Abstract
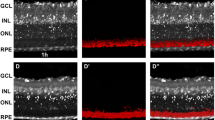
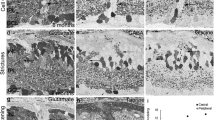
Changes in ultrastructure and DNA synthesis in retinal cells of prenatal and postnatal developing mice were investigated using electron microscopic radioautography after injection of tritiated thymidine. The labeled cells were located in the middle of the bipolar-photoreceptor layer. Major changes in DNA synthesis and morphology occurred in the first week after birth. Silver grains were observed over the nuclei and mitochondria. A marked difference between labeled and unlabeled cells was detected. The cell organelles were not well developed in the cytoplasm of labeled cells. However, well developed organelles including an intracellular membrane system were distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the unlabeled cells. The different types of cells could be distinguished except some labeled cells. From two weeks onward, the retina structurally matured with the disappearance of labeled cells. The results of this study suggest that cell differentiation in mouse retina is completed two weeks after birth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, R. andHatlee, M.: Plasticity and differentiation of embryonic retina cells after terminal mitosis.Nature,243, 391–393 (1989).
Arsenault, P. andMenard, D.: Autoradiographic localization of3H-thymidine incorporation in developing human esophagus.Anat. Rec. 220, 313–317 (1988).
Daun, H., Gao, F., Li, S. andNagata, T.: Postnatal development and aging of esophageal epithelium in mouse: a light and electron microscopic radioautographic study.Cell. Mol. Biol. 39, 309–316 (1993).
Gunarso, W.: Radioautographic studies on nucleic acid synthesis in the retina of chick embryo. 1. Light microscopic radioautography.Shinshu Med. J. 32, 231–240 (1984).
Gunarso, W.: Radioautographic studies on nucleic acid synthesis in the retina of chick embryo. 2. Electron microscopic radioautography.Shinshu Med. J. 32, 241–248 (1984).
Hanai, T.: Light microscopic radioautographic study of DNA synthesis in the kidneys of aging mice.Cell. Mol. Biol. 39, 81–92 (1993).
Ma, H. andNagata, T.: Electron microscopic radioautographic studies on DNA synthesis in the hepatocytes of aging mice as observed by image analysis.Cell. Mol. Biol. 36, 73–84 (1990).
Messier, B. andLeblond, C.P.: Cell differentiation and migration as revealed by radioautography after injection of3H-thymidine into male rats and mice.Am. J. Anat. 106, 247–258 (1960).
Nagata, T. andUsuda, N.: Studies on the nucleic acid synthesis in pancreatic acinar cells of aging mice by means of electron microscopic radioautography.J. Clin. Electron Microsc. 19, 486–487 (1986).
Olea, M.T. andNagata, T.: Simultaneous localization of3H-thymidine incorporation and acid phosphatase activity in mouse spleen: EM radioautography and cytochemistry.Cell. Mol. Biol. 38, 115–122 (1992).
Silver, J.: A study of ocular morphogenesis in the rat using3H-thymidine autoradiography: evidence for thymidine recycling in the developing retina.Dev. Biol. 49, 487–495 (1976).
Gao, F., Toriyama, K. andNagata, T.: Light microscopic radioautographic study on the DNA synthesis of prenatal and postnatal aging mouse retina after labeled thymidine injection.Cell. Mol. Biol. 38, 661–668 (1992).
Kong, Y.: Electron microscopic radioautographic study on DNA synthesis in prenatal mouse retina.Cell. Mol. Biol. 39, 55–64 (1993).
Kong, Y., Usuda, N. andNagata, T.: Radioautographic study on DNA synthesis of the retina and retina pigment epithelium of developing mouse embryo.Cell. Mol. Biol. 38, 263–272 (1992).
Young, R.W.: Cell differentiation in the retina of the mouse.Anat. Rec. 212, 199–205 (1985).
Nagata, T.: Radiolabeling of soluble and insoluble compounds as demonstrated by light and electron microscopy.In: Recent Advances in Cellular and Molecular Biology (Wegmann, R.J. andWegmann, M.A. ed.), p. 9–21, Peeters Press, Leuven, 1992.
Tripathi, B.J., Tripathi, R.C., Living, A.M. andBorisuth, N.S.C.: The role of the growth factors in the embryogenesis and differentiation of the eye.Am. J. Anat. 192, 443–447 (1991).
Sidman, R.L.: Histogenesis of mouse retina studied with thymidine-3H.In The Structure of the Eye (Smelzer, G.K. ed.), p. 487–550, Academic Press, New York, 1961.
Mishima, H. andFujita, H.: Studies on the cytodifferentiation of the neuroblast and visual cells in the chick embryo retina using electron microscopic autoradiography of3H-thymidine.Ophthalmologie,260, 1–10 (1978).
Carter-Dawson, L.D. andLavail, M.M.: Rods and cones in the mouse retina: autoradiographic analysis of cell generation using tritiated thymidine.J. Comp. Neurol. 188, 263–272 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Toriyama, K. & Nagata, T. Electron microscopic radioautographic study on the DNA synthesis of aging mouse retina. Med Electron Microsc 26, 177–184 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347997
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347997