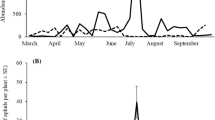
Abstract
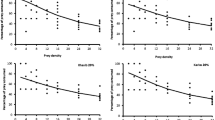
Predation ofAphis pomi DeGeer [Hom.: Aphididae] byAphidoletes aphidimyza (Rondani) [Dipt.: Cecidomyiidae] was simulated in Michigan apple orchards using a computer and output validated against field data collected from sleeve cages enclosing aphid infested apple terminals. Lower and upper temperature thresholds for development were 2.9 and 35°C for nymphs ofA. pomi with a mean immature developmental period of 162.3 heat units. Median survivorship of adultA. pomi was 364.3 heat units with an average fecundity of 60.7 offspring per female.A. aphidimyza egg and larval lower threshold and developmental periods were 10.5 and 25.5, 8.1°C and 65.5 heat units, respectively. Larval functional response showed Type II behavior with a y-asymptote of 45 aphids killed per predator. Multiple generation model runs performed under different initial predator: prey densities indicated that current critical predator: prey ratios used in the field for control decisions may underestimate predator efficacy.
Résumé
La prédation d'A. pomi parAphidoletes aphidimyza a été simulée dans un verger de pommiers du Michigan en employant un ordinateur et les résultats ont été validés par comparaison aux données récoltées à partir de cages de mousseline enfermant des pousses terminales de pommiers infestées d'Aphides. Les seuils de température inférieur et supérieur pour le développement étaient 2.9 et 35°C pour les larves d'A. pomi avec une durée moyenne de développement de 162.3(degré/jour). La survie moyenne d'un adulte d'A. pomi était de 364,3 (degré/jour) avec une fécondité moyenne de 60,7 descendants/♀. Le seuil inférieur et la durée de développement étaient respectivement pour l'œuf d'A. aphidimyza 10,5°C et 25,5 (degré/jour) et pour la larve 8,1°C et 65.5 (degré/jour).
La réponse fonctionnelle des larves était du type II avec sur les ordonnées une asymptote de 45 aphides tués/prédateur. L'utilisation d'un modèle à générations multiples à partir de différentes densités prédateurs/proies indiquait que les rapports critiques courants prédateurs/proie employés à l'extérieur pour décider d'un intervention peuvent sous estimer l'efficacité du prédateur.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. G., Jr. — 1977. Role of predator,Aphidoletes aphidimyza (Rondani) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae], in the management of the apple aphid,Aphis pomi DeGeer [Homoptera: Aphididae] in Massachusets. —Ph. D. Thesis, Univ. Massachussetts. 55pp.
Adams, R. G. Jr. &Prokopy, — 1980.Aphidoletes aphidimyza (Rondani) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae]: an effective predator of the apple aphid [Homoptera: Aphididae] in Massachusets. —Environ. Entomol., 5, 388–396.
Arnold, C. Y. — 1959. The determination and significance of the base temperature in a linear heat unit system. —J. Am. Soc. Hort., 74, 430–435.
Azab, A. K., Tawfik, M. F. S. &Ismail, I. I. — 1965. Morphology and biology of the aphidophagous midge,Phaenobremia aphidivora Rubsaamen. —Bull. Soc. Entomol. Egypte, 49, 25–45.
Baker, A. C. &Turner, W. F. — 1916. Morphology and biology of the green apple aphis. —J. Agric. Res., 5, 955–994.
Campbell, A., Frazer, B. D., Gilbert, N., Gutierriez, A. P. &Mackauer, M. —1974. Temperature requirements of some aphids and their parasites. —J. Apple. Ecol., 11, 431–438.
El-Gayer, F. — 1976. Some effects of a cyclic and an acyclic junenoid onAphidoletes aphidimyza [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae] —Entomophaga, 76, 297–301.
El Titi, A. 1974. Zur Auslosung der Eiablage bei der Aphidophagen GallmuckeAphidoletes aphidimyza [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae]. —Entomol. Exp. Appl., 17, 9–21.
Harris, K. M. — 1973. Aphidophagous Cecidomyiidae: taxonomy, biology and assessments of field populations. —Bull. Entomol. Res., 63, 305–325.
Havelka, J. — 1980. Effects of temperature on the developmental rate of preimaginal stages ofAphidoletes aphidimyza [Diptera, Cecidomyiidae]. —Entomol. Exp. Appl., 27, 83–90.
