Abstract
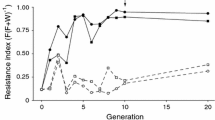
The precise phenotypic measurements, percent multiple oviposition and the number of parasitoids developed per host, can be used to assess quantitative genetic variation governing multiple oviposition and development in the muscoid Diptera parasitoid,Muscidifurax raptorellus Kogan & Legner. Evidence for polygenic control was based on the significance of correlations between expected genomic content and behavioral expression. Data accumulated from 8 oviposition days seem sufficient to measure accurately polygenic expression in this species.
Resúmen
De las varias medidas phenotípicas que indican variación en el sistema polygénico rigiendo oviposición gregaria en el parasitoideMuscidifurax raptorellus Kogan y Legner, que ataca dípteros muscides, dos, porciento de oviposición gregaria y número de parasitoides desarrollando en el hospedero, son más exactas. Se los juzga de la significación de las correlaciones entre contenido genómico y expreción comportamental, y la uniformidad entre 10 hembras replicadas. Datos acumulados de ocho días de oviposición son suficientes para medir con exactitud expreción polygénica en esta especie.
Résumé
Deux facteurs phénotypiques précis, le pourcentage d'ovipositions multiples et le nombre de parasitoïdes développés par hôte, peuvent être utilisés pour établir la variation génétique quantitative gouvernant l'oviposition multiple et le développement chez le parasitoïde du diptèreMuscidifurax raptorellus Kogan & Legner. La preuve d'un contrôle polygénique était basée sur la signification des corrélations entre le contenu du génome et l'expression comportementale. Les données accumulées au cours de 8 jours de ponte semblent suffisantes pour mesurer avec précision l'expression polygénique chez cette espèce.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobzhansky, T. — 1941. Genetics and the Origin of Species, 2nd ed. —Columbia Univ. Press, N.Y., 428 pp.
Ducan, D. B. — 1972.Multiple range and multiple F tests. —Biometrics, 11, 1–41.
Legner, E. F. — 1987. Inheritance of gregarious and solitary oviposition inMuscidifurax raptorellus Kogan & Legner [Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae]. —Can. Entomol., 119, 791–808.
Legner, E. F. — 1988;Muscidifurax raptorellus [Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae] females exhibit post mating oviposition behavior typical of the male genome. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 81, 524–527.
Legner, E. F. — 1989a. Wary genes and accretive inheritance in Hymenoptera. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 82, 245–249.
Legner, E. F. — 1989b. Paternal influences in males ofMuscidifurax raptorellus [Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae]. —Entomophaga, 34, 307–320.
Steel, R. G. D. &Torrie, J. H. — 1980. Principles and Procedures of Statistics, 2nd ed. —McGraw-Hill Book Co., Inc., N.Y., 481 pp.
Wright, S. — 1968. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations, Vol. I. — Genetics and Biometric Foundations,Univ. of Chicago Press, Chicago, 469 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Legner, E.F. Phenotypic expressions of polygenes inMuscidifurax raptorellus [Hym.: Pteromalidae], a synanthropic fly parasitoid. Entomophaga 34, 523–530 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374390
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374390