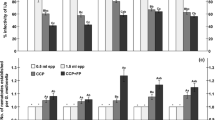
Abstract
There was no significant decrease or increase in the activity of conidia ofNomuraea rileyi after 12in vivo serial passages in larvae ofTrichoplusia ni (Hübner) or after 12in vitro serial passages on a semi-synthetic medium. The LC-50 at the start of the serial passage was 16.8±4.0 conidia/mm2; after 12 serial passages the LC-50 for thein vitro- andin vivo-produced conidia was 16.2±2.5 conidia/mm2 and 12.0±1.9 conidia/mm2, respectively.
Résumé
Il n'y a pas d'augmentation ou de réduction significative dans l'activité des conidies deNomuraea rileyi après 12 passages en sériein vivo chez les larves deTrichoplusia ni (Hübner) ou après 12 passages en sériein vitro sur un milieu semi-synthétique. La concentration léthale 50 au début de ces passages était de 16,8±4,0 conidies/mm2, après 12 passages la CL 50 des conidies produitesin vitro etin vivo fut respectivement de 16,2±2,5 conidies/mm2 et de 12,0±1,9 conidies/mm2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud, M. — 1927. Recherches préliminaires sur les champignons entomophytes. —Ann. Epiphyt., 13, 1–30.
Fargues, J. — 1972. Étude des conditions d'infection des larves de doryphore,Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say, parBeauveria bassiana (Bals.)Vuill.[Fungi Imperfecti]. —Entomophaga, 17, 319–337.
Fargues, J. &Robert, P.H. — 1978. Adaptabilité de deux pathotypes deMetarrhizium anisopliae (Metch.)Sorok., [Fungi Imperfecti, Hyphomycétes] par culture sur milieu artificiel et par passage sur insectehôte d'origine. —C. R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 287, 165–167.
Ferron, P., Deotte, A. &Marchal, M. — 1972. Stabilité de la virulence d'une souche deBeauveria tenella (Delacr.)Siemaszko [Fungi Imperfecti] pour les larves du coléoptèreMelolontha melolontha L. —C. R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 275, 2977–2979.
Fox, C.J.S. &Jaques, R.P. — 1958. Note on the green-muscardine fungusMetarhizium anisopliae (Metch.)Sorok., as a control agent for wireworms. —Can. Entomol. Soc., 90, 314–315.
Ganhao, J.F.P. — 1956.Cephalosporium lecanii Zimm. Um fungo entomógeno de cochonilhas. —Brotéria, 25, 71–135.
Garcia, C. &Ignoffo, C.M. — 1978. A simplified diet-surface treatment technique for determining the infectivity of conidia ofNomuraea rileyi. —J. Invertebr. Pathol., 32, 398–399.
Giard, A. — 1891. Sur l'Isaria densa (Link)Fries., parasite du ver blanc. —C. R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 113, 269–272.
Hall, R.A. — 1980. Effect of repeated subculturing on agar and passaging through an insect host on pathogenicity, morphology, and growth rate ofVerticillium lecanii. —J. Invertebr. Pathol., 36, 216–222.
Hamalle, R.J. &Bell, J.V. — 1976. An apparatus for the mass collection of spores of entomopathogenic fungi. —J. Georgia Entomol. Soc., 11, 221–223.
Hartmann, G.C. &Wasti, S.S. — 1974. Infection of the gypsy moth,Porthetria dispar (L.) with the entomogenous fungus,Conidiobolus coronatus (Cost)Batko. —Entomophaga, 19, 353–360.
Ignoffo, C.M. — 1963. A successful technique for mass-rearing cabbage loopers on a semisynthetic diet. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 56, 178–182.
Ignoffo, C.M. &Boening, O.P. — 1970. Compartmented disposable plastic trays for rearing insects. —J. Econ. Entomol., 63, 1696–1697.
Ignoffo, C.M., Puttler, B., Hostetter, D.L. &Dickerson, W.A. — 1976. Susceptibility of the cabbage looper,Trichoplusia ni, and the velvetbean caterpillar,Anticarsia gemmatalis, to several isolates of the entomopathogenic fungusNomuraea rileyi. —J. Invertebr. Pathol., 28, 259–262.
Ignoffo, C.M., Garcia, C., Alyoshina, O.A. &Lappa, N.V. — 1979. Laboratory and field studies with Boverin: a mycoinsecticidal preparation ofBeauveria bassiana produced in the soviet Union. —J. Econ. Entomol., 72, 562–565.
Kawakami, K. — 1960. On the changes of characteristics of the silkworm muscardines through sucessive cultures. —Bull. Sericult. Exp. Stn., 16, 83–99. (In Japanese; English abstract).
Kerner, G. — 1959. Eine Mykose beiDasychira pudibunda L. und ihre Verwendung zur biologischen Bekämpfung voranderen Forstinsekten. —Trans. 1st Int. Conf. Insect Pathol. Biol. Control (Praha, 1958). — 169–176.
Latch, G.C.M. — 1965.Metarrhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff)Sorokin strains in New Zealand and their possible use for controlling pasture inhabiting insects. —N. Z. J. Agric. Res., 8, 384–396.
Lefèbvre, C.L. — 1931. A destructive fungous disease of the corn borer. —Phytopathology, 21, 124–125.
Lepesme, P. — 1938. Recherches sur une aspergillose des acridiens. —Bull. Soc. Hist. Nat. Afrique Nord, 29, 372–384.
Madelin, M.F. — 1963. Diseases caused by hyphomycetous fungi. In: Insect Pathology: An Advanced Treatise (E.A. Steinhaus, ed.). —Academic Press, New York/London, vol. 2, 223–271.
Masera, E. — 1957.Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff)Sorokin. Parassita del baco da seta. —Ann. Sper. Agric., 11, 281–295.
Müller-Kögler, E. — 1965. Pilzkrankheiten bei Insekten. —Paul Parey, Berlin & Hamburg, 444 pp.
Nagaich, B.B. — 1973.Verticillium species pathogenic on aphids. —Indian Phytopathol., 26, 163–165.
Rockwood, L.P. — 1950. Entomogenous fungi of the familyEntomophthoraceae in the Pacific Northwest. —J. Econ. Entomol., 43, 704–707.
Schaerffenberg, B. — 1964. Biological and environmental conditions for the development of mycoses caused byBeauveria andMetarrhizium. —J. Insect Pathol., 6, 8–20.
Steinhaus, E.A. — 1949. Principles of Insect Pathology. —McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York, NY., 757 pp.
Toumanoff, C. — 1933. Action des champignons entomophytes sur la pyrale du maïs (Pyrausta nubilalis Hübner). —Ann. Parasitol. Humaine Comparée, 11, 129–143.
Vonwyl, E. — 1980. Lactate dehydrogenase isozymes in the genusXenopus: comparison of isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis as separation methods. —Science Tools, 2, 36–38.
Wasti, S.S. &Hartmann, G.C. — 1975. Experimental parasitization of larvae of the Gypsy moth,Porthetria dispar (L.) with the entomogenous fungus,Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo)Vuill. —Parasitology, 70, 341–346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mention of a proprietary product in this paper does not constitute a recommendation for use by the USDA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ignoffo, C.M., McIntosh, A.H., Garcia, C. et al. Effects of successivein vitro andIn vivo passages on the virulence of the entomopathogenic fungus,Nomuraea rileyi . Entomophaga 27, 371–378 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02372059
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02372059