Abstract
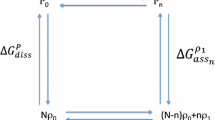
A general monomer-dimer equilibrium system involving ligand interactions ispresented. Cooperativity features of specific limited models are analyzed by selecting the appropriate family of equilibrium constants from this general scheme. Each system is then characterized in terms of Hill coefficient dependency on alterations in values of equilibrium constants and total acceptor concentration. This method permits comparison of predicted cooperativity trends between systems. Contrasting reports concerning cooperativity dependencies for certain defined equilibrium systems are compared and the discrepancies resolved. Characteristics of cooperativity binding patterns are shown to include symmetry about dimerization association constant values, both positive and negative cooperativity for a single set of parameters, and significant changes in cooperativity features with relatively small changes in equilibrium parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ColosimoA., BrunoriM., and WymanJ. (1976).J. Mol. Biol. 100, 47–57.
FriedenC. (1967).J. Biol. Chem. 242, 4045–4052.
FriedenC., and NicholL. W. (eds) (1981).Protein-Protein Interactions. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
HammesG. G., and WuC. (1974).Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 3, 1–33.
HillA. V. (1910).J. Physiol. (Lond.) 40, iv.
InghamK. C., SaroffH. A., and EdelhochH. (1975).Biochemistry 14, 4751–4758.
KlotzI. M. (1946).Arch. Biochem. 9, 109–117.
LevitzkiA., and SchlessingerJ. (1974).Biochemistry 13, 5214–5219.
NeetK. E. (1980).Methods Enzymol. 64, 139–192.
NicholL. W., and WinzorD. J. (1972).Migration of Interacting Systems, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
NicholL. W., and WinzorD. J. (1976).Biochemistry 15, 3015–3019.
NicholL. W., JacksonW. J. H., and WinzorD. J. (1967).Biochemistry 6, 2449–2456.
NicholL. W., SmithG. D., WinzorD. J. (1969).Nature (Lond.) 222, 174–176.
NotidesA. C., and SassonS. (1983). inSteroid Hormone Receptors: Structure and Function (ErikssenH., and GustafssonJ. A., eds.), Elsevier, New York, pp. 103–120.
NotidesA. C., LernerN., and HamiltonD. E. (1981).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 4926–4930.
NotidesA. C., SassonS., and CallisonS. (1985). inMolecular Mechanisms of Steroid Hormone Action (MoudgilV. K., ed.), Walter de Gruyter, New York, pp. 173–197.
SawulaR. V., and SuzukiI. (1970).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 40, 1096–1101.
ScatchardG. (1949).Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 51, 660–672.
SteinerR. F. (1974).J. Theoret. Biol. 45, 93–106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolfer, G.K., Neil, J.L. & Rippon, W.B. Cooperativity of ligand binding as a function of monomer-dimer equilibrium parameters and acceptor concentration. J Protein Chem 6, 441–454 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343341
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343341