Holling, C. S. — 1965. The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. —Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can., 45, 5–60.
Jokinen, D. P. — 1980. Spatial distribution ofAphis pomi (DeGeer) and the predatorAphidoletes aphidimyza (Rondani) relative to growth of the apple tree. —M. S. Thesis, Michigan State Univ., E. Lansing, Michigan.
Lathrop, F. H. — 1923. Influence of temperature and evaporation upon the development ofAphis pomi DeGeer. —J. Agric. Res., 23, 969–987.
LeRoux, E. J. — 1959. Effects of frost, rainfall and aestival temperatures on populations of the apple aphidAphis pomi DeG. [Homoptera: Aphididae] on apple in Quebec. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Quebec, 5, 49–52.
Madsen, H. E., Peters, H. F. &Vakenti, J. M. — 1975. Pest management: experiences in six British Columbia apple orchards. —Can. Entomol., 107, 873–877.
Manetsch, T. J. — 1976. Time-varying distributed delays and their use in aggregative models of large systems. —IEEE Trans. Sys. Man, & Cyber., 6, 547–553.
Manetsch, T. J. &Park, G. L. — 1977. Systems analysis and simulation with application to economic and social systems. Part II. —Dept. EE & Syst. Sci., Michigan State Univ., E. Lansing, MI. 3rd edition.
Mansour, M. H. — 1976. Some factors influencing egg laying and site of oviposition byAphidoletes aphidimyza [Dipt.: Cecidomyiidae] —Entomophaga, 21, 281–288.
Markkula, M. & Tiitanen, T. — 1977. Use of the predatory midgeAphidoletes aphidimyza (Rond.) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae] against aphids in glasshouse cultures. —Proc. Symp. Int. Cong. Entomol., 1976. Publ. Aug. 1977 as ARS-NE-85 by US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC.
Markkula, M., Hamalainen, M. &Forsberg, A. — 1979. The aphid midgeAphidoletes aphidimyza [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae] and its use in biological control of aphids. —Ann. Entomol. Fennici., 45, 89–98.
Matheson, R. — 1919. A study of the plant lice injuring the foliage and fruit of the apple. —Cornell Univ. Agric. Exp. Sta. Mem., 24, 683–730.
Morse, J. G. — 1981. Biological studies onAphidoletes aphidimyza (Rondani) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae] and its use in biological control of the apple aphidAphis pomi DeGeer [Homoptera: Aphididae]. —Ph. D. Thesis, Michigan State Univ., E. Lansing, MI.
Nijveldt, W. — 1966. The food necessity ofPhaenobremia aphidimyza (Rond.) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae]. —Cecidologia Indica, 1, 185–187.
Roberti, D. — 1946. LaPhaenombremia aphidimyza (Rond.) [Diptera: Cecidomyiidae] predatrice diAphis (Dorsalis) frangulae Koch. —Boll. Inst. Entomol. Univ. Bologna, 15, 233–256.
Sprecht, H. B. — 1972. The apple aphid,Aphis pomi [Homoptera: Aphididae], populations on apple under summer conditions in a controlled environmental cabinet —Can. Entomol., 104, 105–111.
Uygun, N. — 1971. Der Einfluss der Nahrungsmenge auf Frucktbarkeit und Lebensdauer vonAphidoletes aphidimyza (Rond.) [Diptera: Itonididae]. —Z. Angew. Entomol., 69, 234–258.
Way, M. J. — 1973. Population structure in aphid colonies. In: Perspectives in aphid biology (A. D. Lowe ed.). —Bull. Entomol. Sco. N. Z., 2, 76–84.
Warner, L. A. &Croft, B. A. — 1982. Toxicities of azinphosmethyl and selected orchard pesticides to an aphid predator,Aphidoletes aphidimyza —J. Econ. Entomol., 75, 410–415.
Westigard, P. H. &Madsen, H. F. — 1965. Studies on the bionomics of summer generations of the apple aphid,Aphis pomi DeGeer [Homoptera: Aphididae] —Can. Entomol., 97, 1107–1114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morse, J.G., Croft, B.A. Biological control ofAphis pomi [Hom.: Aphididae] ofAphidoletes aphidimyza [Dip.: Cecidomyiidae]; a predator-prey model. Entomophaga 32, 339–356 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02372443
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02372443