Summary
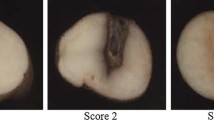
Tubers of clones from a diploid hybrid population ofSolanum phureja andS. stenotomum were screened for resistance to tuber soft rot caused by strains ofErwinia carotovora subsp.atroseptica (Eca),E. carotovora subsp.carotovora (Ecc) andE. chrysanthemi (Ech). Significant, positive correlations between resistance to the different strains and species were observed, indicating that screening for resistance to tuber soft rot could be accomplished by using just one of the three pathogens. Strains of Ecc and Ech were found to be much more virulent than strains of Eca. Inoculating with Ecc and Ech resulted in more distinct differences among susceptible, moderately resistant and resistant clones than inoculating with Eca.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, S., E. Lojkowska, M.K. Ehlenfeldt, A. Kelman & J.P. Helgeson, 1988. Fertile interspecific somatic hybrids ofSolanum: A novel source of resistance toErwinia soft rot.Phytopathology 78:1216–1220.
Bång, H., 1989. Prevalence ofErwinia species in basic seed lots of potatoes grown in Sweden.Acta Agricicultura Scandinvia 39:373–379.
DeBoer, S.H. & A. Kelman, 1975. Evaluation of procedures for detection of pectolyticErwinia species on potato tubers.American Potato Journal 52:117–124.
Elphinstone, J.G., 1987. Soft rot and blackleg of potato:Erwinia spp.Technical Information Bulletin 21. International Potato Center, Lima, Peru. 18pp.
Hidalgo, O.A. & E. Echandi, 1982. Evaluation of potato clones for resistance to tuber and stem rot induced byErwinia chrysanthemi.American Potato Journal 59:585–592.
Hidalgo, O.A. & E. Echandi, 1983. Influence of temperature and length of storage on resistance of potato to tuber rot induced byErwinia chrysanthemi.American Potato Journal 60:1–15.
Lapwood D.H., P.J. Read & J. Spokes, 1984. Methods for assessing the susceptibility of potato tubers of different cultivars to rotting byErwinia carotovora subsp.atroseptica andcarotovora.Plant Pathology 33:13–20.
Maher, E.A., S.H. DeBoer & A. Kelman, 1986. Serogroups ofErwinia carotovora involved in systemic infection of potato plants and infestation of progeny tubers.American Potato Journal 63:1–11.
Michalik, B., P.W. Simon & W.H. Gabelman, 1992. Assessing susceptibility of carrot roots to bacterial soft rot.HortScience 27:1020–1022.
Pérombelon, M.C.M. & A. Kelman, 1980. Ecology of the soft rot Erwinias.Annual Review of Phytopathology 18:61–87.
Powelson, M.L. & J.D. Apple, 1986. Potato blackleg in progeny plantings from diseased and symptomless parent plants.Phytopathology 76:56–60.
Tzeng, K.C., R.G. McGuire & A. Kelman, 1990. Resistance of tubers from different potato cultivars to soft rot caused byErwinia carotovora subsp.atroseptica.American Potato Journal 67:287–305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolters, P.J., Collins, W.W. Evaluation of diploid potato clones for resistance to tuber soft rot induced by strains ofErwinia carotovora subsp.atroseptica, E. carotovora subsp.carotovora andE. chrysanthemi . Potato Res 37, 143–149 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02358715
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02358715