Abstract
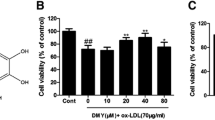
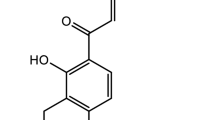
The Chinese herb radix Salviae miltiorrhizae (RSM) is used in traditional Chinese medicine as a treatment for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Several components of the plant extract from salvia mitorrhiza bunge have been determined previously, one of which is protocatechuic acid (PAC). It has been found, in the study, that PAC inhibited TNF-α-induced cell death of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and Jurkat cells in a concentration of 100μM when applied 2 h prior to TNF-α exposure. Molecular studies revealed that PAC activated NF-κB with a maximum effect after 30 min of treatment. Inhibition of NF-κB action by MG132 and NF-κB inhibitory peptide suppressed the cell-protective effect of PAC. Further, degradation of lkBα occurred in response to PAC treatment. The results provide evidence that activation of NF-κB plays an important role in mediating the cell-protecting effect of PAC on HUVECs and Jurkat cells. Further studies are required to test whether PAC, a component of radix salviae miltiorrhizae, could be useful in preventing in vivo cell death resulting from cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkalay, I., Yaron, A., Hatzubai, A., Orian, A., Ciechanover, A., andBen, N. Y. (1995): ‘Stimulation-dependent IB phosphorylation marks the NF-κB inhibitor for degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway’,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA,92, pp. 10599–10603
Arenzana-Seisdedos, F., Thompson, J., Rodriguiez, M. S., Bachelerie, F., Thomas, D., andHay, R. T. (1995): ‘Inducible nuclear expression of newly synthesized I kappa B alpha negatively regulates DNA-binding and transcriptional activities of NF-kappa B’,Mol. Cell. Biol.,15, pp. 2689–2696
Bach, F. H., Ferran, C., Soares, M., Wrighton, C. J., Anrather, J., Winkler, H., Robson, S. C., andHancock, W. W. (1997): ‘Modification of vascular responses in xenotransplantation: inflammation and apoptosis’,Nat. Med.,3, pp. 944–948
Beg, A. A., andBaltimore, D. (1996): ‘An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF—induced cell death’,Science,274, pp. 782–784
Bosserhoff, A. K., Hein, R., Bogdahn, U., andBuettner, R. (1996): ‘Structure and promoter analysis of the gene encoding the human melanoma-inhibiting protein MIA’,J. Biol. Chem.,271, pp. 490–495
Cain, B. S., Harken, A. H., andMeldrum, D. R. (1999): ‘Therapeutic strategies to reduce TNF-alpha mediated cardiac contractile depression following ischemia and reperfusion’,J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.,31, pp. 931–947
Chen, W. Z. (1984): ‘Pharmacology of Salvia miltiorrhiza’,Acta. Pharm. Sin.,19, pp. 876–880
Chen, Z., Hagler, J., Palombella, V. J., Melandri, F., Scherer, D., Ballard, D., andManiatis, T. (1995): ‘Signal-induced sitespecific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway’,Genes. Dev.,9, pp. 1586–1597
Chiao, P. J., Miyamoto, S., andVerma, I. M. (1994): ‘Autoregulation of IκBα activity’,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,91, pp. 28–32
Didonato, J. A., Hayakawa, M., Rothwarf, D. M., Zandi, E., andKarin, M. (1997): ‘A cytokine-responsive IkappaB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB’,Nature,388, pp. 548–554
Israël, A. (2000): ‘The IKK complex: an integrator of all signals that activate NF-κB?’,Trends Cell Biol.,10, pp. 129–133
Itoh, N., Yonehara, S., Ishii, A., Yonehara, M., Mizushima, S., Sameshima, M., Hase, A., Seto, Y., andNagata, S. (1991): ‘The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis’,Cell,66, pp. 233–243
Jaffe, E. A., Nachman, R. L., Becker, C. G., andMinick, R. C. (1973): ‘Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothlial cells’,J. Chin. Invest.,52, pp. 2745–2756
Karsan, A., Yee, E., andHarlan, J. M. (1996): ‘Endothelial cell death induced by tumor necrosis factor-α is inhibited by the Bcl-2 family member, A1’,J. Biol. Chem.,271, pp. 27201–27204
Kuang, P., Li, Z., Zhang, F., Tao, Y., Liu, J., andWu, W. (1995): ‘Protective effect of radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae Composita on cerebral ischemia’,J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (Chinese),15, pp. 135–140
Kuang, P. G. (1991): ‘The effect of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae (RSM) on substance P in cerebral ischemia: animal expriment’,J. Tradit. Chin. Med.,11, p. 123
