Abstract
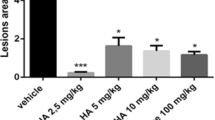
We investigated the therapeutic effects of egualen sodium (KT1-32), a new antiulcer agent, on chronic erosive and atrophic gastritis induced by 5 months' administration of sodium taurocholate (TCA; 5 mM) in rats. The chronic gastritis was manifested by mucosal surface injuries (erosions), reduced mucosal thickness, reduction of the number of parietal cells, infiltration of inflammatory cells, and proliferation of collagenous fiber. Egualen sodium, (10–100 mg/kg, t.i.d) administered orally to the rats for 2 weeks after the withdrawal of TCA, dose-dependently and significantly decreased the total length of erosions. The indicators of atrophic gastritis, i.e., reduced mucosal thickness and reduction in the number of parietal cells, were improved dose-dependently by the administration of this agent. Egualen sodium also reduced the inflammatory cell infiltration and the proliferation of collagenous fiber in the gastric mucosa in a dose-dependent manner. The reduced staining of neutral gastric mucus was improved by a high dose (100 mg/kg) of egualen sodium. The therapeutic effects of egualen sodium on experimental gastritis were superior to those of sofalcone and sodium guaiazulene 3-sulfonate. These results suggest that egualen sodium may be a promising agent for the treatment of erosive and atrophic gastritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okabe S, Takeuchi K, Mori Y, et al. Effects of KT1-32 on acute gastric lesions and duodenal ulcers induced in rats (in Japanese with English abstract). Folia Pharmacol Jpn 1986;88:467–476.
Rogers C, Brown A, Szabo S. Gastric mucosal protection by new aryl sulfhydryl drugs. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33:324–329.
Mochizuki S, Wakabayashi S, Matsumoto M, et al. Protective effect of azuletil sodium (KT1-32) on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 1991;55(Suppl I):387.
Wakabayashi S, Mochizuki S, Kosakai K, et al. Healing promoting effect of azuletil sodium (KT1-32) on experimental chronic gastric ulcers and acceleration of healing in SPF environment (in Japanese with English abstract). Folia Pharmacol Jpn 1991; 97:105–113.
Yano S, Horie S, Wakabayashi S, et al. Increasing effect of sodium 3-ethyl-7-isopropyl-1-azulenesulfonate 1/3 hydrate (KT1-32), a novel antiulcer agent, on gastric mucosal blood flow in anesthetized rats. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 1990;70(2):253–256.
Mochizuki S, Wakabayashi S, Tomiyama A, et al. Thromboxane A2 antagonistic action of a new anti-ulcer agent, azuletil sodium (KT1-32). Scand J Gastroenterol 1989;24(Suppl 162):194–197.
Peskar BM, Trautmann M, Szabo S. Gastric mucosal protection and inhibition of leukotriene C4 formation by egualen sodium in rats. Gastroenterology 1991;100: A139.
Yanagisawa T, Wakabayashi S, Tomiyama T, et al. Synthesis and anti-ulcer activities of sodium alkylazulene sulfonates. Chem Pharm Bull 1988;36:641–647.
Mackman S, Lemmer KE, Morrissey JF. Postoperative reflux alkali gastritis and esophagitis. Am J Surg 1971;121:694–697.
Van Heerden JA, Philips SF, Adson MA, et al. Postoperative reflux alkali gastritis and esophagitis. Am J Surg 1975;129:82–87.
Davenport HW. Effect of lysolecithin, digitonin and phospholipase A upon the dog's gastric mucosal barrier. Gastroenterology 1970;59:505–509.
Black RB, Hole D, Rhodes J. Bile damage to the gastric mucosal barrier: The influence of pH and bile acid concentration. Gastroenterology 1971;61:178–184.
Stern AI, Hogan DL, Isenberg JI. Effect of sodium taurocholate on human gastric mucosa at acid and neutral pHs. Gastroenterology 1984;87:1272–1276.
