Summary
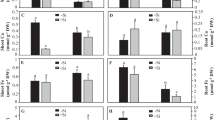
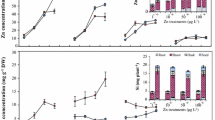
Maximum uptake of Zn in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings occurred from nutrient solutions containing SO4−S at 3.5 ppm and K at 6 ppm. Decreased translocation of Zn from roots to tips was observed when plants were grown with lower levels of S and K. Cysteine substituted for SO4-ion as a source of S in Zn absorption, and more Zn was absorbed with cysteine than with sulfate. The effect of K on Zn absorption seems to be influenced by S nutrition in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedri A W, Wallace A and Rhoads W A 1960 Assimilation of bicarbonate by roots of different plant species. Soil Sci. 89, 257–263.
Bhumbla D R and Abrol I P 1971 Use of gypsum for getting good yields from sodic soils. Indian Farming 21, 11.
Biswas C R, Rajinderjit S and Sekhon G S 1977 Zinc availability to maize and wheat in relation to P and K status of the soil in a long term fertilizer experiment. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 25, 414–421.
Brar M S and Sekhon G S 1976 Interaction of Zn with other micronutrient cations. I. Effect of Cu on Zn absorption by wheat seedlings and its translocation within the plants. Plant and Soil 45, 137–143.
Chaudhry F M, Alam S M, Rashid A and Latif A 1977 Mechanism of differential susceptibility of two rice varieties to Zn deficiency. Plant and Soil 46, 637–642.
Chaudhry F M and Loneragan J F 1972 Zinc absorption by wheat seedlings: I. Inhibition by macronutrient ions in short-term experiments and its relevance to long-term nutrition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 36, 323–331.
Dabin P, Marafante E, Monsny J M and Myttenacre C 1978 Absorption, distribution and binding of Cd and Zn in irrigated rice plants. Plant and Soil 50, 329–341.
Fitzgerald J W 1976 Sulfate ester formation and hydrolysis; a potentially important yet often ignored aspect of the sulfur cycle of aerobic soils. Bacteriol. Rev. 40, 698–721.
Fox R L 1976 Sulfur and nitrogen requirements of sugar cane. Agron. J. 68, 891–896.
Freney J R, Melville G E and Williams C H 1975 Soil organic matter fractions as sources of plantavailable sulfur. Soil Biol. Biochem. 7, 217–221.
Freney J R, Stevenson F L and Beavers A H 1972 Sulfur-containing amino acids in oil hydrolysates. Soil Sci. 114, 468–476.
Janseen K A 1975 Sulfur status of Virginia's Eastern shore soils. Vegetable Growers News 29, 7.
Lindsay W L 1972 Inorganic phase equilibria of micronutrients in soils.In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Eds. J J Mortvedt, P M Giordano and W L Lindsay Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Publication.
Massoumi A and Cornfield A H 1963 A rapid method for determining sulfate in water extracts of soils. Analyst 88, 321–322.
Negrew V N and Tarasov B M 1978 The effect of basal fertilizers and Zn on rosette disease of the apple tree in the Crimean Steppe. Isvestiya Timiryazevski Selskokohzyaistvennoi Akademi 1, 124–132. Abstracted in Soils Fert. 41, 2932, 1978.
Nouri H and Olsen R A 1966 Influence of applied sulfur on availability of soil nutrients for corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 30, 284–286.
Parfit R L and Smart R C 1978 The mechanism of sulfate adsorption on iron oxides. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 48–50.
Rashid A, Chaudhry F M and Sharif M 1976 Micronutrient availability to cereals from calcareous soils III. Plant and Soil 45, 613–623.
Rehab F I and Wallace A 1978 Excess trace metal effects on cotton II. Cu, Zn, Co and Mn in yolo loam soil. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 9, 519–527.
Reisenauer, H. M. 1966 Mineral nutrients in soil solution.In Environmental Biology. Eds. P L Altman and D S Dittmer Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda, pp 507–508.
Rhue R D and Kamprath E J 1973 Leaching losses of S during winter months when applied as gypsum, elemental S or prilled S. Agron. J. 65, 603–605.
Schricker B R 1978 Studies of an endogenous Zn-chelator of rat intestine. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois.
Spratt E D and Smid A E 1978 Yield and elemental composition of flax as affected by P and micronutrients. Agron J. 70, 633–637.
Takkar P N and Singh T 1978 Zn nutrition of rice as influenced by rates of gypsum and Zn fertilization of alkali soils. Agron. J. 70, 447–450.
Viets F G Jr, Boawn L C and Crawford C L 1957 The effect of N carriers on uptake of indigenous and applied Zn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 21, 197–201.
Walker T W 1955 Sulfur responses in pasture in Australia and New Zealand. Soils Fert. 18, 185–187.
Westerman D T 1974 Indexes of sulfur deficiency in alfalfa. I. Extractable soil SO4-S. Agron. J. 66, 578–581.