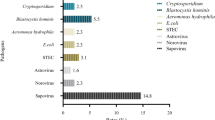
Abstract
In a survey for oothecal parasites of cockroaches in India, 6 species of cockroaches were recorded. Of theseNeostylopyga rhombifolia (Stoll.) was restricted to thatched huts whileBlattella germanica (L.),Periplaneta americana (L.),P. australasiae (F.),P. brunnea Burmeister andSupella longipalpa (F.) were common in other types of buildings. Eight species of parasites, of which 4 are new records, were reared:Anastatus tenuipes Bolivar.,Comperia merceti Compere,Evania appendigaster (L.),Evania sp. nearantennalis Westw., Genus et sp. nov. nearAnastatus. Tetrastichus asthenogmus (Waterston),T. hagenowii (Ratzeburg) andTetrastichus sp. (miser group) which is hyperparasitic. The natural and experimental hosts of these parasites are discussed. The low levels of field parasitism suggest there is scope for introducing more promising parasite species into India for biological control of cockroaches.
Résumé
Au cours de la recherche des parasites des oothèques des blattes aux Indes 6 espèces de blattes ont été répertoriées. Parmi ellesNeostylopyga rhombifolia (Stoll.) ne se trouve que dans des huttes en chaume tandis queBlatella germanica (L.),Periplaneta americana (L.),P. australasiae (F.),P. brunnea Burmeister etSupella longipalpa (F.) sont communes dans les autres types d’habitations. Huit espèces de parasites, dont 4 nouvelles pour l’Inde, ont été obtenues:Anastatus tenuipes Bolivar.,Comperia merceti Compere,Evania appendigaster (L.),Evania sp. proche deantennalis Westw., un parasite d’un genre et d’une espèce proche deAnastatus. Tetrastichus asthenogmus (Waterston),T. hagenowii (Ratzeburg) etTetrastichus sp. (du groupemiser) qui est hyperparasite. Les hôtes naturels et expérimentaux de ces parasites sont discutés. Les faibles taux de parasitisme naturel suggèrent l’intérêt d’introduire aux Indes des parasites plus efficaces pour la lutte biologique contre les blattes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Amonkar, S. V., Vijayalakshmi, L. V. &Rahalkar, G. V. — 1974. Control of American cockroach,Periplaneta americana L. by its egg parasiteTetrastichus hagenowii Ratz.: a field trial. —Symposium on Biological Approach to Problems in Medicine, Industry and Agriculture. Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Bombay, 228–233.
Cornwell, P. B. — 1968. The Cockroach, Vol. 1. —Hutchinson, Lond., 391 pp.
Fleet, R. R. &Frankie, G. W. — 1975. Behavioral and ecological characteristics of an eulophid egg parasite of two species of domiciliary cockroaches. —Environ. Entomol., 4, 282–284.
Flock, R. A. — 1941. Biological control of the brown-banded roach. —Bull. Brooklyn Entomol. Soc., 36, 178–181.
Gordh, G. — 1973. Biological investigations onComperia merceti Comp., an encyrtid parasite of the cockroachSupella longipalpa Serv.. —J. Entomol. A, 47, 115–123.
Hoyt, C. P. — 1957. Parasites and predators introduced into the Pacific islands for the biological control of insects and other pests. —South Pacific Commission Tech. Paper. No. 101, 40 pp. (An Erratum issued later states that the author of this paper was actuallyL. J. Dumbleton).
Kanayama, A., Yoshida, E. &Houma, T. — 1976. The parasitism byTetrastichus hagenowii Ratz On oothecae of the smoky brown cockroach,Periplaneta fuliginosa Serv. collected in Shizuoka city. —Jap. J. Sani. Zool., 27, 157–162 (in Japanese).
Roth, L. M. &Willis, E. R. — 1954. The biology of the cockroach egg parasiteTetrastichus hagenowii [Hym. Eulophidae]. —Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc., 80, 53–72.
Roth, L. M. & Willis, E. R. — 1957. The medical and veterinary importance of cockroaches. —Smithsonian Misc. Coll., 134, 147 pp.
Roth, L. M. & Willis, E. R. — 1960. The biotic associations of cockroaches. —Smithsonian Misc. Coll. 141, 470 pp.
Usman, S. — 1949. Some observations on the biology ofTetrastichus hagenowii Ratz. — An egg parasite of the house-cockroach,Periplaneta americana L. —Curr. Sci., 18, 407–408.
Vargas, M. V. &Fallas, F. B. — 1974. Notes on the biology ofTetrastichus hagenowii [Hym. Eulophidae] a parasite of cockroach oothecae. —Entomol. News, 85, 23–26.
Waterston, J. — 1915. New species of chalcidoidea from Ceylon. —Bull. Entomol. Res., 5, 325–342.
Yoshikawa, K. &Ikushima, I. — 1956. Some biological notes on a parasitic wasp on cockroach,Tetrastichus hagenowii Ratzeburg [Hym. Eulophidae]. —Medicine and Biology, 40, 127–129 (in Japanese).
Zimmerman, E. C. — 1948. Insects of Hawaii. Vol. 2, Apterygota to Thysanoptera, inclusive. — Honolulu, 475 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is published with the permission of the Director-General, Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narasimham, A.U., Sankaran, T. Domiciliary cockroaches and their oothecal parasites in India. Entomophaga 24, 273–279 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374241
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374241