Kishimoto S, Ogawa M, Takaba N, et al. Experimental model of gastritis induced by sodium taurocholate in rat. Hiroshima J Med Sci 1986;35:143–147.
Kishimoto S, Kosaka T, Takaba N, et al. Experimental gastritis and sofalcone. Part 1. Therapeutic effect on gastritis after 6 months of treatment with sodium salt of taurocholic acid (in Japanese with English abstract). Jpn Arch Int Med 1986;33:291–299.
Kishimoto S, Kobuke H, Kobayashi H, et al. Treatment of established taurocholate-induced chronic erosive gastritis in rats with cimetidine. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 1991;71:273–292.
Glass GB, Pitchumoni CS, Atrophic gastritis. Structural and ultrastructural alterations, exfoliative cytology and enzyme cytochemistry and histochemistry, proliferation kinetics, immunological derangements and other causes and clinical associations and sequellae. Hum Pathol 1975;6:219–250.
Morson BC, Dawson IMP. Chronic atrophic gastritis. In: Morson BC (ed) Gastrointestinal pathology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific, 1979;99–101.
Szabo S, Trier JS, Frankel PW. Sulfhydryl compounds may mediate gastric cytoprotection. Science 1981;214:200–202.
Szabo S, Hollander D. Pathways of gastrointestinal protection and repair. Mechanisms of action of sucralfate. Am J Med 1989;86(Suppl. 6A):23–31.
Calcamuggi G, Lanzio M, Babini G, et al. Sodium taurocholate affects prostacyclin constitutive production by cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Lab Clin Med 1990;115:756–760.
Whittle BJR, Kauffman GL, Moncada S. Vasoconstriction with thromboxane A2 induces ulceration of the gastric mucosa. Nature 1981;292:472–474.
Esplugues JV, Whittle BJR. Close-arterial administration of the thromboxane mimetic U-46619 induces damage to the rat gastric mucosa. Prostaglandins 1988;35:137–148.
Johnson LR. Gut hormones on growth of gastrointestinal mucosa. In: Chey NY, Brooks FP (eds) Endocrinology of the gut. London: Charles B Slack, 1964;163–177.
Robert A. Cytoprotection by prostaglandins. Gastroenterology 1979;77:761–767.
Muramatsu M, Tanaka M, Suwa T, et al. Effect of 2′-carboxymethoxy-4.4′-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyloxy) chalcone (SU-88) on prostaglandin metabolism in hog gastric mucosa. Biochem Pharmacol 1984;33:2629–2633.
Williams TJ, Morley J. Prostaglandins as potentiators of increased vascular permeability. Nature 1973;246:215–217.
Williams TJ, Peck MJ. Role of prostaglandin—mediated vasodilatation in inflammation. Nature 1977;270:530–532.
Till G, Kownatzki E, Seitz M. et al. Chemokinetic and chemotactic activity of various prostaglandins for neutrophil granulocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1979;12:111–118.
Rabson AR, Anderson R, Lomnitzer R, et al. In vitro effects of prostaglandins on polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. S Afr Med J 1974;48(Suppl):44–50.
Kaley G, Weiner R. Prostaglandin E1: A potential mediator of the inflammatory response. Ann NY Acad Sci 1971;180:338–350.
Kitchen EA, Boot JR, Dawson W. Chemotactic activity of thromboxane B2, prostaglandin and their metabolites for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Prostaglandins 1978;16:239–244.
Mizumachi S, Takeuchi K, Matsuda K, et al. Histological and functional studies of experimental gastritis in rats (in Japanese with English abstract). Jpn J Gastroenterol 1986;83:7–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, S., Matsumoto, M., Wakabayashi, S. et al. Therapeutic effect of egualen sodium (KT1-32), a new antiulcer agent, on chronic gastritis induced by sodium taurocholate in rats. J Gastroenterol 31, 785–792 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02358603
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02358603