Abstract
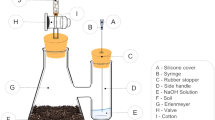
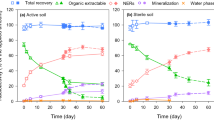
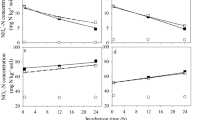
[Carbonyl-14C] methabenzthiazuron (MBT) was applied to an arid region soil at a rate of 5mg kg−1 soil to give a14C content of 2400 KB kg−1 soil. After 15 weeks of incubation at 22°C and 50% of the maximum water holding capacity of the soil, 7.2% of the applied14C was mineralized to14CO2. Where the soil was amended with wheat straw, total mineralization increased to 17.3%. Soil disturbance caused a significant increase while chloroform fumigation caused a significant decrease in the rate of14CO2 production, both from amended and unamended soils. These results suggest that MBT is degraded mainly through microbial co-metabolism.
Wheat straw amendment resulted in increased transformation of MBT into soil humus. In unamended soil, a major portion of14C was recovered in fulvic acid and in fractions extracted with organic solvents. Recovery of14C in non-extractable bound residues (humins) increased as incubation progressed and seemed to be derived from the fulvic acid fraction, which showed a concomitant decrease.
More than 99% of the residual14C in unamended soil consisted of unaltered MBT; the remainder occurred as 1-methyl-1 (benzthiazolyl) urea. In amended soil, a relatively higher percentage of the extractable14C was found in the metabolite. Small amounts of three unidentified14C-labelled compounds were also observed.
In amended soil, disturbance caused a decrease in extractable-14C whereas fumigation caused a significant increase, as compared to the untreated control. The effects were more pronounced when the soils were reated at an early stage of incubation. In general, soil disturbance increased the availability of MBT for further transformations while chloroform fumigation decreased the process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M 1983 Ecologically significant microbial transformations of synthetic chemicals. Ecol. Bull (Stockholm) 35, 503–510.
Azam F, Haider K and Malik K A 1985 Transformation of14C-labelled plant components in relation to immobilization and remineralization of15N fertilizer. Plant and Soil 86, 15–25.
Becker R and Plughan A 1969 Zweijährige Erfahrungen mit Tribunil zur Unkrautbekämpfung im Herbst in Norddeutschland. Pflanzenschutz-Nachrichten Bayer 22, 415–426.
Bottner P 1985 Response of microbial biomass to alternate moist and dry conditions in a soil incubated with14C-and15N labelled plant material. Soil Biol. Biochem. 17, 329–337.
Cheng H H and Fuhr F 1973 radioisotope tracer studies in the degradation of methabenzthaizuron in the soil. Agron. Abs. 90.
Cheng H H and Fuhr F 1976 Extraction of methabenzthiazuron from the soil. J. Agric. and Foof Chem. 24, 421–424.
Cheng H H, Fhur F, Jarczyk H J and Mittelstaedt W 1978 Degradation of MBT in the soil. J. Agric. and Food Chemistry. 26, 595–599.
Cheng H H, Fuhr F and Mittelstaedt W 1975 Fate of methabenzthiazuron in the plant-soil system. Environ. Qual. Saf. Suppl. 3, 271–276.
Doyle R C and Kaufman D D 1978, Effect of dairy manure and sewage sludge on14C-pesticide degradation in the soil. J. Agric Fd. Chem. 26, 987–989.
Duah-Yentumi S and Kuwatsuka S 1980 Effect of organic matter and chemical fertilizers on the degradation of benthiocarb and MCPA herbicides in the soil. Soil Sci. Pl. Nutr. 26, 541–549.
Fuhr F and Mittelstaedt W 1975 Das Verhalten von methabenzthiazuron in Boden und Pflanze nach Applikation von methabenzthiazuron [benzolkern-U-14C] an Sommerweizen unter Freilandbedingungen im Anwendungsjahr und Nachbau. Landw. Forschung, SH 32, 286–294.
