Summary
Ionic interactions may occur as cation-cation interactions, anion-anion interactions, or cation-anion interactions.
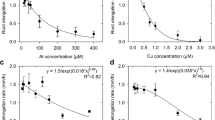
Greater knowledge of this subject is warranted, due to the intensification of agriculture, in devising efficient fertilization systems. The present study was undertaken to elucidate the interaction among P, K, Ca and Mg absorption by the intact rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants from dilute solutions. The uptake of P was independent of Ca concentrations up-to 250 μM Ca but-there was a small decrease at the higher concentrations.
Absorption of K and Mg was stimulated in the presence of Ca ions at low concentrations. But K and Mg absorption was decreased at higher Ca concentrations. Increasing concentrations of K in the nutrient solution depressed P and Ca uptake. Magnesium uptake was stimulated at lower concentrations of K, but at higher concentrations it was also decreased.
Similarly, absorption of K and Ca was also decreased with increasing concentrations of Mg. Magnesium at lower concentrations stimulated P uptake but at higher concentraions it was decreased.
In the present study maximum growth of rice plants was achieved at about 250μM Ca, 260 μM K, and 33μM Mg in the nutrient solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry W B and Johanson C M 1966 Determination of calcium and magnesium in plant material and cultural solutions, using atomic absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 20, 209–211.
Epstein E and Hagen C E 1952 A kinetic study of the absorption of alkali cations by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 27, 457–474.
Fageria N K 1974 Continuous-nutrient-flow method: a new approach to determine nutrient uptake. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 44, 262–266.
Fageria N K 1976 Effect of P, Ca and Mg concentrations in solution culture on growth and uptake of these ions by rice. Agron. J. 68, 726–732.
Fawzy M R, Overstreet H R and Jocobson L 1954 The influence of H ion on cation obsorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 29, 234–237.
Florell C 1956 The influence of calcium on root mitochondria. Physiol. Plant. 9, 23–242.
Hanson J B 1960 Impairment of respiration, ion accumulation and ion relation in root tissue treated with ribonuclease and ethylendediamine tetraacetic acid. Plant Physiol. 35, 372–379.
Hiatt A J and Legget J E 1974 Ionic interactions and antagonisms in plants.In The Plant Root and its Environment Ed. E W Carson. University Press of Virginia, Charlottesville, pp 101–134.
Jackson M L 1958 Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.
Jacobson L, Hannapel R J, Moore D P and Schaedle M 1961 Influence of calcium on selectivity of ion absorption process. Plant Physiol. 36, 58–61.
Jacobson L, Moore D P and Hannapel R J 1960 Role of calcium in the absorption of monovalent cations. Plant Physiol. 35, 352–358.
Jacobson, L, Overstreed R, King H M and Handley R 1950 A study of potassium absorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 25, 639–647.
Johson C, Edwards D G and Loneragan J F 1968 Interactions between potassium and calcium in their absorption by intact barley plants. I. Effects of potassium on calcium absorption. Plant Physiol. 43, 1717–1721.
Kahn J S and Hansen J B 1957 The effects of calcium on potassium accumulation in corn and soybean roots. Plant Physiol. 32, 312–316.
Loeb J 1916 The mechanism of the diffusion of electrolytes through the membrans of living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 27, 339.
Lundergardh H 1934 Mineral nutrition of plants. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 3, 485–498.
Mass E V 1969 Calcium uptake by excised maize roots and interactions with alkali cations. Plant Physiol. 44, 985–989.
Marschner H 1961 Untersuchungen über die Aufnahme von Cäsium durch isolierte Gerstewurzeln. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Dueng. Bodenkd. 95, 30–51.
Nielson T R and Overstreet R 1955 Study of the role of the hydrogen ion in the mechanism of potassium absorption by excised barley roots. Plant Physiol. 30, 303–309.
Omar M A and Kobbia T E 1966 Some observations on the interlationships of potassium and magnesium. Soil Sci. 101, 437–439.
Osterhout W J V 1915 On the decrease of permeability due to certain bivalent cations. Bot. Gaz. 59, 317.
Overstreet R 1957 Comments on the absorption of inorganic ions by roots cells. Plant Physiol. 32, 491–492.
Overstreet R, Jacobson L and Handley R 1952 The effects of calcium on the absorption of potassium by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 27, 583–590.
Skeen J R 1930 Experiments with trianea on antagonism and absorption. Plant Physiol. 5, 105.
Tanada T 1962 Localization and mechanism of calcium stimulation of rubidium absorption in the mung bean root. Ann. J. Bot. 49, 1068–1072.
Hai T V and Laudelout H 1966 Phosphate uptake by intact rice plants by the continuous flow method at low phosphate concentrations. Soil Sci. 101, 408–417.
Waisel Y 1962 The effect of calcium on the uptake of monovalent ions by excised barley roots. Physiol. Plant. 15, 709–724.
Wall M E 1940 The role of potassium in plants. Soil Sci. 49, 393–408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part of the Doctoral thesis submitted by the author to the Faculty of Agronomy, Catholic University of Louvain, Belgium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fageria, N.K. Ionic interactions in rice plants from dilute solutions. Plant Soil 70, 309–316 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374887
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374887