Abstract
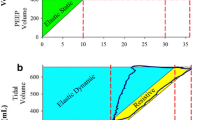
The regulation of cerebral blood flow (CBF) following changes in arterial blood pressure (ABP) and end-tidal pCO2 (EtCO2) are of clinical interest in assessing cerebrovascular reserve capacity. Linear finite-impulse-response modelling is applied to ABP, EtCO2 and CBF velocity (CBFV, from transcranial Doppler measurements), which allows the CBFV response to ideal step changes in EtCO2 to be estimated from clinical data showing more sluggish, and additional random variations. The confounding effects of ABP changes provoked by hypercapnia on the CBFV are also corrected for. Data from 56 patients suffering from stenosis of the carotid arteries (with normal or diminished cerebrovascular reactivity to EtCO2 changes—CVRCO 2 were analysed. The results show the expected significant differences (p<0.05) between EtCO2 steps up and down, the significant contribution from ABP variation, and also differences in the dynamic responses of patients with reduced CVRCO 2 (p<0.01 after 10 s). For the latter the CBFV response appears exhausted after about 15s, whereas for normals CBFV continues to increase. While dispersion of individual step responses remains large, the method gives encouraging results for the non-invasive study of compromised haemodynamics in different patient groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaseid, R., Lindegaard, K.-F., Sorteberg, W., andNornes, H. (1989): ‘Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in humans’,Stroke,20, pp. 45–52
Birch, A. A., Dirnhuber, M. J., Hartley-Davies, R., Iannotti, F., andNeil-Dwyer, G. (1995): ‘Assessment of autoregulation by means of periodic changes in blood pressure,Stroke,26, pp. 834–837
Bishop, C. C. R., Powell, S., Rutt, D., andBrowse, N. L. (1986): ‘Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity: a validation study’,Stroke,17, pp. 913–915
Derdeyn, C. P., Grubb, R. L., andPowers, W. J. (1999): ‘Cerebral haemodynamic impairment: methods of measurement and association with stroke risk’,Neurology,53, pp. 251–259
Diehl, R. R., Linden, D., Lücke, D., andBerlit, P. (1995): ‘Phase relationship between cerebral blood flow velocity and blood pressure: a clinical test of autoregulation’,Stroke,26, pp. 1801–1804
Djurberg, H. G., Seed, R. F., Evans, D. A. P., Brohi, F. A., Pyper, D. L., Tjan, G. T., andAl Moutaery, K. R. (1998): ‘Lack of effect of CO2 on cerebral arterial diameter in man’,J. Clin. Anesth.,10, pp. 646–651
Dumville, J., Panerai, R. B., Lennard, N. S., Naylor, A. R., andEvans, D. H. (1998): ‘Can cerebrovascular reactivity be assessed without measuring blood pressure in patients with carotid artery disease?’,Stroke,29, pp. 968–974
Garnham, J., Panerai, R. B., Naylor, A. R., andEvans, D. H. (1999): ‘Cerebrovascular response to dynamic changes in pCO2’,Cerebrovasc. Dis.,9, pp. 146–151
Giller, C. A. (1990): ‘The frequency dependent behaviour of cerebral antoregulation’,Neurosurg.,27, pp. 362–368
Giller, C. A., Bowman, G., Dyer, H., Mootz, L., andKrippner, W. (1993): ‘Cerebral arterial diameter during changes in blood pressure and carbon dioxide during craniotomy’,Neurosurg.,32, pp. 737–741
Hetzel, A., Braune, S., Guschlbauer, G., andDohms, K. (1999): ‘CO2 reactivity testing without blood pressure monitoring?’Stroke,30, pp. 398–401
Hu, H.-H., Kuo, T. B.-J., Wong, W.-J., Luk, Y.-O., Chern, C.-M., Hsu, L.-C., andSheng, W.-Y. (1999): ‘Transfer function analysis of cerebral hemodynamics in patients with carotid stenosis’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,19, pp. 460–465
Kontos, H. (1989): ‘Validity of cerebral arterial blood flow calculations from velocity measurements’,Stroke,20, pp. 1–3
Markwalder, T.-M., Grolimund, P., Seiler, R. W., Roth, F., andAaslid, R. (1984): ‘Dependency of blood flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery on end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure—a transcranial Doppler study’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,4, pp. 368–372
