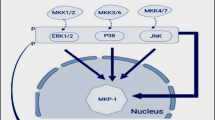
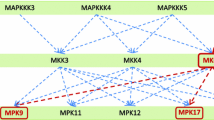
Abstract
Plants have the ability to respond to pathogen invasion by specific defense reactions. Components of mammalian signal transduction chains have been identified in plants, and several lines of evidence have implicated such components in elicitor signal transmission in defense responses. In particular, it has been assumed that elicitor signals are transduced via a protein kinase cascade, although the identity of the protein kinases and the function of the phosphorylated proteins remain to be determined. The purpose of this review is to discuss the roles of protein kinases in elicitor signal transduction pathways in plant cells based on recent progress in this field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- avr :
-
gene. avirulence gene
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- HR:
-
hypersensitive response
- IL-1R:
-
interleukin-1 receptor
- IRAK:
-
IL-R associated protein kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-teminal kinase
- JNKK, JNK:
-
kinase
- LRR:
-
leucine-rich repeat
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MAPKK:
-
MAPK kinase
- MAPKKK:
-
MAPKK kinase
- MBP:
-
myelin basic protein
- MEK:
-
MAPK and ERK kinase
- MEKK1, MEK:
-
kinase 1
- MKK4, MAPK:
-
kinase 4
- PR:
-
protein, pathogenesisrelated protein
- PR5K:
-
PR5-like receptor kinase; pcd, programmed cell death
- PGIP:
-
polygalacturonase inhibitor protein
- PLA2 :
-
phospholipase
- A2 :
-
R gene, resistance gene
- SAPK:
-
stressactivated protein kinase
- SEK, SAPK and ERK:
-
kinase
- SLG:
-
S-locus glycoprotein
- SRK:
-
S-locus receptor kinase
References
Atkinson, M.M., Keppler, L.D., Orlandi, E.W., Baker, C.J., andMischke, C.F. 1990. Involvement of plasma membrane calcium influx in bacterial induction of the K+/H+ and hypersensitive responses in tobacco Plant Physiol.92: 215–221.
Baker, C.J., Orlandi, E.W. andMock, N.M. 1993. Harpin, an elicitor of the hypersensitive response in tobacco caused byErwinia amylovora, elicits active oxygen production in suspension cells. Plant Physiol.102: 1341–1344.
Benna, J.E., Faust, L.P. andBablor, B.M. 1994. The phosphorylation of the respiratory burst oxidase component p47 phox during neutrophil activation. J. Biol. Chem.289: 23431–23436.
Bent, A.F., Kunkel, B.N., Dahlbeck, D., Brown, K.L., Schmidt, R., Giraudat, J., Leung, J. andStaskawicz, B.J. 1994.RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science265: 1856–1860.
Bergmann, C.W., Ito, Y., Singer, D., Albersheim, P., Darvill, A. G., Benhamou, N., Nuss, L., Salvi, G., Gervone, F., andDe Lorenzo, G. 1994. Polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein accumulates inPhaseolus vulgaris L. in response to wounding, elicitors and fungal infection. Plant J.5: 625–634.
Braun, D.M. andWalker, J.C. 1996. Plant transmembrane receptors: new pieces in the signaling puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci.21: 70–73.
Cano, E. andMahadevan, L.C. 1994. Parallel signal processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem. Sci.20: 117–122.
Cao, Z., Henzel, W.J. andGao, X. 1996. IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science271: 1128–1131.
Chandra, S., Heinstein, P.F. andLow, P.S. 1996. Activation of phospholipase A by plant defense elicitors. Plant Physiol.110: 979–986.
Chandra, S. andLow, P.S. 1995. Role of phosphorylation in elicitation of the oxidative burst in cultured soybean cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA92: 4120–4123.
Chasan, R. 1995. Eliciting phosphorylation. Plant Cell7: 495–497.
Chen, Y.-R., Meyer, C.F. andTan, T.-H. 1996. Persistent activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in γ radiation-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem.271: 631–634.
