Summary
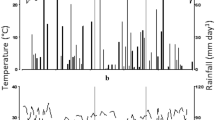
Cultivars ofPhaseolus vulgaris (L.) from contrasting geographic locations were cultivated under fields conditions for measurements of nitrogenase and nitrate reductase activities. A first trial with two cultivars indicated that a tropical cultivar B-789 has a higher nitrogenase activity than a temperate one Elsa. And the converse was true for the nitrate reductase activity. While where a post flowering application was made, a renewal of nitrate reductase activity occurred.
Further similar comparisons of both enzymatic activities upon eight tropical and temperate cultivars of equivalent vegetative cycles indicated, on the average, that tropical cultivars have a higher level of (C2H2) reduction and a lower nitrate reductase activity than temperature cultivars.
These observations suggest that there exists an inverse relationship between the two enzymatic activities in common beans, and there probably exists genetic variability for a possible improvement of N-fixation ability.
An early application of N-fertiliser upon the Elsa and B-789 plots promotes later nitrogenase activity while a post flowering application shows obvious a renewal of nitrate reductase activity. Thus, analyses of nitrate reductase and nitrogenase activities of a common bean crop at different physiological stages may give us an indication of the best time to apply supplementary nitrogen fertilisation to common beans to increase seed yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Balandreau, J. and Dommergues, Y. 1971 Mesuresin situ de l'activité nitrogénase. C.R. Acad. Sci.273, 2020–2023.
Brakel, J. and Manil, P. 1964 Fumure azotée et fixation symbiotique d'azote chezPhaseolus vulgaris L. Rev. Agric.4, 465–482.
Brakel, J. 1966 Fixation symbiotique de l'azote chez le haricot (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Comparaison de l'activité fixatrice de diverses souches. Bull. Rech. Agron. Gembloux34, 525–533.
Eaglesman, A. R. J. and Dart, P. J. 1974 Field inoculation of Navy Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Rothamsted Exp. Stn. Rep. Pt1, 246–253.
Franco, A. A. 1977 Nutritional restraints for tropical grains legumes symbiosis. pp 237–253.In Exploiting the Legumes Rhizobium Symbiosis in tropical Agriculture. Eds. J. M. Vincent, A. S. Whitney and J. Bose.
Franco, A. A., Peireira, J. C. and Neyra, C. A. 1979 Seasonal patterns of nitrate reductase and nitrogenase activity inPhaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol.63, 421–424.
Graham, P. H. and Rosas, J. C. 1977 Growth and development of intermediate bush and climbing cultivars ofPhaseolus vulgaris L. inoculated with Rhizobium. J. Agric. Sci.88, 503–508.
Graham, P. H. and Halliday, J. 1977 Inoculation and nitrogen fixation in the genus Phaseolus pp 313–314.In Exploiting the Legume-Rhizobium Symbiosis in tropical Agriculture. Eds. J. M. Vincent, A. S. Whitney and J. Bose.
Habish, H. A. and Ishag, H. N. 1974 Nodulation of legumes in Sudan. III Response of haricot beans to nodulation. Exp. Agric.10, 45–50.
Hageman, R. H. and Harper, J. E. 1972 Canopy and seasonal profiles of nitrate reductase in soybeans (Glycine max. L. Merr.) Plant Physiol.49, 146–154.
Hardaker, J. M. and Hardwick, R. C. 1978 A note on Rhizobium inoculation of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) using the fluid drill technique. Exp. Agric.14, 17–21.
Hardy, R. W. F., Holsten, R. D., Jackson, E. K. and Burns, R. C. 1968 The acetylene-ethylene essays for N2 fixation: Laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol.43, 1185–1207.
Harper, J. E., Nicolas, J. C. and Hageman, R. H. 1972 Seasonal and canopy variation in nitrate reductase activities of soybean varieties. Crop. Sci.49, 146–154.
Harper, J. E. 1974 Soil and symbiotic nitrogen requirements for optimum soybean production. Crop. Sci.14, 225–260.
Jaworski, E. G. 1971 Nitrate reductase essays in intact plant tissues. Bioch. Biophys. Res. Commun.43, 1274–1279.
Micquel, M., Obaton, M., Conejero, G., Robin, P., Salsac, L., Domenach, A. M. and Bardin, R. 1980 Détermination de l'activité nitrate réductase et nitrogénase chez le soja au champ. 5e colloque international sur le contrôle de l'alimentation des plantes cultivées. Castelfranco veneto, 1–10.
Nicolas, D. J. D. and Nason, A. 1957 Determination of nitrate and nitrite.In Methods of Enzymology3, 981–984.
Obaton, M. 1967 Inoculation des légumineuses. Bull. Technique Inform.219, 1–9.
Randall, P. J. 1969 Changes in nitrate reductase levels on respiration of molybdenum to molybdenum-deficient plants. Aust. J. Agric. Res.20, 635–642.
Vessereau, A. and Boeuf, F. 1948 Recherche et expérimentation en agriculture (Méthode statistique en biologie et agronomie). Librairie J. B. Baillere et Fils, Paris, 1962.
Westerman, D. T. and Kolar, J. J. 1978 Symbiotic N2(C2H2) fixation by beans. Crop. Sci.18, 986–990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felix, J.F., Obaton, M., Messiaen, C.M. et al. Nitrate reductase and nitrogenase activities of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) from different geographic locations. Plant Soil 63, 427–438 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370042
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370042