Abstract
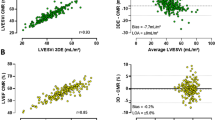
Two-dimensional echocardiography (2DE) performed during flights with a parabolic trajectory to simulate weightlessness provides a unique means to study left ventricular (LV) modifications to prevent post-flight orthostatic intolerance in astronauts. However, conventional analysis of 2DE is based on manual tracings and depends on experience. Accordingly, the aim was objectively to quantify, from 2DE images, the LV modifications related to different gravity levels, by applying a semi-automated level-set border detection technique. The algorithm validation was performed by the comparison of manual tracing results, obtained by two independent observers with 20 images, with the semi-automated measurements. To quantify LV modifications, three consecutive cardiac cycles were analysed for each gravity phase (1 Gz, 1.8 Gz, 0 Gz). The level-set procedure was applied frame-by-frame to detect the LV endocardial contours and obtain LV area against time curves, from which end-diastolic (EDA) and end-systolic (ESA) areas were computed and averaged to compensate for respiratory variations. Linear regression (y=0.91x+1.47, r=0.99, SEE:0.80 cm2) and Bland-Altman analysis (bias=−0.58 cm2, 95% limits of agreement=±2.14 cm2) showed excellent correlation between the semi-automatic and manually traced values. Inter-observer variability was 5.4%, and the inter-technique variability was 4.1%. Modifications in LV dimensions during the parabola were found: compared with 1 Gz values, EDA and ESA were significantly reduced at 1.8 Gz by 8.8±5.5% and 12.1±10.1%, respectively, whereas, during 0 Gz, EDA and ESA increased by 13.3±7.3% and 11.6±5.1%, respectively, owing to abrupt changes in venous return. The proposed method resulted in fast and reliable estimations of LV dimensions, whose changes caused by different gravity conditions were objectively quantified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., andSethian, J. A. (1994): ‘A fast level-set method for propagating interfaces’,J. Comp. Phys.,112, pp. 334–363
Angelini, E. D., Laine, A. F., Takuma, S., Holmes, J. W., andHomma, S. (2001): LV volume quantification via spatiotemporal analysis of real-time 3-D echocardiography’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging,20, pp. 457–469
Ashton, E. A., andParker, K. J. (1999): ‘Multiple resolution bayesian segmentation of ultrasound images’,Ultrason. Imag.,17, pp. 291–304
Bailliart, O., Capderou, A., Cholley, B., Kays, C., Techoueyeres, P., Lachaud, J. L., andVaida, P. (1998): ‘Changes in lower limb volume in humans during parabolic flights’,J. Appl. Physiol.,85, pp. 2100–2105
Belogay, E., Cabrelli, C., Molter, U., andShonkwiler, R. (1997): ‘Calculating the Hausdorff distance between curves’,Inform. Process. Lett.,64, pp. 17–22
Bland, J. M., andAltman, D. G. (1986): ‘Statistical method for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement’,The Lancet,1, pp. 307–310
Boukerroui, D., Baskurt, A., Noble, J. A., andBasset, O. (2003): ‘Segmentation of ultrasound images—multiresolution 2D and 3d algorithm based on global and local statistics’,Pattern Recognit. Lett.,24, pp. 779–790
Caiani, E. G., Porta, A., Baselli, G., Turiel, M., Muzzupappa, S., Pagani, M., Malliani, A., andCerrutti, S. (2002). “Analysis of left ventricular volume based on time warping averaging’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,40, pp. 225–233
Coppini, G., Poli, R., andValli, G. (1995): ‘Recovery of 3-D shape of the left ventricle from echocardiographic images,’IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging,14 pp. 301–317
Corsi, C., Borsari, M., Sarti, A., Lamberti, C., Travaglini, A., Shiota, T., andThomas, J. D. (2001): ‘Left ventricular endocardial surface detection based on real time 3D echocardiographic data’,Eur. J. Ultrasound,13, pp. 41–51
Corsi, C., Saracino, G., Sarti, A., andLamberti, C. (2002): ‘Left ventricular volume estimation for real-time-dimensional echocardiography’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging,21, pp. 1202–1208
Feng, J., Lin, W., andChen, C. (1991): ‘Epicardial boundary detection using fuzzy reasoning’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging.,10, pp. 187–199
Guell, A., andBraak, L. (1989): ‘Cardiovascular deconditioning syndrome during space flight’,Ann. Cardiol. Angiol.,38, pp. 499–502
Herlin, L., Bereziat, D., Giraudon, G., Nguyen, C., andGraffigne, C. (1994a): ‘Comparison of different Markov random fields model for segmenting echocardiographic images’. Research report, INRIA.