Conrath, U., Jeblick, W. andKauss, H. 1991. The protein kinase inhibitor, K-252a, decreases elicitor-induced Ca2+ uptake and K+ release, and increases coumarin synthesis in parsley cells. FEBS Lett.279: 141–144.
Després, C., Subramanlam, R., Matton, D.P. andBrisson, N. 1995. The activation of the potato PR-10a gene requires the phosphorylation of the nuclear factor PBF-1. Plant Cell7: 589–598.
Dietrich, A., Mayer, J.E. andHahlbrock, K. 1990. Fungal elicitor triggers rapid, transient, and specific protein phosphorylation in parsley cell suspension cultures. J. Biol. Chem.265: 6360–6368.
Dietrich, R.A., Delancy, T.P., Uknes, S.J., Ward, E.R., Ryals, J.A. andDangl, J.L. 1994.Arabidopsis mutants simulating disease resistance response. Cell77: 565–577.
Dinesh-Kumar, S.P., Whitham, S., Choi, D., Hehl, R., Corr, C. andBaker, B. 1995. Transposon tagging of tobacco mosaic virus resistance geneN: its possible role in the TMV-N-mediated signal transduction pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA92: 4175–4180.
Dixon, M.S., Jones, D.A., Keddie, J.S., Thomas, C.M., Harrison, K. andJones, J.D.G. 1996. The tomatoCf-2 disease resistance locus comprises two functional genes encoding leucine-rich repeat proteins. Cell84: 451–459.
Dong, X. 1995. Finding the missing pieces in the puzzle of plant disease resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA92: 7137–7139.
Drayer, A.L. andHaastert, P.J.M. 1994. Transmembrane signaling in eukaryotes: a comparison between higher and lower eukaryotes. Plant Mol. Biol.26: 1239–1270.
Ebel, J. andCosio, E.G. 1994. Elicitors of plant defense responses. Int. Rev. Cytol.148: 1–36.
Farmer, E.E. 1994. Fatty acid signaling in plants and their associated microorganisms. Plant Mol. Biol.26: 1423–1473.
Farmer, E.E. andRyan, C.A. 1990. Interplant communication: air-borne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA87: 7713–7716.
Felix, G., Grosskopf, D.G., Regenass, M. andBoller, T. 1991. Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA88: 8831–8834.
Felix, G., Regenass, M. andBoller, T. 1993. Specific perception of subnanomolar concentrations of chitin fragments by tomato cells: induction of extracellular alkalinization, changes in protein phosphorylation, and establishment of a refractory state. Plant J.4: 307–316.
Felix, G., Regenass, M., Spanu, P. andBoller T. 1994. The protein phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A mimics elicitor action in plant cells and induces rapid hyperphosphorylation of specific proteins as revealed by pulse labeling with [33P] phosphate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA91: 952–956.
Flor, H.H. 1946. Genetics of pathogenecity inMelamspora lini. J. Agr. Res.73: 335–357.
Fukuda, Y. andShinshi, H. 1994. Characterization of a novelcis-acting element that is responsive to a fungal elicitor in the promoter of tobacco class 1 chitinase gene. Plant Mol. Biol.24: 485–493.
Grab, D., Ferger, M. andEbel, J. 1989. An endogenous factor from soybean (Glycine max L.) cell cultures activates phosphorylation of a protein which is dephosphorylatedin vivo in elicitor-challenged cells. Planta179: 340–348.
Grant, M.R., Godiard, L., Straube, E., Ashfiel, T., Lewald, J., Sattler, A., Innes, R.W. andDangl, J.L. 1995. Structure of theArabidopsis RPM1 gene enabling dual specificity disease resistance. Science269: 843–846.
Greenberg, J.T. andAusubel, F.M. 1993.Arabidopsis mutants compromised for the control of cellular damage during pathogenesis and aging. Plant J.4: 327–341.
Greenberg, J.T., Guo, A., Klessig, D.F. andAusubel, F.M. 1994. Programmed cell death in plants: a pathogentriggered response activated coordinately with multiple defense functions. Cell77: 551–563.