Menke, J., Rabe, M. H., Bresser, B. W., Grohs, B., Schmitt, R. M., andJorch, G. (1993): ‘Simultaneous influence of blood pressure, PCO2, and PO2 on cerebral blood flow velocity in preterm infants of less than 33 weeks gestation’,Pediatr. Res.,34, pp. 173–177
Naylor, A. R., Merric, M. V., Gillespie, I., Sandercock, P. A. G., Warlow, C. P., Cull, R. E., Griffin, T. M. G., andRuckley, C. V. (1994): ‘Prevalence of impaired cerebrovascular reserve in patients with symptomatic carotid artery disease’,Br. J. Surg.,81, pp. 45–48
Newell, D. W., Aaslid, R., Lam, A., Mayberg, T. S., andWinn, H. R. (1994): ‘Comparison of flow and velocity during dynamic autoregulation testing in humans’,Stroke,25, pp. 793–797
Panerai, R. B. (1998): ‘Assessment of cerebral pressure autoregulation in humans—a review of measurement methods’,Physiol. Meas.,19, pp. 305–338
Panerai, R. B., Kelsall, W. R., Rennie, J. M., andEvans, D. H. (1995): ‘Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in premature newborns’,Stroke,26, pp. 74–80
Panerai, R. B., Kelsall, A. W. R., Rennie, J. M., andEvans, D. H. (1996): ‘Analysis of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in neonates’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,BME-43, pp. 779–788
Panerai, R. B., Rennie, J. M., Kelsall, A. W. R., andEvans, D. H. (1996): ‘Frequency-domain analysis of cerebral autoregulation from spontaneous fluctuations in arterial blood pressure’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,36, pp. 315–322
Panerai, R. B., Simpson, D. M., Deverson, S. T., Mahoney, P., Hayes, P., andEvans, D. H. (2000): ‘Multivariate dynamic analysis of cerebral blood flow regulation in humans’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,BME-47, pp. 419–423
Poulin, M. J., Liang, P.-J., andRobbins, P. A. (1996): ‘Dynamics of the cerebral blood flow response to step changes in end-tidal PCO2 and PO2 in humans’,J. Appl. Physiol.,81, pp. 1084–1095
Ringelstein, E. B., Sievers, C., Ecker, S., Schneider, P. A., andOtis, S. M. (1988): ‘Noninvasive Assessment of CO2-induced cerebral vasomotor response in normal individuals and patients with internal carotid artery occlusion’,Stroke,19, pp. 963–969
Tiecks, F. P., Lam, A. M., Aaslid, R., andNewell, D. W. (1995): ‘Comparison of static and dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurements’,Stroke,26, pp. 1014–1019
Valdueza, J. M., Draganski, B., Hoffmann, O., Dirnagel, O., andEinhaupl, K. M. (1999): ‘Analysis of CO2 vasomotor reactivity and vessel diameter changes by simultaneous venous and arterial Doppler recordings’,Stroke,30, pp. 81–86
Vis, A., andFolgering, H. (1980): ‘The dynamic effect of PETCO2 on vertebral blood flow in cats’,Respir. Physiol.,42, pp. 131–143
Widder, B., Paulat, K., Hackspacher, J., andMeyr, E. (1986): ‘Transcranial Doppler CO2 test for the detection of hemodynamically critical carotid artery stenoses and occlusions’,Eur. Arch. Psychiatr. Neurol. Sci.,236, pp. 162–168
Zhang, R., Zuckerman, J. H., Giller, C. A., andLevine, B. D. (1998a): ‘Transfer function analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans’,Am. J. Physiol.,274, pp. H233-H241
Zhang, R., Zuckerman, J. H., andLevine, B. D. (1998b): ‘Deterioration of cerebral autoregulation during orthostatic stress: insights from the frequency domain’,J. Appl. Physiol.,85, pp. 1113–1122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simpson, D.M., Panerai, R.B., Evans, D.H. et al. Estimating normal and pathological dynamic responses in cerebral blood flow velocity to step changes in end-tidal pCO2 . Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 38, 535–539 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345749
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345749