Abstract
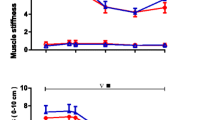
To provide basic data for serum HA research in joint diseases, we attempted to determine whether there was any characteristic diurnal variation in serum hyaluronate (HA) levels in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA). We studied diurnal variations in the serum concentration of HA in 25 female patients, 16 with RA and 9 with OA. In the RA patients serum HA concentration was higher during the day and lower at night. We found no significant diurnal variation in the OA patients. In the RA patients, the variation was not as marked in patients who exhibited severe joint contracture and mobility disturbances as in patients who had preserved joint mobility and who showed sufficient functional capacity. Contracture of the joint, that is, pathologic immobilization, is thought to be one cause of the loss of variation in serum HA in RA patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 Revised Criteria for the Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:315–24.
Bellamy N, Sothern RB, Campbell J, et al. Circadian rhythm in pain, stiffness, and manual dexterity in rheumatoid arthritis: Relation between discomfort and disability. Ann Rheum Dis 1991;50:243–8.
Dahl IMS, Husby G. Hyaluronic acid production in vitro by synovial lining cells from normal and rheumatoid joints. Ann Rheum Dis 1985;44:647–57.
Engström-Laurent A, Lööf L, Nyberg A, et al. Increased serum levels of hyaluronate in liver disease. Hepatology 1985;5:638–42.
Engström-Laurent A, Hällgren R. Circulating hyaluronate in rheumatoid arthritis: Relationship to inflammatory activity and the effect of corticosteroid therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 1985;44:83–8.
Engström-Laurent A, Felterius N, Felterius N, Hällgren R, et al. Raised serum hyaluronate levels in scleroderma: an effect of growth factor induced activation of connective tissue cells? Ann Rheum Dis 1985;44:614–20.
Engström-Laurent A, Laurent UBG, Laurent KL. Concentration of sodium hyaluronate in serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1985;45:497–504.
Engström-Laurent A, Hällgren R. Circulating hyaluronic acid levels vary with physical activity in healthy subjects and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 1987;30:1333–8.
Fraser JRE, Laurent TC, Pertoft H, et al. Plasma clearance, tissue distribution and metabolism of hyaluronic injected intravenously in the rabbit. Biochem J 1981;200:415–24.
Frébourg T, Delpech B, Bercoff E, et al. Serum hyaluronate in liver diseases: Study by enzymoimmunological assay. Hepatology 1986;6:392–5.
Harkness JAL, Richter MB, Panayi GS, et al. Circadian variation in disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 1982;284:551–4.
Konttinen YT, Michelsson L-E, Grönblad M, et al. Plasma hyaluronan levels in rabbit immobilization osteoarthritis: Effect of remobilization. Scand J Rheumatol 1991;20:392–6.
Kowanko IC, Powanall R, Knapp MS, et al. Circadian variation in the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and in the therapeutic effectiveness of flurbiprofen at different times of day. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1981;11:477–84.
Lansbury J, Methods for evaluating rheumatoid arthritis. In: Hollander JL. Arthritis and allied conditions. 7th ed.. Philadelphia; Lea and Febiger, 1966:269–97.
Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M, et al. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn 1977;18:481–91.
Laurent UBG, Tengblad A. Determination of hyaluronate in biological samples by a specific radioassay technique. Anal Biochem 1980;109:386–94.
Levesque H, Delpech B, Le loet X, et al. Serum hyaluronate in rheumatoid arthritis: Study by affino-immunoenzymatic assay. Br J Rheumatol 1988;27:445–9.
McCarty DJ. Arthritis and allied conditions. 11th ed. Philadelphia. Lea and Febiger, 1989:281–5.
Petersen I, Baatrup G, Brantslund I, et al. Circadian and diurnal variation of circulating immune complexes, complement-mediated solubilization, and the complement split product C3d in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 1986;15:113–8.
Seibel MJ, Raiman S, Segrias J, et al. Serum-Hyaluronsäure und amino-terminales Protokollagen-3-Peptid bei entzündlichen und degenerativen Gelenkenkrankungen. Z Rheumatol 1988;47:98–106.
Steinblocker O, Traeger CH, Batterman RC. Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 1949;140:659–62.
Tengblad A. Quantative analysis of hyaluronate in nanogram amounts. Biochem J 1980;185:101–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, A., Arai, M., Sato, K. et al. Diurnal variations of serum hyaluronate in rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Sci 1, 187–192 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349817
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349817