Grosskopf, D.G., Felix, G. andBoller, T. 1990. K-252a inhibits the response of tomato cells to fungal elicitorsin vivo and their microsomal protein kinasein vitro. FEBS Lett.275: 177–180.
Haecker, G. andVaux, D.L. 1994. Viral, worm and radical implications for apoptosis. Trends Biochem. Sci.19: 99–100.
He, S.Y., Bauer, D.W., Collmer, A. andBeer, S.V. 1994. Hypersensitive response elicited byErwinia amylovora harpin requires active plant metabolism. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact.7: 289–292.
Heguy, A., Baldari, C.T., Macchia, G., Telford, J.L. andMelli, M. 1992. Amino acids conserved in interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs) and theDrosophila Toll protein are essential for IL-1R signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem.267: 2605–2609.
Hill, C.S. andTreisman, R. 1995. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell80: 199–211.
Jonak, C., Heberle-Bros, E. andHirt, H. 1994. MAP kinases: universal multi-purpose signaling tools. Plant Mol. Biol.24: 407–416.
Jones, A.M. andDangl, J.L. 1996. Logiam at the Styx: programmed cell death in plants. Trends Plant Sci.1: 114–119.
Jones, D.A., Thomas, C.M., Hammond-Kosack, K.E., Balint-Kurti, P.J. andJones, J.D.G. 1994. Isolation of the tomatoCf-9 gene for resistance toCladosporium fulvum by transposon tagging. Science266: 789–793.
Karin, M. 1995. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogenactivated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem.270: 16483–16486.
Kauss, H., Jeblick, W. andConrath, U. 1992. Protein kinase inhibitor K-252a and fusicoccin induce similar initial changes on ion transport of parsley suspension cells. Physiol. Plant.85: 483–488.
Kobe, B. andDeisenhofer, J. 1994. The leucine-rich repeat: a versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem. Sci.19: 415–421.
Kombrink, E. andSomssich, I.E. 1995. Defense responses of plant to pathogens. Adv. Bot. Res.21: 1–34.
Korfhage, U., Trezzini, G.F., Meier, I., Hahlbrock, K. andSomssich, I.E. 1994. Plant homeodomain protein involved in transcriptional regulation of a pathogen defense-related gene. Plant Cell6: 695–708.
Kuehl, F.A. andEgan, R.W. 1980. Prostaglandins, arachidonic acid and inflammation. Science210: 978–984.
Lawrence, G.J., Finnegan, E.J., Ayliffe, M.A. andEllis, J.G. 1995. TheL6 gene for flax rust resistance is related to the Arabidopsis bacterial resistance geneRPS2 and the tobacco viral resistance geneN. Plant Cell7: 1195–1206.
Levine, A., Pennell, R.I., Alvarez, M.E., Palmer, R. andLamb, C. 1996. Calcium-mediated apoptosis in a plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Curr. Biol.6: 427–437.
Levine, A., Tenhaken, R., Dixon, R. andLamb, C. 1994. H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell79: 583–593.
Lin, L.-L., Wartmann, M., Lin, A.Y., Knopf, J.L., Seth, A. andDavis, R.J. 1993. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell72: 269–278.
MacKintosh, C. andCohen, P. 1989. Identification of high levels of type 1 and type 2 protein phosphatases in higher plants. Biochem. J.262: 335–339.
MacKintosh, C., Lyon, G.D. andMacKintosh, R.W. 1994. Protein phosphatase inhibitors activate anti-fungal defense responses of soybean cotyledons and cell cultures. Plant J.5: 137–147.
Marshall, C.J. 1994. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase, and MAP kinase. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev.4: 82–89.
Martin, G.B., Brommonschenkel, S.H., Chunwongse, J., Frary, A., Ganal, M.W., Spivey, R., Wu, T., Earle, E.D. andTankley, S.D. 1993. Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science262: 1432–1436.