Herlin, L., Bereziat, D., Giraudon, G., Nguyen, C., andGraffigne, C. (1994b): ‘Segmentation of echocardiographic images with Markov fields’,Proc. Eur. Conf. Computer Vision, pp. 201–206
Huttenlocher, D. P., Klanderman, G. A., andRucklidge, W. J. (1993): ‘Comparing images using the Hausdorff distance’,IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,15, pp. 850–863
Johns, J. P., Vernalis, M. N., White, C. D., Karemaker, J. M., andLatham, R. D. (1992): ‘Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac function during parabolic flight’,Physiologist,35, pp. S117-S118
Johns, J. P., Vernalis, M. N., Karemaker, J. M., andLatham, R. D. (1994): ‘Doppler evaluation of cardiac filling and ejection properties in humans during parabolic flight’,J. Appl. Physiol.,76, pp. 2621–2626
Kotropoulos, C., Magnisalis, X., Pitas, I., andStrintzis, M. G. (1994): ‘Nonlinear ultrasonic image processing based on signaladaptive filters and self-organizing neural networks’,IEEE Trans. Image Process,3, pp. 65–77
Lathers, C. M. Charles, J. B., Elton, K. F., Holt, T. A., Mukal, C. N., Bennet, B. S., andBungo, M. W. (1989): ‘Acute hemodynamic responses to weightlessness in humans’,J. Clin. Pharmacol.,29, pp. 615–627
Malladi, R., Sethian, J. A., andVemuri, B. C. (1995): ‘Shape modeling with front propagation: a level-set approach’,IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,17, pp. 158–175
Martin, D. S., South, D. A., Garcia, K. M., andArbeille, P. (2003): ‘Ultrasound in space’,Ultrasound Med. Biol.,29, pp. 1–12
Morel, J. M., andSolimini, S. (1995): ‘Varational methods in image segmentation’, in Progress in nonlinear differential equation and their applications’, Vol. 14 (Birkauser, Boston, 1995)
Mukai, C. N., Lathers, C. M., Charles, J. B., andBennet, B. S. (1994): ‘Cardiovascular responses to repetitive exposure to hyperand hypo-gravity states produced by parabolic flights’,J. Clin. Pharmacol.,34, pp. 472–479
Mulet-Parada, M., andNoble, J. A. (2000): ‘2D+T acoustic boundary detection in echocardiography’,Med. Image Anal.,4, pp. 21–30
Nicogossian, A. E., Huntoon, C. L., andPool, S. L. (1994): ‘Space physiology and medicine’ (Lea and Febiger, Malvern, PA, 1994)
Norsk, P., Foldager, N., Bonde-Petersen, F., Elmann-Larsen, B., andJohansen, T. S. (1987): ‘Central venous pressure in humans during short periods of weightlessness’,J. Appl. Physiol.,63, pp. 2433–2437
Osher, S., andSethian, J. A. (1988): ‘Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithm based on Hamilton Jacobi formulation’,J. Comp. Phys.,79, pp. 12–49
Papademetris, X., Sinusas, A. J., Dione, D. P., andDuncan, J. S. (2001): ‘Estimation of 3D left ventricular deformation from echocardiography’Med. Image Anal.,5, pp. 17–28
Perona, P., andMalik, J. (1990): ‘Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion’,IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,12, pp. 629–639
Picano, E., Lattanzi, F., Orlandini, A., Marini, C., L'Abbate, A. (1991): ‘Stress echocardiography and the human factor: the importance of being expert’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,17, pp. 666–669
Popp, R. L., Agaston, A., Armstrong, W. F., Nanda, N. C., Pearlman, A., Rakowski Seward, J. B., Silverman, N. H., Smith, M., Stewart, W. J., Taylor, R., Thys, D., andDavis, C. (1998): ‘Recommendations for training in performance and interpretation of stress echocardiography’,J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr.,11, pp. 95–96
Sanchez-Ortiz, G. I., Wright, G. J. T., Clarke, N., Declerck, J., Banning, A., andNoble, J. A. (2002): ‘Automated 3D echocardiography analysis compared with manual delineation and MUGA’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging,21, pp. 1069–1076
Sarti, A., Malladi, R., andLamberti, C. (2002): ‘A geometric level-set model for ultrasound analysis’, in ‘Geometric methods in bio-medical image processing’ (Springer, 2002), pp. 43–61
Satarehdan, S. K., andSoraghan, J. J. (1999): ‘Automatic cardiac LV boundary detection and tracking using hybrid fuzzy temporal and fuzzy multiscale edge detection’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,46, pp. 1364–1378
Sethian, J. A. (1999): ‘Level set methods and fast marching methods’ (Cambridge University Press, 1999)
Videbaek, R., andNorsk, P. (1997): ‘Atrial distension in humans during weightlessness induced by parabolic flights’,J. Appl. Physiol.,83, pp. 1862–1866
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corsi, C., Lamberti, C., Cerutti, S. et al. Quantification of left ventricular modification in weightlessness conditions from the spatio-temporal analysis of 2D echocardiographic images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 610–617 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347542
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347542