Summary
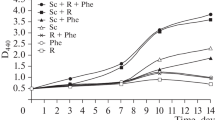
The ability of rhizobia to utilize catechol, protocatechuic acid, salicylic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and catechin was investigated. The degradation pathway of p-hydroxybenzoate byRhizobium japonicum, R. phaseoli, R. leguminosarum, R. trifolii andRhizobium sp. isolated from bean was also studied.R. leguminosarum, R. phaseoli andR. trifolii metabolized p-hydroxybenzoate to protocatechuate which was cleaved by protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenasevia ortho pathway.R. japonicum degraded p-hydroxybenzoate to catechol which was cleaved by catechol 1,2-dioxygenase.Rhizobium sp., a bean isolate, dissimilatedp-hydroxybenzoate to salicylate. Salicylate was converted to gentisic acid prior to ring cleavage. The rhizobia convertedp-hydroxybenzoate to Rothera positive substance. Catechol and protocatechuic acid were directly cleaved by the species.R. japonicum converted catechin to protocatechuic acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra T, Madhavakrishna W and Nayaudamma Y 1969 Astringency in fruits. I. Microbial degradation of catechin. Can. J. Microbiol. 15, 303–306.
Dagley S 1978 Microbial catabolism in the carbon cycle and environmental pollution. Naturwissenschaften 65, 85–95.
Evans W C 1977 Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature London 270, 17–22.
Fujisawa H 1970 Protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase (Pseudomonas).In Methods in Enzymology Vol. 17 Metabolism of amino acids and amines. Eds. H Tabor and C W Tabor. Academic Press, New York, p 526.
Hegeman C D 1966 Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway byPseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by wild types. J. Bacteriol. 91, 1140–1154.
Hussien Y A, Tewfik M S and Hamdi Y A 1974 Degradation of certain aromatic compounds by rhizobia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 6, 377–381.
Hussien Y A, Tewfik M S and Hamdi Y A 1975 Metabolism of certain aromatic compounds by rhizobia. Egypt. J. Bot. 18, 91–99.
Ibrahim R K and Towers G H N 1960 The identification by chromatography of plant phenolic acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 87, 125–128.
Kalaichelvan P T 1980 Prohibitins in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea). Ph. D. thesis, University of Madras, Madras.
Lowry O H, Rosenberg N J, Farr A L and Randall R J 1951. Protein measurements with Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Muthukumar G 1980 Effect of Tannins of Soil Micro-organisms and Crops. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Madras, Madras.
Muthukumar G and Mahadevan A 1981 Effect of tannins on soil respiration and glucose oxidation by micro-organisms. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 19, 1083–1085.
Rice E L and Pancholy S K 1973 Inhibition of nitrification by climax ecosystems. II. Additional evidence and possible role of tannins. Am. J. Bot. 60, 691–702.
Rothera A C H 1908 Note on the sodium nitroprusside reaction for acetone. J. Physiol. 37, 491–494.
Vincent J M 1970 A Manual for the Practical Study of Root Nodule Bacteria. International Biological Programme, Blackwell, Oxford, p 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthukumar, G., Arunakumari, A. & Mahadevan, A. Degradation of aromatic compounds byRhizobium spp.. Plant Soil 69, 163–169 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374511
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374511