Martin, G.B., Frary, A., Wu, T., Brommonschenkel, S., Chunwongse, J., Earle, E.D. andTanksley, S.D. 1994. A member of the tomatoPto gene family confers sensitivity to fenthion resulting in rapid cell death. Plant Cell6: 1543–1552.
Mehdy, M. 1994. Active oxygen species in plant defense against pathogens. Plant Physiol.105: 467–472.
Midrions, M., Katagiri, F., Yu, G.-L. andAusubel, F.M. 1994. TheA. thaliana disease resistance geneRPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell78: 1089–1099.
Mittler, R. andLam, E. 1995. Identification, characterization, and purification of a tobacco endonuclease activity induced upon hypersensitive response cell death. Plant Cell7: 1951–1962.
Mittler, R., Shulaev, V. andLam, E. 1995. Coordinate activation of programmed cell death and defense mechanisms in transgenic tobacco plants expressing a bacterial proton pump. Plant Cell7: 29–42.
Morel, F., Doussiere, J. andVignais, P.V. 1991. The superoxide-generating oxidase of phagocytotic cells: physiological, molecular and pathological aspects. Eur. J. Biochem.201: 523–546.
Nasrallah, J.B., Rundle, S.J. andNasrallah, M.E. 1994a. Genetic evidence of the requirement of theBrassica S locus receptor kinase gene in the self-incompatibility response. Plant J.5: 373–384.
Nasrallah, J.B., Stein, J.C., Kandasamy, M.K. andNasrallah, M.E. 1994b. Signaling the arrest of pollen tube development in self-incompatible plants. Science266: 1505–1508.
Nishihama, R., Banno, H., Shibata, W., Hirano, K., Nakashima, M., Usami, S. andMachida, Y. 1995. Plant homologues of components of MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signal pathways in yeast and animal cells. Plant Cell Physiol.36: 749–757.
Nürnberger, T., Nennstiel, D., Jabs, T., Sacks, W.R., Hahlbrock, K. andScheel, D. 1994. High affinity binding of a fungal oligopeptide elicitor to parsley plasma membranes triggers multiple defense responses. Cell78: 449–460.
Raz, V. andFluhr, R. 1993. Ethylene signal is transduced via protein phosphorylation events in plants. Plant Cell5: 523–530.
Ryerson, D.E. andHeath, M.C. 1996. Cleavage of nuclear DNA into oligonucleosomal fragments during cell death induced by fungal infection or by abiotic treatments. Plant Cell8: 393–402.
Salmeron, J.M., Barker, S.J., Carland, F.M., Mehta, A.Y. andStaskawicz, B.J. 1994. Tomato mutants altered in bacterial disease resistance provide evidence for a new locus controlling pathogen recognition. Plant Cell6: 511–520.
Schneider, D.S., Hudson, K.L., Lin, T.Y. andAnderson, K.V. 1991. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal-ventral polarity in theDrosophila embryo. Genes Dev.5: 797–807.
Schwacke, R. andHager, A. 1992. Fungal elicitors induce a transient release of active oxygen species from cultured spruce cells that is dependent on Ca2+ and protein-kinase activity. Planta187: 136–141.
Seo, S., Okamodo, M., Seto, H., Ishizuka, K., Sano, H. andOhashi, Y. 1995. Tobacco MAP kinase: a possible mediator in wound signal transduction pathways. Science270: 1988–1991.
Serrano, R. 1989. Structure and function of plasma membrane ATPase. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol.40: 61–94.
Shelton, C.A. andWasserman, S.A. 1993 pelle encodes a protein kinase required to establish dorsoventral polarity in theDrosophila embryo. Cell72: 515–525.
Song, W.-Y., Wang, G.-L., Chen, L.-L., Kim, H.-S., Pi, L.-Y., Holsten, T., Gardner, J., Wang, B., Zhai, W.-X., Zhu, L.-H., Fauquet, C. andRonald, P. 1995. A receptor-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene,Xa21. Science270: 1804–1806.