Fuhr F and Mittelstaedt W 1979 Effects of varying soil temperatures on the degradation of MBT, Isocarbamide and Metamitron. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 142, 657–668.
Fuhr F and Mittelstaedt W 1980 Plant experiments on the bioavailability of unextracted [carbonyl-14C]MBT residues from soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 28, 122–125.
Gerstl Z and Helling C S 1985 Fate of bound methyl parathion residues in soils as influenced by agronomic practices. Soil Biol Biochem. 17, 667–673.
Hack H 1969 Tribunil, ein neues wirksames Herbizid für den Getreidebau. Pflanzenschutz-Nachrichten Bayer 22, 341–360.
Hansper M 1986 Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Übertragbarkeit von Ergebnissen aus standardisierten Gefäss-und Lysimeterversuchen auf reale Feldbedingungen am Beispiel der Rückstandssituation in Pflanzen nach Sprintzung von Goltix und Tribunil. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Bonn, FRG.
Jackobson S N, Omara N L and Alexander M 1980 Evidence of co-metabolism in sewage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 40, 917–921.
Jenkinson D S 1966 Studies on the decomposition of plant materials in soil II-Partial sterilization of soil and the soil biomass. J. Soil. Sci. 17, 280–302.
Jenkinson D S and Powlson D S 1976 The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil. V-A method for measuring soil biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 8, 209–213.
Jensen H L 1963 Carbon nutrition of some microorganisms decomposing halogen-substituted aliphatic acids. Acta Agric. Scand. 13, 404–412.
Kassim G, Stott Diane D, Partin J P and Haider K 1982 Incorporation of a wide variety of organic substrate carbons into soil biomass as estimated by the fumigation procedure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 45, 1106–1112.
Kassim G, Stott Diane D, Martin J P and Haider K 1982 Stabilization and incorporation into biomass of phenolic and benzenoid carbons during biodegradation in soil. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 305–309.
Kubiak R 1986 Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Übertragbarkeit von Ergebnissen aus standardisierten laborversuchen und Agrarökosystemausschnitten auf die reale Feldsituation am Beispiel des Abbau-und Verlagerungsverhaltens der Herbizidwirkstoffe Metamitron und Methabenzthiazuron in einer Parabraunerde. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Bonn, FRG.
Mittelstaedt W, Still G, Durbeck H and Fuhr F 1977 Extraction and identification of major metabolite of [carbonyl-14C]MBT after degradation in the soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 25, 908–912.
Novik N T and Alexander M 1985 CO-metabolism of low concentrations of prepachlor, alachlor, and cycloate in sewage and lake water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 737–743.
Ross D J, Tate K R, Kairns A and Pansier E A 1980 Microbial biomass estimations in soils from tussock grasslands by three biochemical procedures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 12, 375–383.
Siebert K 1981 Der Einfluss der Pflanzenwurzel auf den Abbau der Herbizide Atrazin und 2,4-D im boden. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Bonn, FRG.
Seibert K, Fuhr F and Mittelstaedt W 1982 Experiments on the influence of roots and soils on degradation. Landw. Forschung 35, 5–13.
Soulas G, Chaussod R and Verguet A 1984 Chloroform fumigation technique as a means of determining the size of specialized soil microbial populations: application to pesticidedegrading microorganisms. Soil biol. Biochem. 5, 497–501.
Subba-Rao R V and Alexander M 1985 Bacterial and fungal co-metabolism of 1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) and its breakdown products. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 509–516.
Wang Y-S, Subba Rao R V and Alexander M 1984 Effect of substrate concentration and organic and inorganic compounds on the occurrence and rate of mineralization and co-metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47, 1195–1200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, F., Fuhr, F. & Mittelstaedt, W. Fate of [carbonyl-14C]methabenzthiazuron in an arid region soil — effect of organic amendment, soil disturbance and fumigation. Plant Soil 107, 149–158 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370541
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370541