Summary
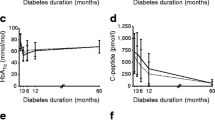
We studied associations of 24-h serum insulin profiles with insulin dose, age, gender, haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and C-peptide values, as well as blood glucose profiles in 77 consecutive childrennine aged 2–4, 14 aged 5–8, 26 aged 9–12, and 28 aged 13–17 years—2 years after the onset of insulindependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Mean weightbased insulin doses in the four age groups were similar (0.7±0.2 U·kg−1·day−1 in all); body surface-area-based doses differed. Insulin doses correlated significantly with the 24-h mean and area-under-thecurve (AUC) values, and with mean values at 03.00 hours of serum insulin in the children aged 5–8 and 13–17 years. The mean insulin concentrations of the age groups (95% confidence intervals) increased with age [6.1 (3.8, 9.7), 7.6 (5.9, 9.8), 10.4 (8.6, 12.4), and 14.0 (11.6, 16.8) mU/l;p<0.0002]. The 24-h mean of serum insulin together with HbA1c concentration predicted 32% of the variation of mean blood glucose concentrations. Of children aged less than 9 years, 50% had insulin values less than 5 mU/l (healthy subjects' lower reference limit), and 14% were of less than 2 mU/l (detection limit of the assay) at 03.00 hours. At 07.00 hours, 82% had insulin values of less than 5 mU/l, and 36% were of less than 2 mU/l, respectively. Some young children had night-time hypoglycaemia with simultaneous hypoinsulinaemia. Insulin profiles correlated poorly with the HbA1c and peak C-peptide values. We conclude that in children the mean and AUC values of serum insulin profiles are age-dependent but C-peptide independent 2 years after the diagnosis of IDDM despite similar weight-based mean insulin doses. Nocturnal and morning hypoinsulinaemia was a frequent finding in the younger children, as was biochemical hypoglycaemia. These findings suggest that insulin kinetics and sensitivity differ markedly in children according to age. [Diabetologia (1995) 38:97–105]
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IDDM:
-
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- BMI:
-
body mass index
References
Hansen AP, Johansen K (1970) Diurnal patterns of blood glucose, serum free fatty acids, insulin, glucagon and growth hormone in normals and juvenile diabetics. Diabetologia 6:27–33
Di Natale B, Devetta M, Rossi L et al. (1973) Circadian rhythm of plasma growth hormone, cortisol and insulin in obese and diabetic children. Helv Pediat Acta 28: 591–602
Schmidt MI, Lin QX, Gwynne JT, Jacobs S (1984) Fasting early morning rise in peripheral insulin: evidence of the Dawn phenomenon in nondiabetes. Diabetes Care 7:32–35
Waldhäusl W (1989) Circadian rhythms of insulin needs and actions. Diabetes Res Clin Practice 6:S17-S24
Knip M, Åkerblom HK (1981) Plasma C-peptide and insulin in neonates, infants, and children. J Pediatr 99:103–105
Lautala P, Åkerblom HK, Viikari J et al. (1985) Atherosclerosis precursors in Finnish children and adolescents. VII. Serum immunoreactive insulin. Acta Paediatr Scand [Suppl] 318:127–133
Laron Z, Aurbach-Klipper Y, Flasterstein B, Litwin A, Dickerman Z, Heding LG (1988) Changes in endogenous insulin secretion during childhood as expressed by plasma and urinary C-peptide. Clin Endocrin 29:625–632
Smith CP, Williams AJK, Thomas JM et al. (1988) The patterns of basal and stimulated insulin responses to intravenou glucose in first degree relatives of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children and unrelated adults aged 5 to 50 years. Diabetologia 31:430–434
Werther GA, Turner RC, Jenkins PA, Baum JD (1982) Twenty-four hour profiles of plasma C-peptide in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children. Diabetologia 22: 245–249
Davis SN, McGuinness OP, Cherrington AD (1990) Insulin action in vivo. In: Alberti KGMM, Krall LP (eds) The Diabetes Annual/5. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 585–614
Home PD, Thow JC (1990) Insulin injection therapy. In: Alberti KGMM, Krall LP (eds) The Diabetes Annual/5. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 152–165
Genuth SM (1973) Plasma insulin and glucose profiles in normal, obese, and diabetic persons. Ann Intern Med 79: 812–822
Griffin NK, Spanos A, Jenkins PA, Turner RC, Werther G, Baum JD (1980) 24-hour metabolic profiles in diabetic children. Arch Dis Child 55:112–117
Werther GA, Jenkins PA, Turner RC, Baum JD (1980) Twenty-four-hour metabolic profiles in diabetic children receiving insulin injections once or twice daily. Br Med J 281:414–418