Staskawicz, B.J., Ausubel, F.M., Baker, B.J., Ellis, J.G. andJones, J.D.G. 1995. Molecular genetics of plant disease resistance. Science268: 661–667.
Su, B., Jacinto, E., Hibi, M., Kallunki, Karin, M. andBen-Neriah, Y. 1994. JNK is involved in signal integration during costimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell77: 727–736.
Suzuki, K., Fukuda, Y. andShinshi, H. 1995. Studies on elicitor-signal transduction leading to differential expression of defense genes in cultured tobacco cells. Plant Cell Physiol.36: 281–289.
Suzuki, K. andShinshi, H. 1995. Transient activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of a protein kinase in tobacco cells treated with a fungal elicitor. Plant Cell7: 639–647.
Suzuki, K., Yano, A. andShinshi, H. 1996. Characterization of elicitor-responsive 47-kD protein kinase in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Physiol.37: s188.
Tenhaken, R., Levine, A., Brisson, LF., Dixon, R. andLamb, C. 1995. Function of the oxidative burst in hypersensitive disease resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA92: 4158–4163.
Usami, S., Banno, H., Ito, Y., Nishihama, R. andMachida, Y. 1995. Cutting activates a 46-kilodalton protein kinase in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA92: 8660–8664.
Vaux, D.L. andStrasser, A. 1996. The molecular biology of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA93: 2239–2244.
Verheij, M., Bose, R., Lin, X.H., Yao, B., Javis, W.D., Grant, S., Birrer, M.J., Szabo, E., Zon, L.I., Kyriakis, J.M., Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Funks, Z. andKolesinck, N. 1996. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signaling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature380: 75–79.
Viard, M.-P., Martin, F., Pugin, A., Ricci, P. andBlein, J.-P.. 1994. Protein phosphorylation is induced in tobacco cells by the elicitor cryptogein. Plant Physiol.104: 1245–1249.
Wang, H., Li, J., Bostock, R.M. andGilchrist, D.G. 1996. Apoptosis: a functional paradigm for programmed plant cell death induced by a host-selective phytotoxin and invoked during development. Plant Cell8: 375–391.
Wang, X., Zafian, P., Choudhary, M. andLawton, M. 1996. The PR5K receptor protein kinase fromArabidopsis thaliana is structurally related to a family of plant defense proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA93: 2598–2602.
Weymann, K., Hunt, M., Uknes, S., Neuenschwander, U., Lawton, K., Steiner, H. andRyals, J. 1995. Suppression and restoration of lesion formation in ArabidopsisIsd mutants. Plant Cell7: 2013–2022.
Whitham, S., Dinesh-Kumar, S.P., Choi, D., Hehl, R., Corr, C. andBaker, B. 1994. The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance geneN: similarity to Toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell78: 1101–1115.
Xia, Z., Dickens, M., Raingeaud, J., Davis, R.J. andGreenberg, M.E. 1995. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science270: 1326–1331.
Yano, A., Suzuki, K., Uchimiya, H. andShinshi, H. 1996. Induction of cell death by fungal elicitor in tobacco suspension culture. Plant Cell Physiol.37: s187.
Yang, H.S., Huang, H.C. andCollmer, A. 1993.Pseudomonas syringae pv.syringae Harpin: a protein that is secreted via the Hrp pathway and elicits the hypersensitive response in plants. Cell73: 1255–1266.
Yu, L.M., Lamb, C. andDixon, R.A. 1993. Purification and biochemical characterization of proteins which bind to the H-boxcis-element implicated in transcriptional activation of plant defense genes. Plant J.3: 805–816.
Zhou, J., Loh, Y.-T., Bressan, R.A. andMartin, G.B. 1995. The tomato gene Pti1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is phosphorylated by Pto and is involved in the hypersensitive response. Cell83: 925–935.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, K., Shinshi, H. Protein kinases in elicitor signal transduction in plant cells. J. Plant Res. 109, 253–263 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344472
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344472