E, Matson W R and Jordan R A 1970 On the significance of metal complexing agents in secondary sewage effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 4, 520–521.
Brown J C 1969 Metal chelation in soils — a symposium: Agricultural use of synthetic metal chelates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 33, 59–61.
Crerar D A, Means J L, Yuretich R F, Borcsik M P, Amster J L, Hastings D W, Knox G W, Lyon K E and Quiett R F 1981 Hydrogeochemistry of the New Jersey Coastal Plain. 2. Transport and deposition of Fe, Al, dissolved organic matter and selected trace elements in stream, ground and estuary water. Chem. Geol. 33, 23–44.
Florence T M and Batley G E 1977 Determination of the chemical forms of trace metals in natural waters, with special reference to Cu, Pb, Cd and Zn. Talanta 24, 151–158.
Hine P T and Bursill D B 1984 Gel permeation chromatography of humic acid — Problems associated with Sephadex gel. Water Res. 18, 1461–1465.
Kríbek B, Kaigl J and Oruzinský V 1977 Characteristics of di- and tri-valent metal-humic acid complexes on the basis of their molecular-weight distribution. Chem. Geol. 19, 73–81.
Lindsay W L 1974 The role of chelation in micronutrient availability.In The Plant Root and its Environment, Ed. E W Carson. pp 507–525. Univ. Press of Virginia.
Merckx R, Van Ginkel J H, Sinnaeve J and Cremers 1986 A Plant induced changes in the rhizosphere of maize and wheat. I. Production and turnover of root-derived material in the rhizosphere of maize and wheat. Plant and Soil. 96, 85–93.
Mubarak A and Olsen R A 1976 Immiscible displacement of soil solution by centrifugation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 329–331.
Neddermeyer P A and Rogers L B 1968 Gel filtration behaviour of inorganic salts. Anal. Chem. 40, 755–762.
Norvell W A 1971 Equilibria of metal chelates in soil.In Micronutrients in Agriculture, Soil Science Society of America Inc. 1972, Madison, Wisc. USA, Proc. Symp. Muscle Shoals, Alabama, April 20–22, 1971, pp 115–139.
Plumb R H and Lee G F 1973 A note on the iron-organic relationship in natural water. Water Res. 7, 581–585.
Saar R A and Weber J H 1982 Fulvic acid: modifier of metal-ion chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 510–517A.
Shibukawa M, Ohta N and Kuroda R 1981 Distribution processes of inorganic solutes in gel chromatography. Anal. Chem. 53, 1620–1627.
Sposito G 1981 Trace metals in contaminated waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 396–403.
Sposito G. Holtzclaw K M and Baham J 1976 Analytical properties of the soluble, metal-complexing fractions in sludge-soil mixtures: II. Comparative structural chemistry of fulvic acid. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 691–697.
Yoza N 1973 Gel chromatography of inorganic compounds. J. Chromatogr. 86, 325–349.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 2250 of the Radiation Protection Programme of the Commission of the European Communities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merckx, R., van Ginkel, J.H., Sinnaeve, J. et al. Plant-induced changes in the rhizosphere of maize and wheat. Plant Soil 96, 95–107 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374999
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374999