Åkerblom HK, Käär M-L, Knip M, Puukka R (1985) Serum free immunoreactive insulin in poorly controlled diabetic children. J Pediatr Endocrin 1:151–155
de Beaufort CE, Bruining GJ, Home PD, Houtzagers CMGJ, van Strik R (1986) Overnight metabolic profiles in very young insulin-dependent diabetic children. Eur J Pediatr 145:73–76
Soltész G, Molnár D, Decsi T, Hamar A, Klujber L (1988) The metabolic and hormonal effects of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy in diabetic children. Diabetologia 31:30–34
Edge JA, Matthews DR, Dunger DB (1990) Failure of current insulin regimes to meet the overnight requirements of adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes Res 15:109–112
Edge JA, Harris DA, Phillips PA, Pal BR, Matthews DR, Dunger DB (1993) Evidence for a role for insulin and growth hormone in overnight regulation of 3-hydroxybutyrate in normal and diabetic adolescents. Diabetes Care 16: 1011–1018
Knip M, Ilonen J, Mustonen A, Åkerblom HK (1986) Evidence of an accelerated B-cell destruction in HLA-Dw3/Dw4 heterozygous children with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 29:347–351
Sochett EB, Daneman D, Clarson C, Ehrlich RM (1987) Factors affecting and patterns of residual insulin secretion during the first year of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in children. Diabetologia 30:453–459
Wallensteen M, Dahlquist G, Persson B et al. (1988) Factors influencing the magnitude, duration, and rate of fall of B-cell function in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children followed for two years from their clinical diagnosis. Diabetologia 31:664–669
Simell T, Kaprio E, Mäenpää J, Tuominen J, Simell O (1991) Randomised prospective study of short-term and long-term initial stay in hospital by children with diabetes mellitus. Lancet 337:656–660
Francis AJ, Hanning I, Alberti KGMM (1985) The effect of mixing human soluble and human crystalline zinc-suspension insulin: plasma insulin and blood glucose profiles after subcutaneous injection. Diabet Med 2:177–180
Koivisto VA (1985) Various influences on insulin absorption. Neth J Med 28 [Suppl 1]:25–28
Wether GA (1985) Insulin. In: Baum JD, Kinmonth A-L (eds) Care of the child with diabetes. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 64–84
Bolli GB (1989) The pharmacokinetic basis of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 6:S3-S16
Tunbridge FKE, Newens A, Home PD et al. (1989) Double-blind crossover trial of isophane (NPH)- and lentebased insulin regimens. Diabetes Care 12:115–119
Henriksen JE, Djurhuus MS, Vaag A et al. (1993) Impact of injection sites for soluble insulin on glycaemic control in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients treated with a multiple insulin injection regimen. Diabetologia 36:752–758
Amiel SA, Sherwin RS, Simonson DC, Lauritano AA, Tamborlane WV (1986) Impaired insulin action in puberty. A contributing factor to poor glycemic control in adolescents with diabetes. N Engl J Med 315:215–219
Rosenbloom AL, Giordano BP (1977) Chronic overtreatment with insulin in children and adolescents. Am J Dis Child 131:881–885
Simell T, Simell O, Lammi E-M et al. (1993) Glucose profiles in children two years after the onset of type diabetes. Diabet Med 10:524–529
Robert JJ, Deschamps I, Chevenne D, Roger M, Mogenet A, Boitard C (1991) Relationship between first-phase insulin secretion and age, HLA, islet cell antibody status, and development of type I diabetes in 220 juvenile first-degree relatives of diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 14:718–723
Skor DA, White NH, Thomas L, Santiago JV (1985) Influence of growth hormone on overnight insulin requirements in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 34:135–139
Parillo M, Mura A, Iovine C, Rivellese AA, Iavicoli M, Riccardi G (1992) Prevention of early-morning hyperglycemia in IDDM patients with long-acting zinc insulin. Diabetes Care 15:173–177
Yki-Järvinen H, Koivisto VA (1986) Natural course of insulin resistance in type I diabetes. N Engl J Med 315:224–230
Berger M (1989) Towards more physiological insulin therapy in the 1990s. A Comment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 6: S25-S31
Yki-Järvinen H, Helve E, Koivisto VA (1987) Hyperglycemia decreases glucose uptake in type I diabetes. Diabetes 36:892–896
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simell, T., Mäenpää, J., Kaprio, E.A. et al. Serum insulin profiles in consecutive children 2 years after the diagnosis of IDDM. Diabetologia 38, 97–105 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02369358
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02369358