Lebail, O., Schmidt-Ullrich, R., andIsraël, A. (1993): ‘Promoter analysis of the gene encoding the IκB-α/MAD-3 inhibitor of NF-κB: positive regulation by members of the rel/NF-κB family’,EMBO J.,12, pp. 5043–5049
Li, C. Z., Yang, S. C., andZhao, F. D. (1984): ‘Effect of tanshinone II-A sulfonate on thrombus formation, platelet and conjunction in rats and mice’,Acta. Pharmacol. Sin.,5, pp. 39–42
Li, N. L., Tan, R., andChen, W. M. (1984): ‘Salvianolic acid A, a new depside from roots of salvia miltiorrhiza’,Planta. Med.,50, pp. 227–228
Lin, Y. Z., Yao, S. Y., Veach, R. A., Torgerson, T. R., andHawiger, J. (1995): ‘Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-κB by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence’,J. Biol. Chem.,270, pp. 14255–14258
Liu, G. T., Zhang, T. M., Wang, B. E., andWang, Y. W. (1992): ‘Protective action of seven natural phenolic compounds against peroxidative damage to biomembranes’,Biochem. Pharmacol.,43, pp. 147–152
Mercurio, F., Zhu, H., Murray, B. W., Shevchenko, A., Bennett, B. L., Li, J., Young, D. B., Barbosa, M., Mann, M., Manning, A., andRao, A. (1997): ‘IKK-1 and IKK-2: Cytokine-activated IB kinases essential for NF-κB activation’,Science,278, pp. 860–866
Nagata, S. (1997): ‘Apoptosis by death factor (review)’,Cell,88, pp. 355–365
Regnier, C. H., Song, H. Y., Gao, X., Goeddel, D. V., Cao, Z., andRothe, M. (1997): ‘Identification and characterization of an IkappaB kinase’,Cell,90, pp. 373–383
Scherer, D. C., Brockman, J. A., Chen, Z., Maniatis, T., andBallard, D. W. (1995): ‘Signal-induced degradation of IB requires site-specific ubiquitination’,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA,92, pp. 11259–11263
Simeonidis, S., Stauber, D., Chen, G., Hendrickson, W. A., andThanos, D. (1999): ‘Mechanisms by which IkappaB proteins control NF-kappaB activity’,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA,96, pp. 49–54
Sun, S. C., Ganchi, P. A., Ballard, D. W., andGreene, W. C. (1993): ‘NF-κB controls expression of inhibitor IκBα: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway’,Science,259, pp. 1912–1915
Traenckner, E. B., Pahl, H. L., Henkel, T., Schmidt, K. N., Wilk, S., andBaeuerle, P. A. (1995): ‘Phosphorylation of human I kappa B-alpha on serines 32 and 36 controls I kappa B-alpha proteolysis and NF-kappa B activation in response to diverse stimuli’,EMBO. J.,14, pp. 2876–2883
Van-Antwerp, D. J., Martin, S. J., Kafri, T., Green, D. R., andVerma, I. M. (1996): ‘Suppression of TNF—induced apoptosis by NF-κB’,Science,274, pp. 787–789
Wang, C. Y., Mayo, M. W., andBaldwin, A. S. J. (1996): ‘TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB’,Science,274, pp. 784–787
Wu, W., Kuang, P., andZhu, K. (1992): ‘The effect of radix salviae miltiorrhizae on the changes of ultrastructure in rat brain after cerebral ischemia’,J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (Chinese),12, pp. 183–186
Xi, S. C., Che, D. Y., andZhang, W. R. J. (1994): ‘The inhibitory effect of Radix Salviae miltiorrhizaeon hypoxic structural remodeling of intra-acinar pulmonary arteries’,Tongji Med. Univ. (Chinese),14, pp. 149–152
Xia, P., Wang, L., Gamble, J. R., andVadas, M. A. (1999): ‘Activation of sphingosine kinase by tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits apoptosis in human endothelial cells’,J. Biol. Chem.,274, pp. 34499–34505
Yonehara, S., Ishii, A., andYonehara, M. (1989): ‘A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (anti-Fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor’,J. Exp. Med.,169, pp. 1747–1756
Zhang, X., Wu, W., Kuang, P., Takemichi, K., Kogo, O., Hirobumi, M., andYasaburo, O. (1994): ‘The effect of radix salviae miltiorrhizae composita and ligustrazine on lipid peroxidation in low density lipoprotein due to copper dichloride’,J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (Chinese),14, pp. 292–297
Zou, Z. W., Xu, L. N., andTian, J. Y. (1993): ‘Antithrombotic and antiplatelet effects of rosmarinic acid, a water-soluble component isolated from radix Salviae miltiorrhizae (danshen)’,Yao Hsueh Hsueh Pao (Chinese),28, pp. 241–245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou-Stache, J., Buettner, R., Artmann, G. et al. Inhibition of TNF-α induced cell death in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and Jurkat cells by protocatechuic acid. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 698–703 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345308
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345308