Abstract
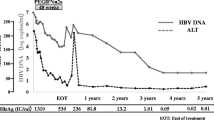
Intermittent interferon (IFN) therapy appears to be effective for patients with e-antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B who exhibit abnormal fluctuations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and histological evidence of disease progression. To determine the optimal dose of IFN in such patients, we studied the effects of natural IFN-β in a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial in 36 patients with e-antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B who repeatedly demonstrated abnormal fluctuations in ALT levels. Thirty-six patients were randomly assigned to three groups, receiving doses of: 0.3 MIU IFN (group 1;n=12), 1 MIU (group 2;n=12), or 3 MIU (group 3;n=12), administered twice per week for 24 weeks. Patients were regarded as responders if ALT levels remained within the normal range and HBV-DNA tested negative for 6 months after the initiation of the therapy. According to this criterion, treatment was effective in 16.7% of the patients (2/12) in group 1, 33.3% (4/12) in group 2, and 75% (9/12) in group 3, the efficacy rate in group 3 being significantly higher than that in the other two groups. However, in 12 of the 15 responders, (80%) ALT levels were frequently elevated again within 3 years of the termination of IFN therapy. Although IFN was effective in controling the manifestations of hepatitis in terms of e-antigen-negative patients who exhibited abnormal fluctuations in ALT, it appears that continuous treatment with intermittent high-dose IFN is necessary to maintain ALT levels within the normal range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Realdi G, Alberti A, Rugge M, et al. Sero-conversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 1980;79:195–199.
Hoofnagle JH, Dusheiko GM, Seeff LB, et al. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody in chronic type B hepatitis. Ann Intern Med 1981;94:744–748.
Bonino F, Rosina F, Rizzetto M, et al. Chronic hepatitis in HBs Ag carriers with serum HBV-DNA and anti HBe. Gastroenterology 1986;90:1268–1273.
Fattovich G, Rugge M, Brollo L, et al. Clinical virologic and histologic outcome following seroconversion from HBeAg to anti HBe in chronic hepatitis Type B. Hepatology 1986;6:167–172.
Fattovich G, Brollo L, Albert A, et al. Long-term follow up of anti HBe-positive chronic active hepatitis B. Hepatology 1988;8(6):1651–1654.
Rossana M, Oliveri F, Rocca G, et al. Natural course and response to interferon of chronic hepatitis B accompanied by antibody to hepatitis B e antigen. Hepatology 1989;10:198–202.
Rossana M, Giarim M, Saracco G, et al. Hepatitis B virus unable to secrete e antigen and response to interferon in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 1993;105:845–850.
Pastore G, Santonio T, Milella M, et al. Anti-HBe-positive chronic hepatitis B with HBV-DNA in the serum: Response to a 6-month course of lymphoblastoid interferon. J Hepatol 1992; 14:221–225.
Fattovich G, Rugge M, Brollo L, et al. A randomized controlled trial of lymphoblastoid interferon-alpha in patients with chronic hepatitis B lacking HBe Ag. Hepatology 1992;15:584–589.
Alberti A, Pontisso P, Fattovich G, et al. Changes in serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA positivity in chronic infection: Results of a long-term follow-up study of 138 patients. J Infect Dis 1986;154:562–569.
Pasek M, Goto T, Gilbert W, et al. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression inE. coli. Nature 1979;317:489–495.
Tiollaris P, Porcel C, Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature 1985;317:575–579.
Bianchi L, De Croote J, Desmet VJ, et al. Acute and chronic hepatitis revisited. Lancet 1977;II:914–919.
Dixon WJ, Brown MB, Engelman L, et al. BMDP statistical software. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1985.
Carman WF, Jacyna MR, Hadziyannis S, et al. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet 1980:588–590.
Brunetto MR, Stemler M, Schodel F, et al. Identification of HBV variants which cannot produce precore-derived HBeAg and may be responsible for severe hepatitis. Ital J Gastroenterol 1989; 21:151–154.
Foster GR, Carman WF, Thomas HC, et al. Replication of hepatitis B and delta viruses: Appearance of viral mutant. Semin Liver Dis 1991;11:121–127.
Bonino F, Brunetto MR, Rizzetto M, et al. Hepatitis B virus unable to secrete e antigen. Gastroenterology 1991;100:1138–1141.
Brunetto MR, Giarin MM, Oliveri F, et al. Wild type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of chronic hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991;88:4186–4190.
Arase Y, Kumada H, Ikeda K, et al. Retrospective analysis of the histological course by use of GPT integration value in anti-HBe positive cases with abnormal GPT. Jpn J Gastroenterology 1988; 85:871–875.
Arase Y, Kumada H, Ikeda K, et al. Interferon therapy in chronic type B hepatitis, defined as anti-HBe-positive chronic liver disease with elevated transaminase. Acta Hepat Jap 1990;31:504–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arase, Y., Chayama, K., Tsubota, A. et al. A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of natural interferon-β therapy for e-antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with abnormal transaminase levels. J Gastroenterol 31, 559–564 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02355057
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02355057