Abstract
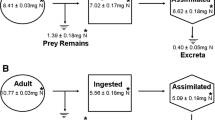
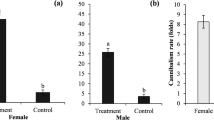
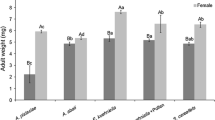
Adults ofGeocoris punctipes (Say),Tropiconabis capsiformis Germar,Nabis roseipennis Reuter andColeomegilla maculata (DeGeer) were confined inside petri dishes and fed phosphorus-32 (32p)-labeledHeliothis virescens (F.) eggs. Observations of bioelimination of32p over a 72 h period allowed derivation of equations for predicting the number ofH. virescens eggs ingested by each species. Twenty-four to 72 h after eggs were eaten, the percentages of32p eliminated ranged from ca. 14% forG. punctipes to 42 % forT. capsiformis. Cautious use of the results will aid researchers in assessing predation on32p labeledHeliothis.
Résumé
Des adultes deGeocoris punctipes (Say),Tropiconabis capsiformis germar,Nabis roseipennis Reuter etColeomegilla maculata (DeGeer) ont été confinés à l'intérieur de boîtes de Pétri et nourris d'œufs d'Heliothis virescens marqués au P32. Les observations sur la bioélimination du P32 sur une période de 72 h permettraient l'établissement d'équations destinées à prévoir le nombre d'œufs d'H. virescens ingérés par chaque espèce.
Vingt quatre à 72 h après que les œufs aient été mangés les pourcentages de P32 éliminé s'échelonnaient de 14 % pourG. punctipes à 42 % pourT. capsiformis. L'emploi prudent de ces résultats aidera les scientifiques en évaluant la prédation sur lesHeliothis marqués au P32.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
House, H. L. — 1974. Digestion. In: The physiology of insects. (Rockstein, M., ed.). —Acad. Press., New York., 5, 63–117.
McDaniel, S. G., Keeley, L. L. &Sterling, W. L. — 1978. RadiolabelingHeliothis virescens eggs by32p injection of adult females. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 71, 432–434.
Moore, S. T., Schuster, M. F. &Harris, F. A. — 1974. Radioisotope techniques for estimating lady beetle consumption of tobacco budworm eggs and larvae. —J. Econ. Entomol., 67, 703–705.
Neter, J., &Wasserman, W. — 1974. Applied Linear Statistical Models. —Richard D. Irwin, Inc., Homewood, Illinois., 842 pp.
Thead, L. G., Pitre, H. N. &Kellogg, T. F. — 1987. Predation on egg and larvae ofHeliothis virescens (F.) [Lep.: Noctuidae] by an adult predator complex in cage studies on cotton. —Entomophaga, 32, 197–207.
Waldbauer, G. P. — 1968. The consumption and utilization of food by insects. —AdV. Insect Physiol., 5, 229–288.
Wang, C. H., Willis, D. L. &Loveland, W. D. — 1975. Radiotracer Methodology in the Biological, Environmental, and Physical Sciences. —Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey., 480 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publication No 5935. Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station, Mississippi State, MS 39762.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thead, L.G., Pitre, H.N. & Kellogg, T.F. Phosphorus-32 bioelimination by arthropod predators fed labeled eggs ofHeliothis virescens [Lep.: Noctuidae] . Entomophaga 32, 191–195 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373130
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373130
Key-Words
- Bioelimination
- Coleomegilla maculata
- Geocoris punctipes
- Heliothis virescens
- Nabis roseipennis
- Tropiconabis capsiformis
- Phosphorus-32
- Predation