Abstract
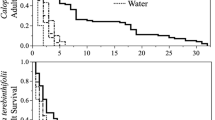
The host specificity of a chrysomelid beetle,Calligrapha pantherina Stål, from Mexico, was verified in the CSIRO quarantine facilities in Brisbane, Australia on 80 species of plants in 28 families, either closely related to Malvaceae or in families containing economically important species.C. pantherina oviposited and developed successfully on its preferred host,S. acuta, and less successfully onS. rhombifolia andS. spinosa, all of which are weeds in Australia. Aspects of oviposition, larval development, and adult feeding and longevity ofC. pantherina are described.C. pantherina was released in Australia during 1989 and readily established onS. acuta but established at only a few sites onS. rhombifolia.
Résumé
La spécificité de la chrysomèle originaire du Mexique,Calligrapha pantherina, vis-à-vis de son hôte a été contrôlée, dans les installations de la quarantaine du C.S.I.R.O. à Brisbane (Australie), sur 80 espèces de plantes appartenant à 28 familles, étroitement liées aux Malvacées ou comprenant des espèces d'importance économique.
C. pantherina pond et se développe avec succès sur son hôte préférentielS. acuta et avec moins de succès surS. rhombifolia etS. spinosa, qui sont toutes des mauvaises herbes d'Australie.
On a décrit les aspects de l'oviposition, du développement larvaire, de l'alimentation des adultes et de la longévité deC. pantherina. C. pantherina fut lâchée en Australie en 1989 et s'est bien installée surS. acuta mais seulement en quelques sites surS. rhombifolia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gillett, J. D., Harley, K. L. S., Kassulke, R. C. &Miranda, H. J. — 1991. Natural enemies ofSida acuta andS. rhombifolia (Malvaceae) in Mexico and their potential for biological control of these weeds in Australia. —Environ. Entomol., 20, 882–888.
Holm, L. G., Plucknett, D. L., Pancho, J. V. &Herberger, J. P. — 1977. The world's worst weeds: Distribution and biology. —The University Press of Hawaii, Honolulu, pp 621.
Kleinschmidt, H. E. & Johnson, R. W. — 1977. Weeds of Queensland. —Q. DPI., pp. 469.
Mott, J. J. — 1980. Germination and establishment of the weedsSida acuta andPennisetum pedicellatum in the Northern Territory. —Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb., 20, 463–469.
Sturtz, J. D., Harrison, P. G. andFalvey, L. — 1975. Regional pasture development and associated problems II Northern Territory. —Tropical Grasslands, 9, 83–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forno, I.W., Kassulke, R.C. & Harley, K.L.S. Host specificity and aspects of the biology ofCalligrapha pantherina (Col.: Chrysomelidae), a biological control agent ofSida acuta [Malvaceae] andS. rhombifolia in Australia. Entomophaga 37, 409–417 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373114
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373114
Key-Words
- Calligrapha pantherina
- chrysomelid
- biological control
- weed
- host specificity
- Sida acuta
- Sida rhombifolia